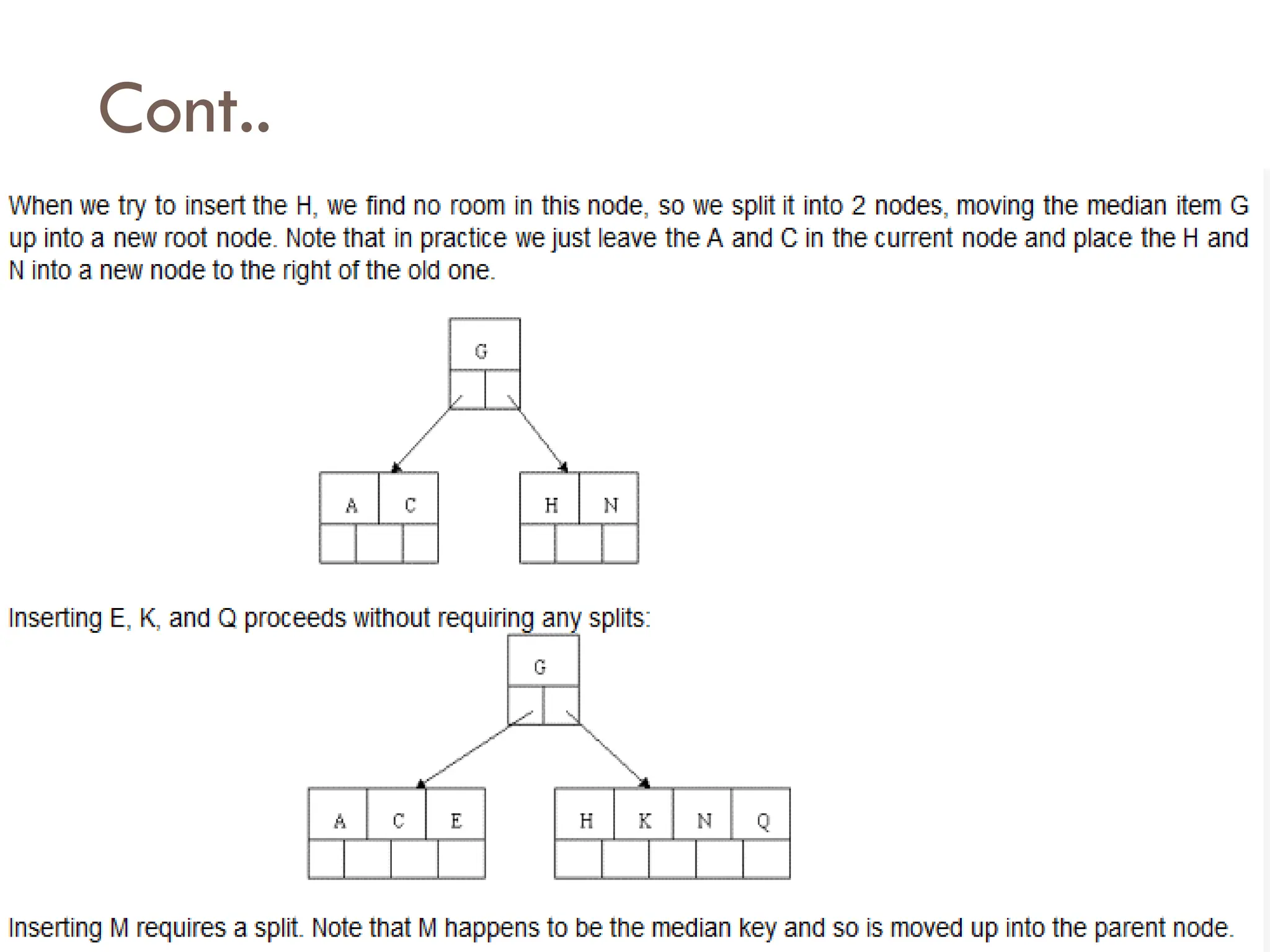
