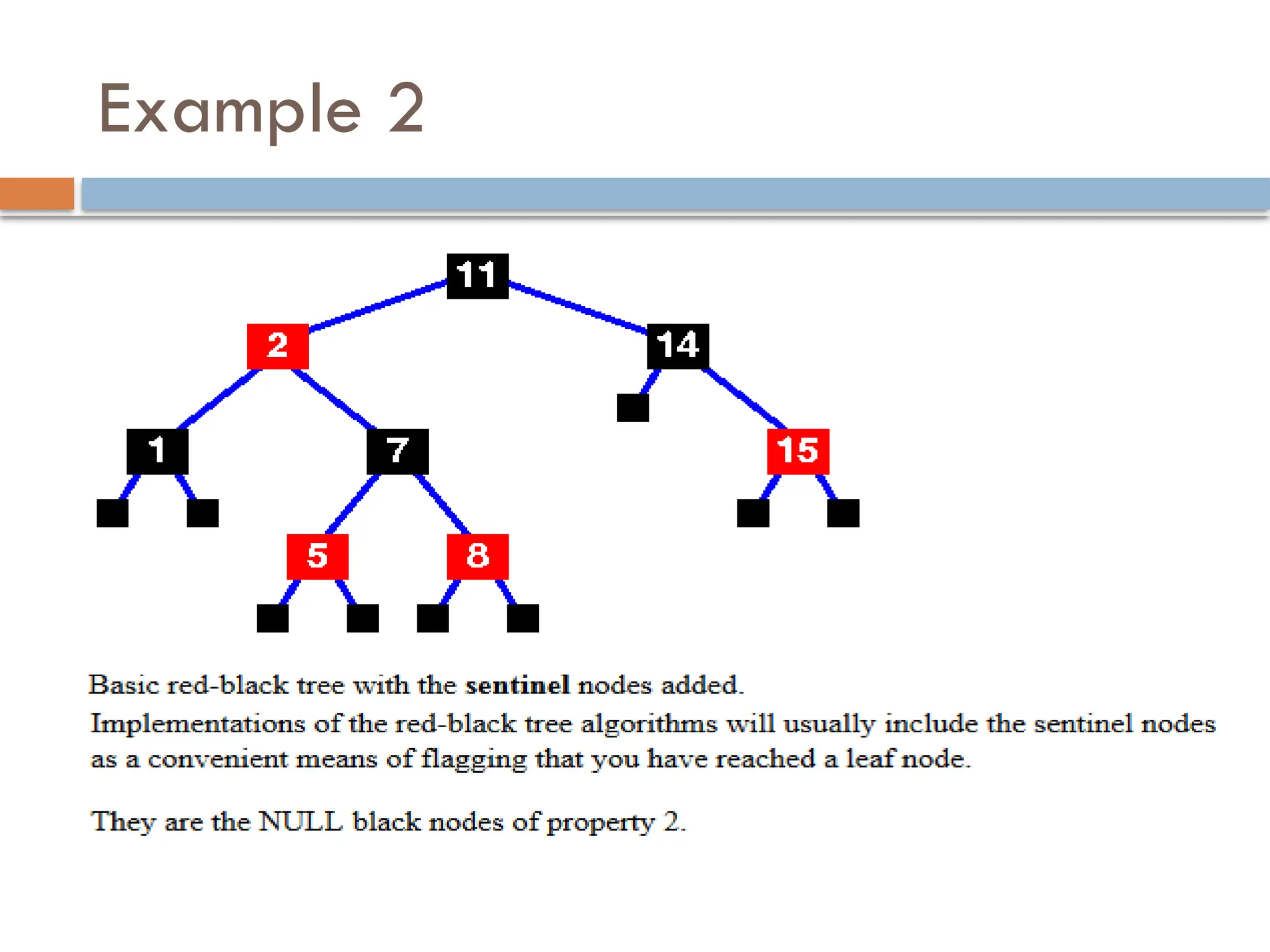
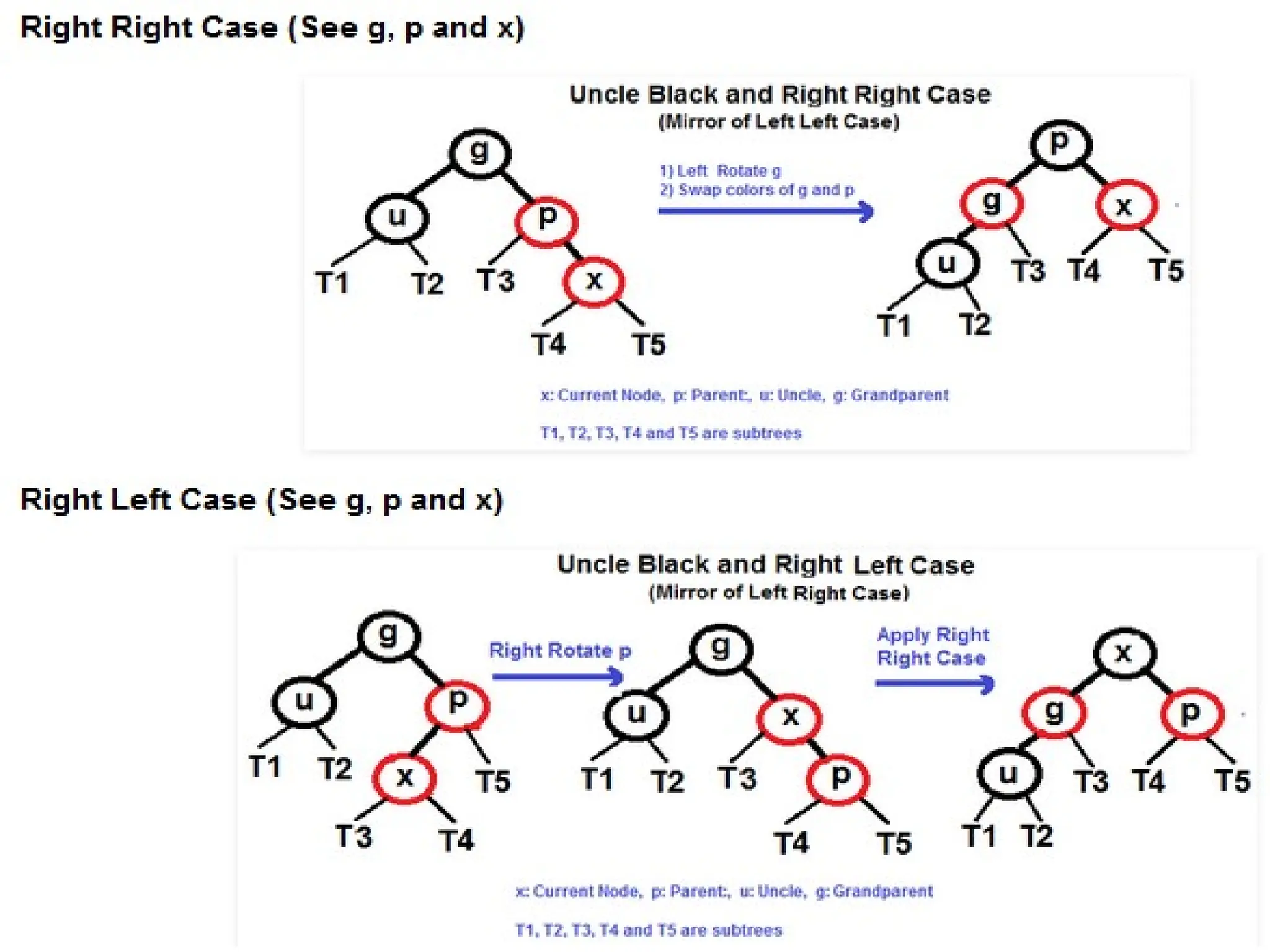
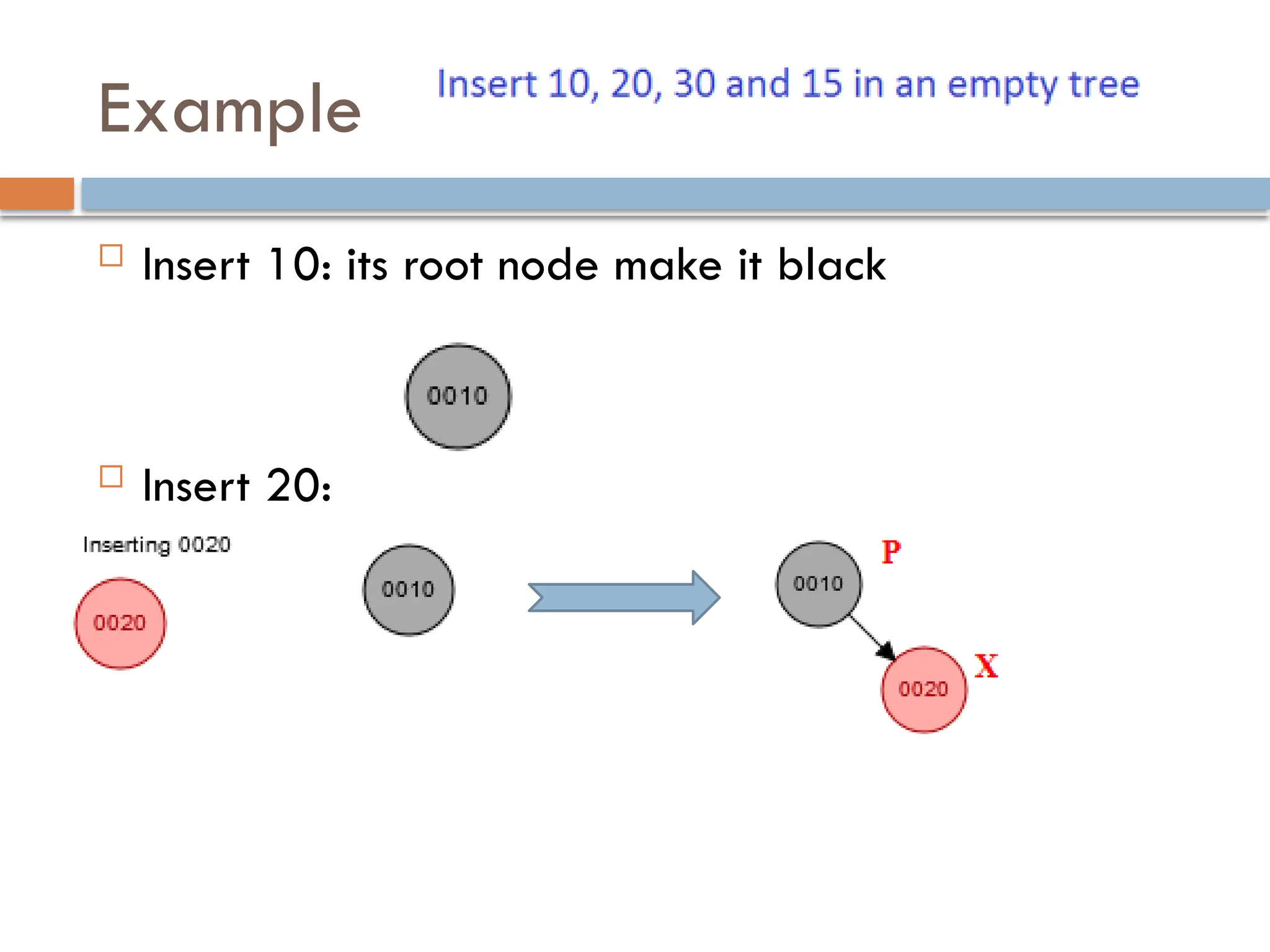