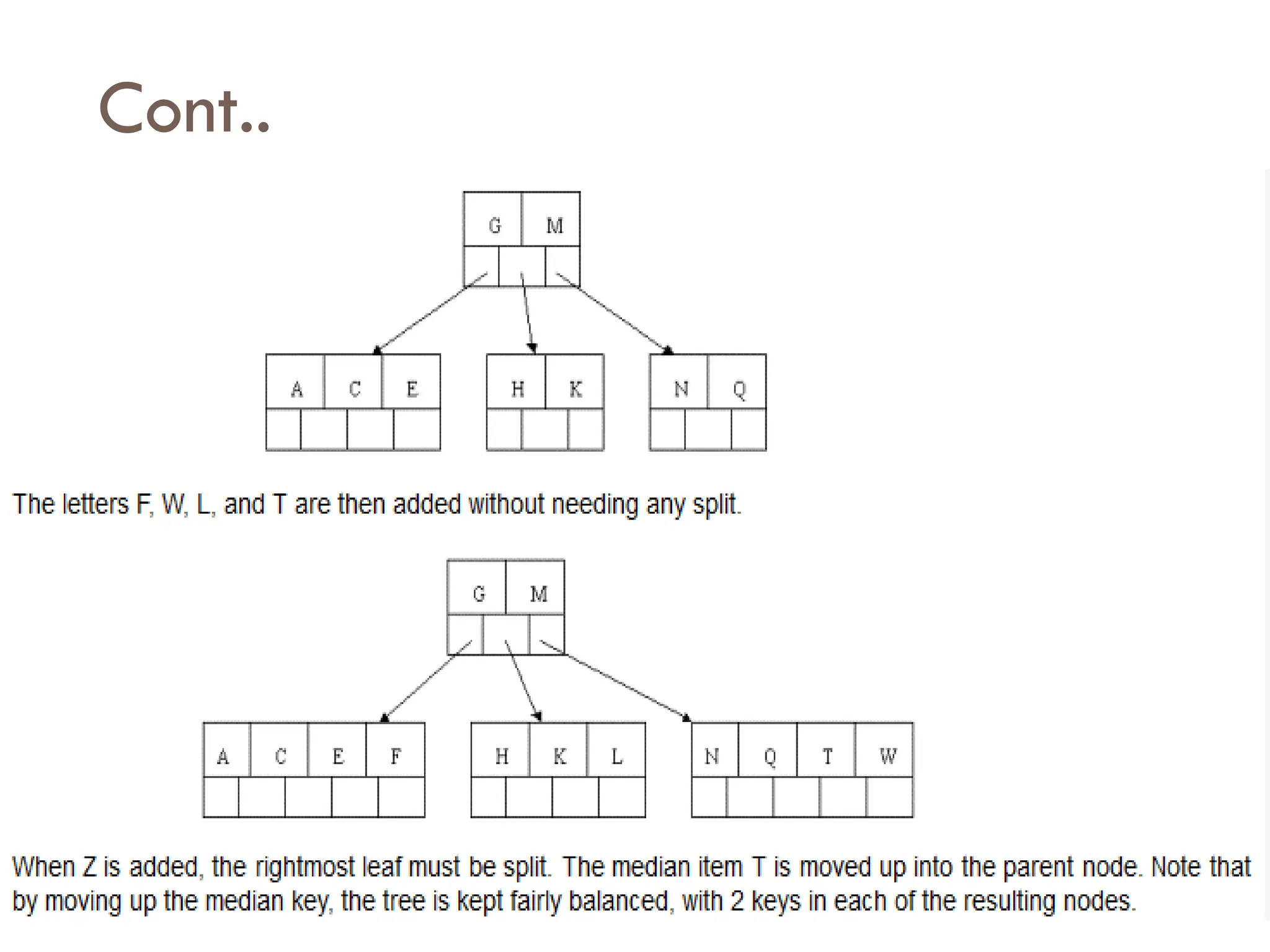
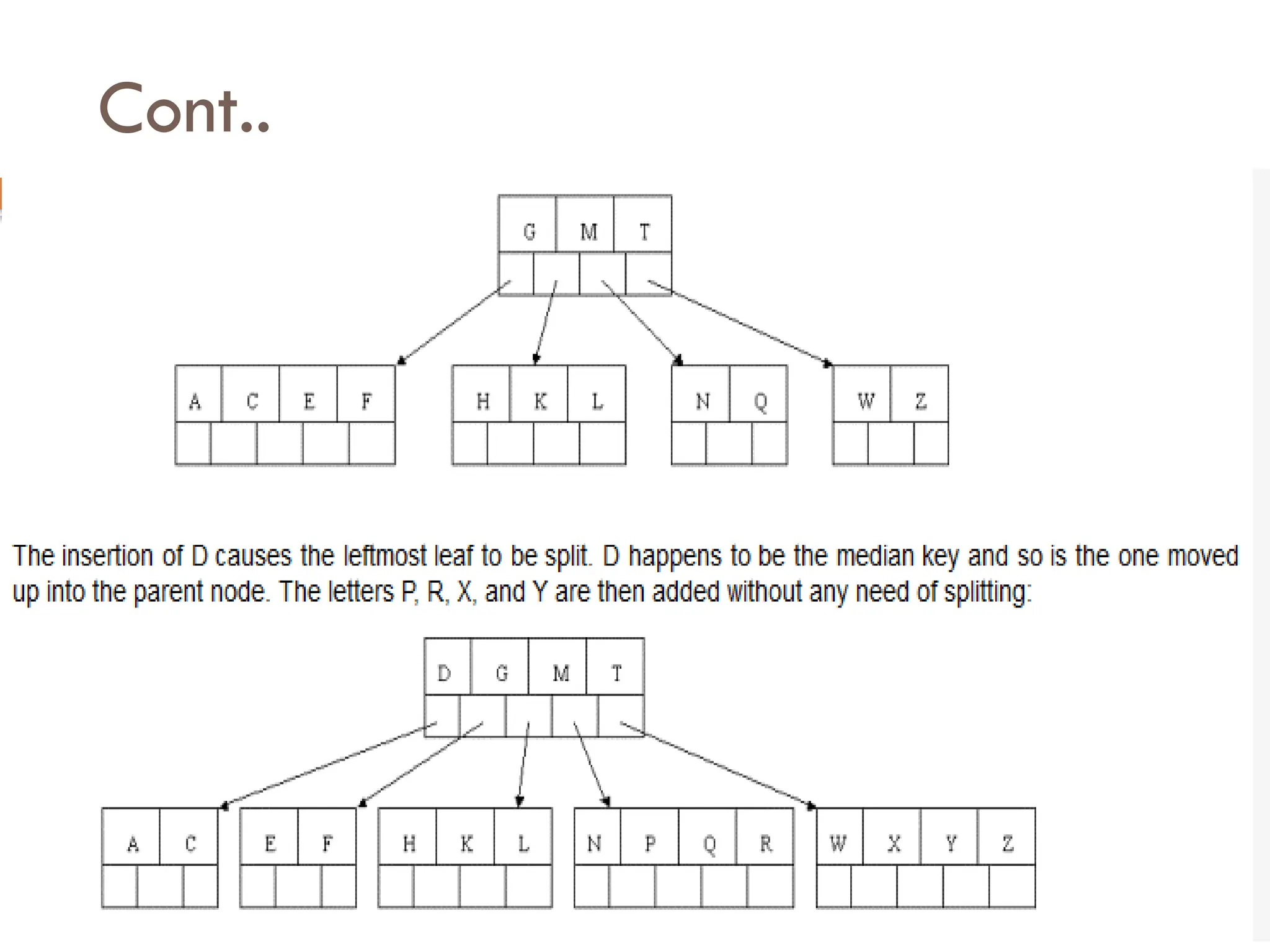