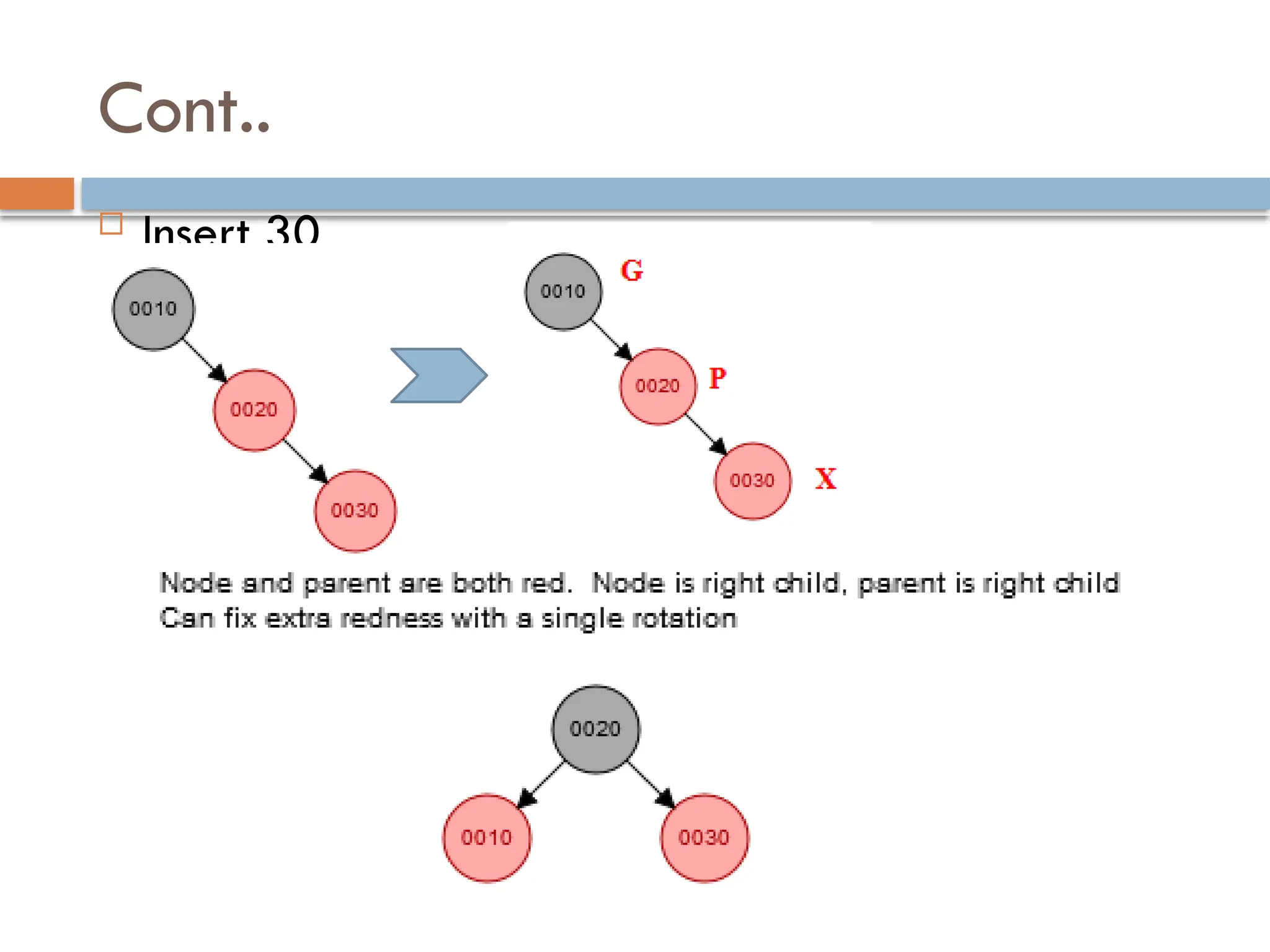
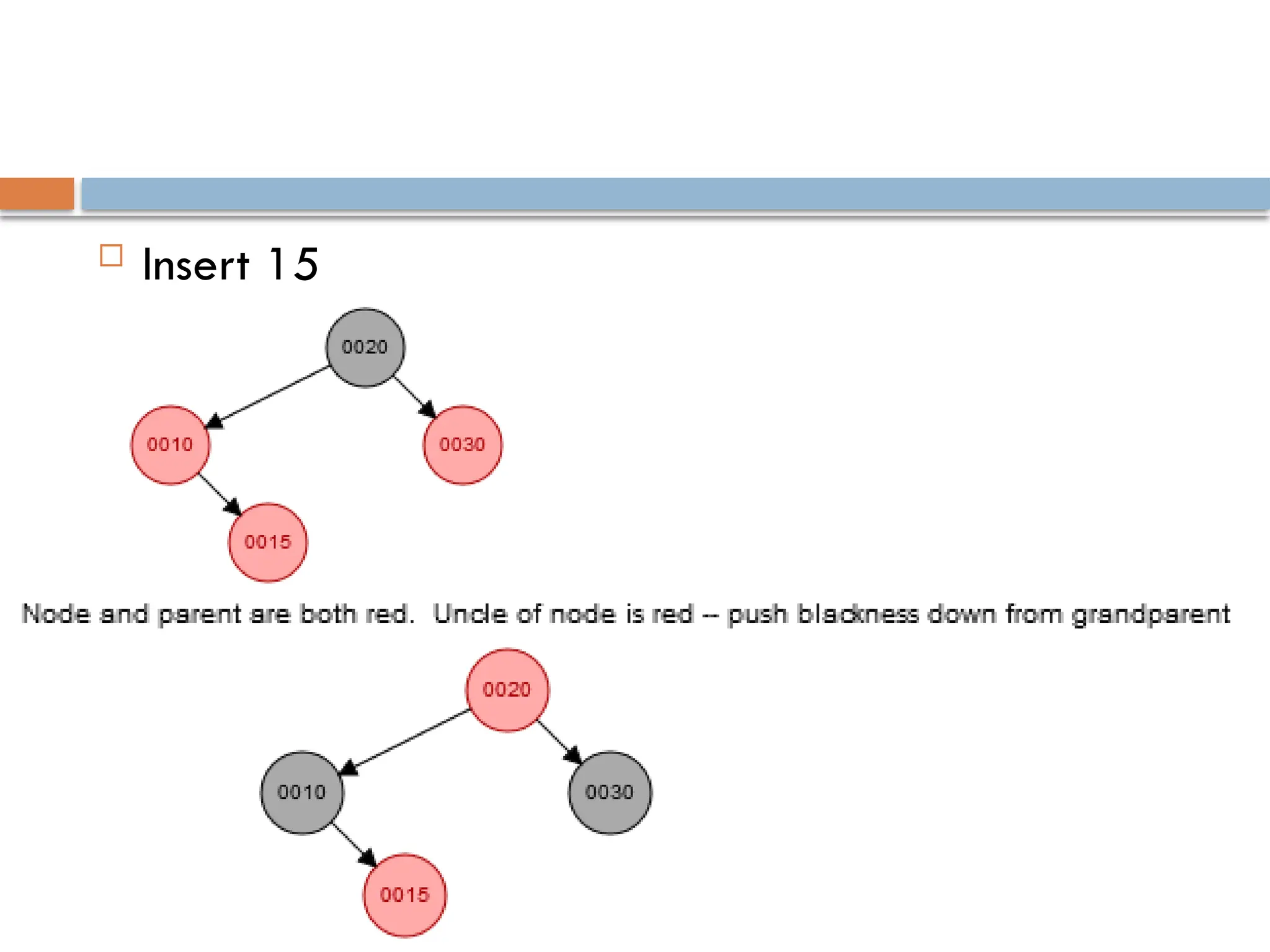
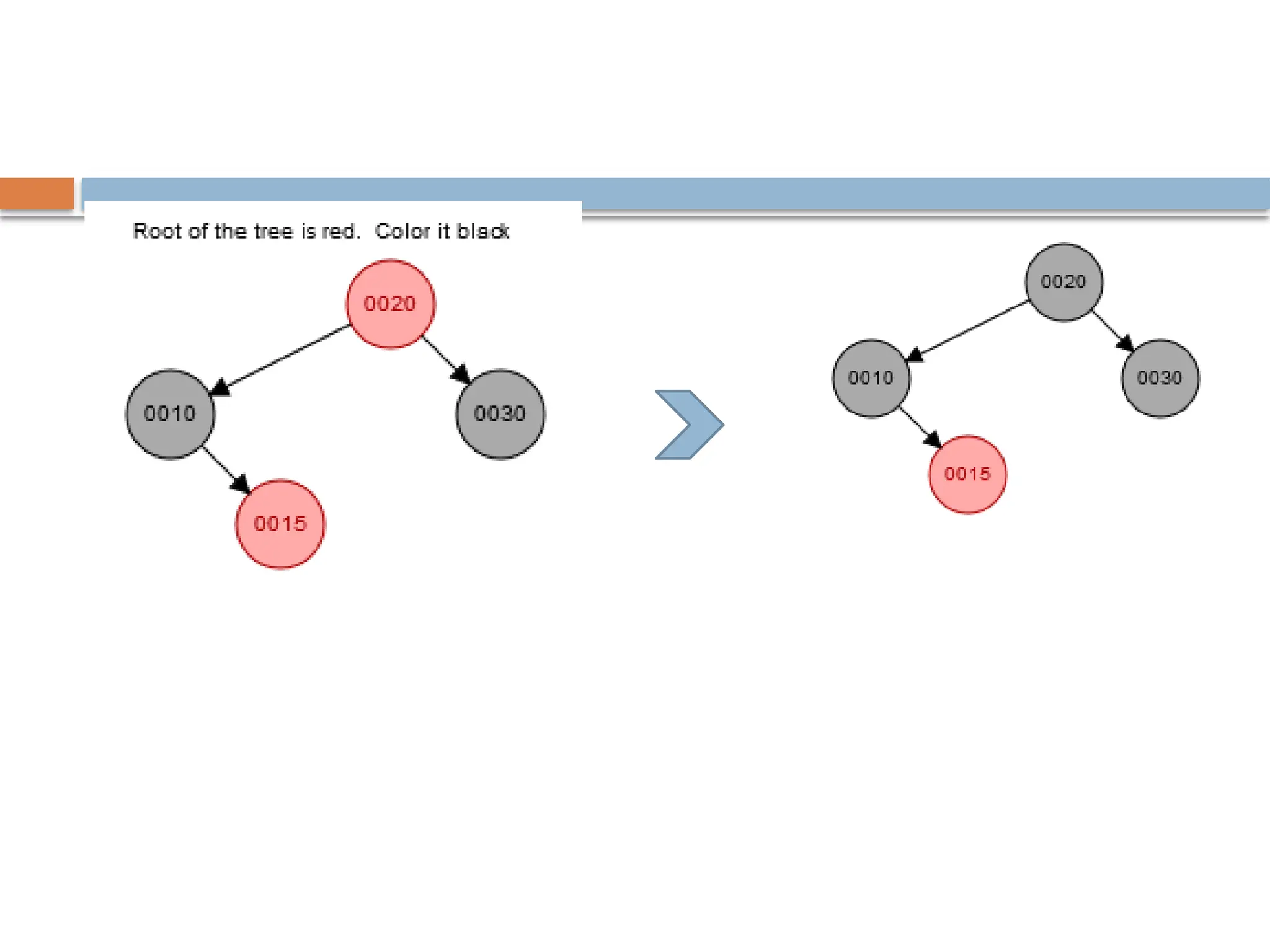
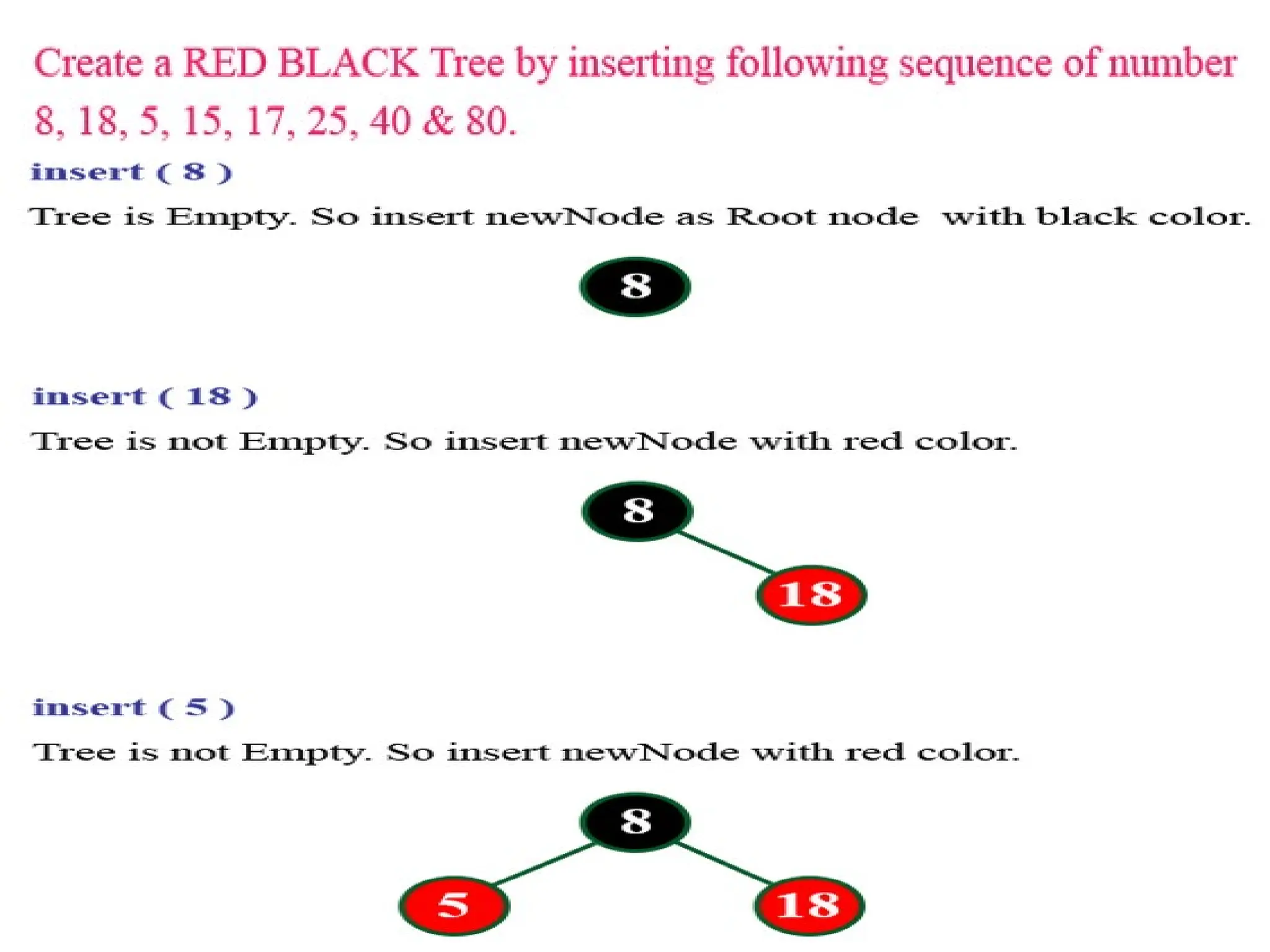
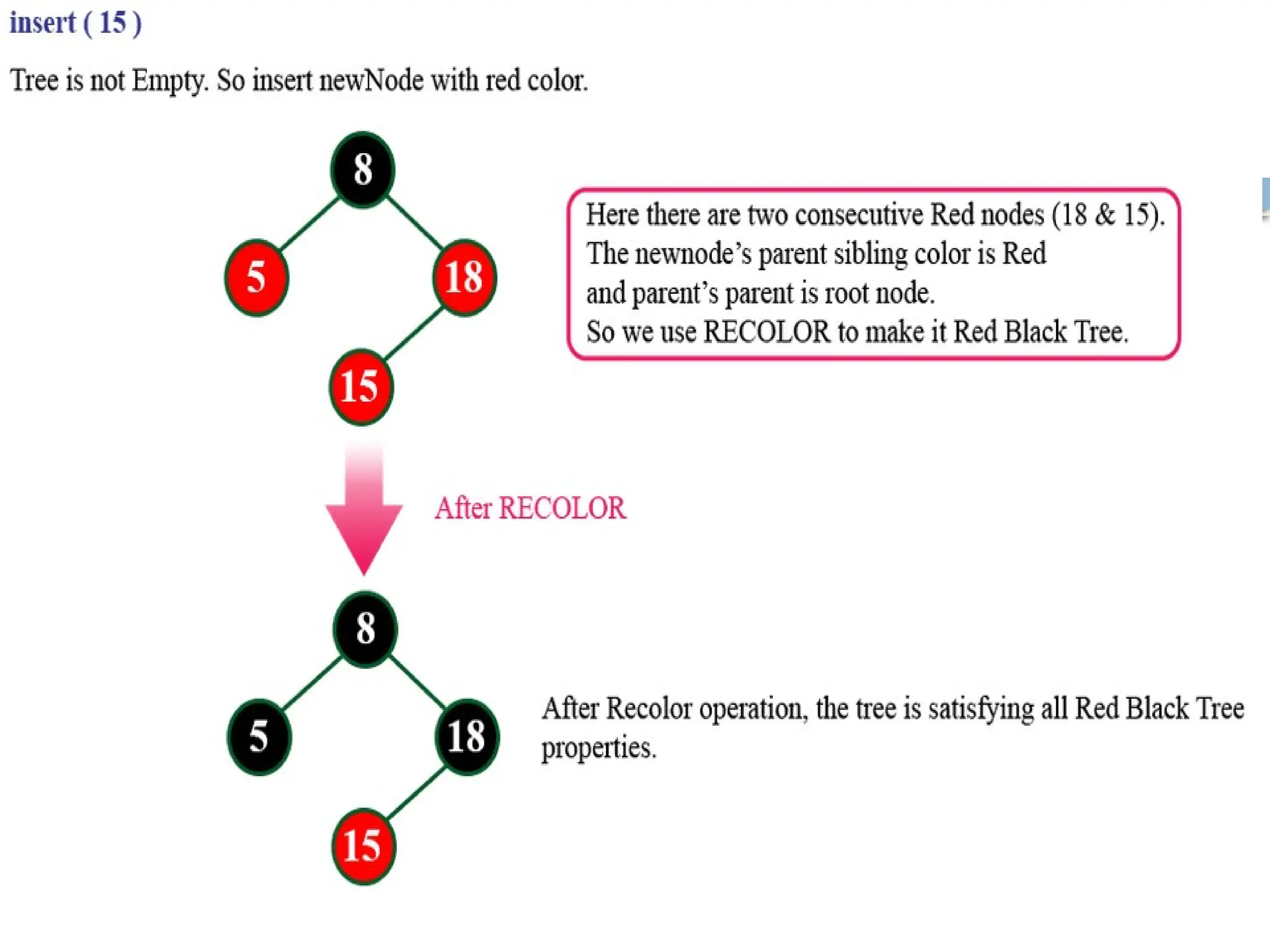
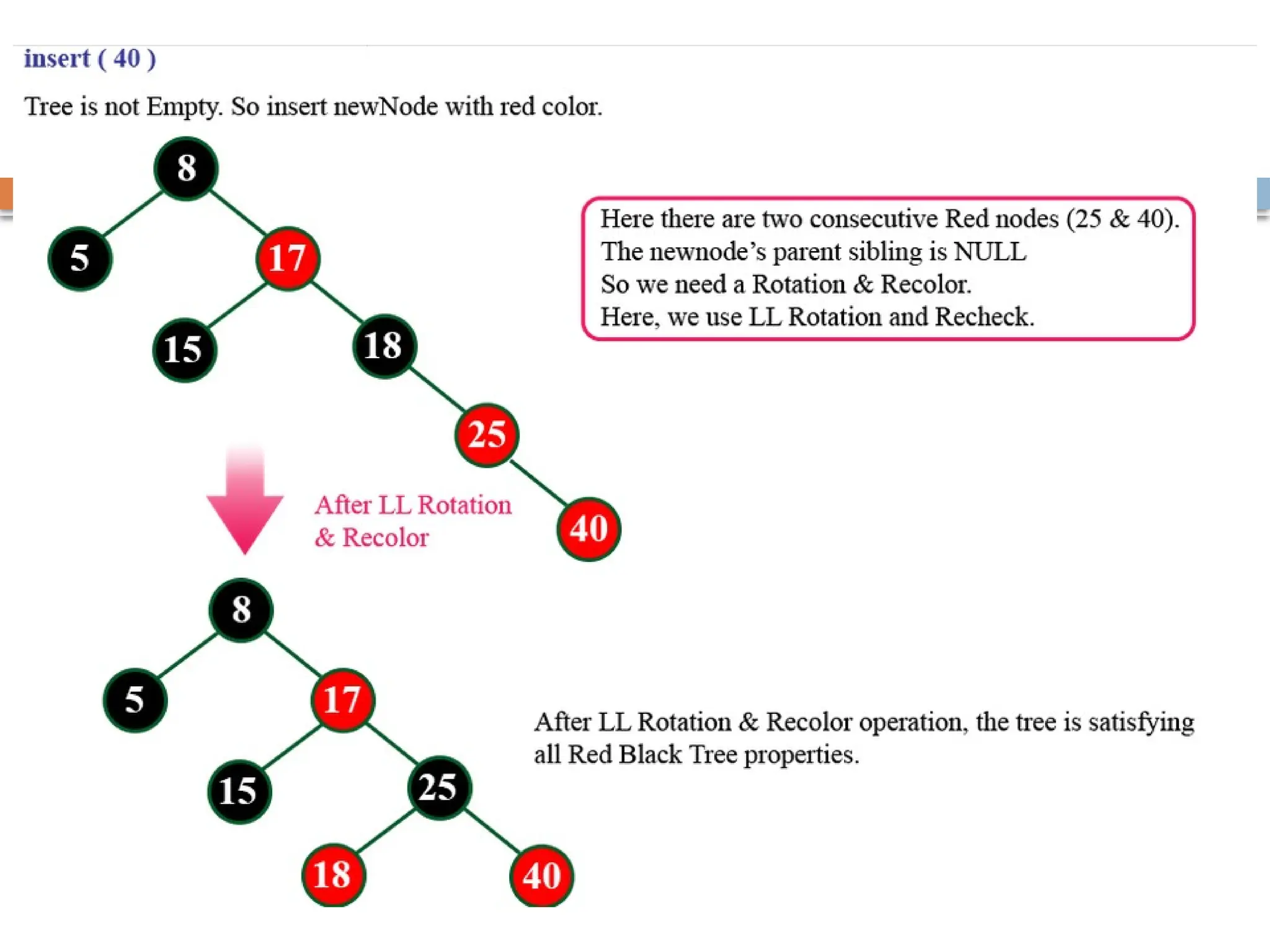
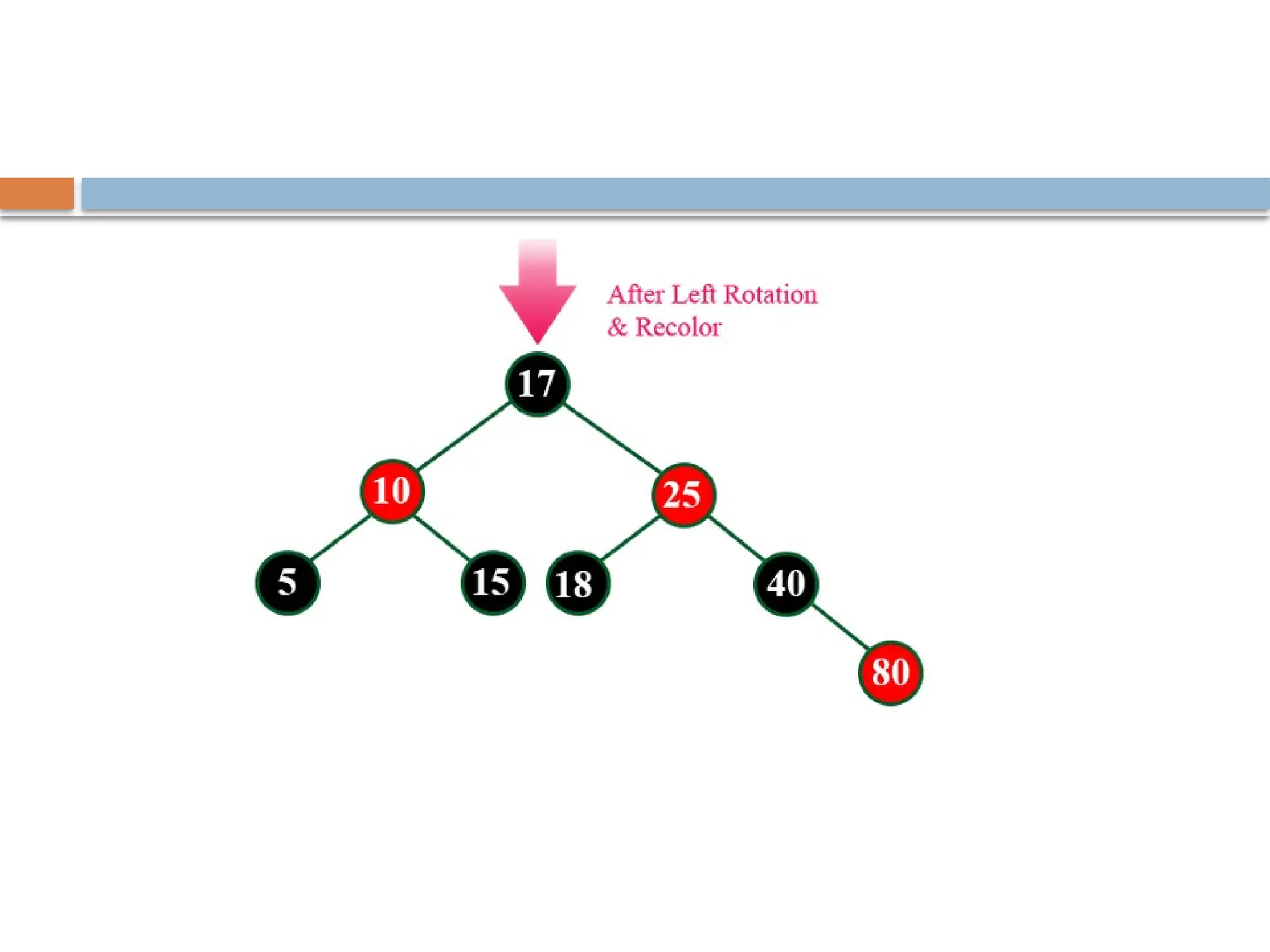
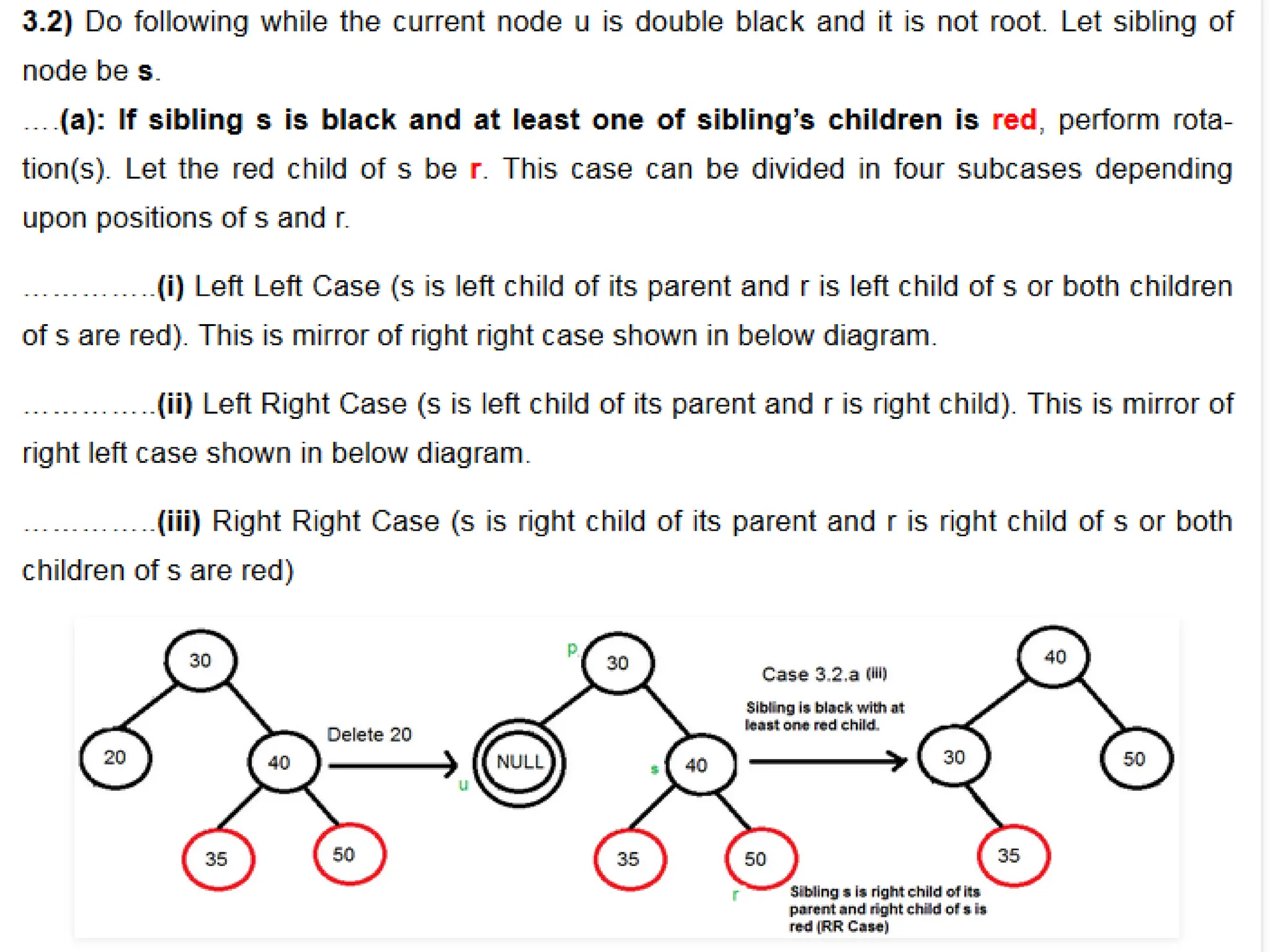
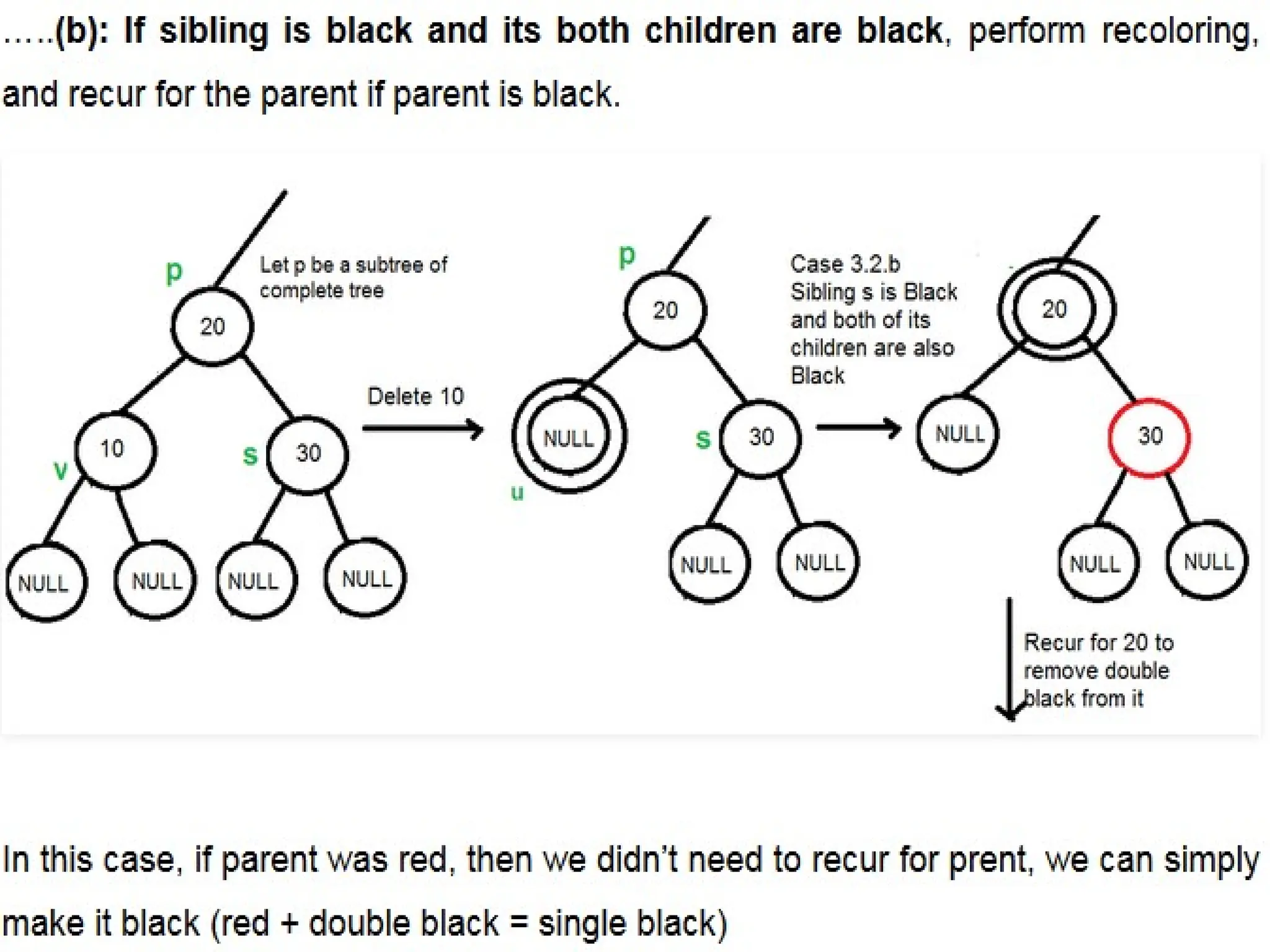
A red-black tree is a self-balancing binary search tree where each node is colored red or black to maintain balance during insertions and deletions. The root is always black, and various properties must be adhered to, such as red nodes having black children and equal black heights across all paths. Balancing is achieved through recoloring and rotations during insertions and deletions, with specific cases based on the colors of the node's uncle or sibling.