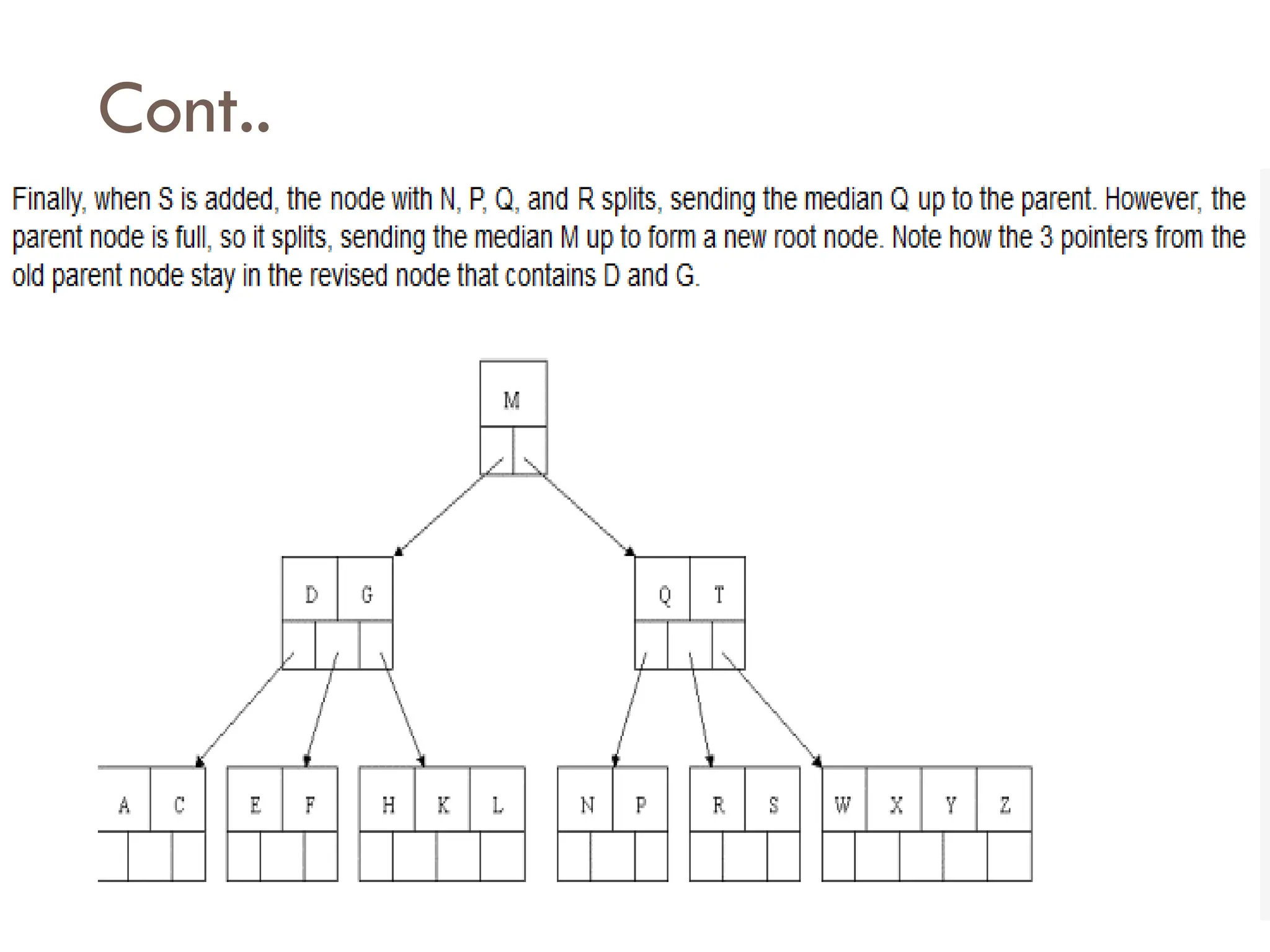
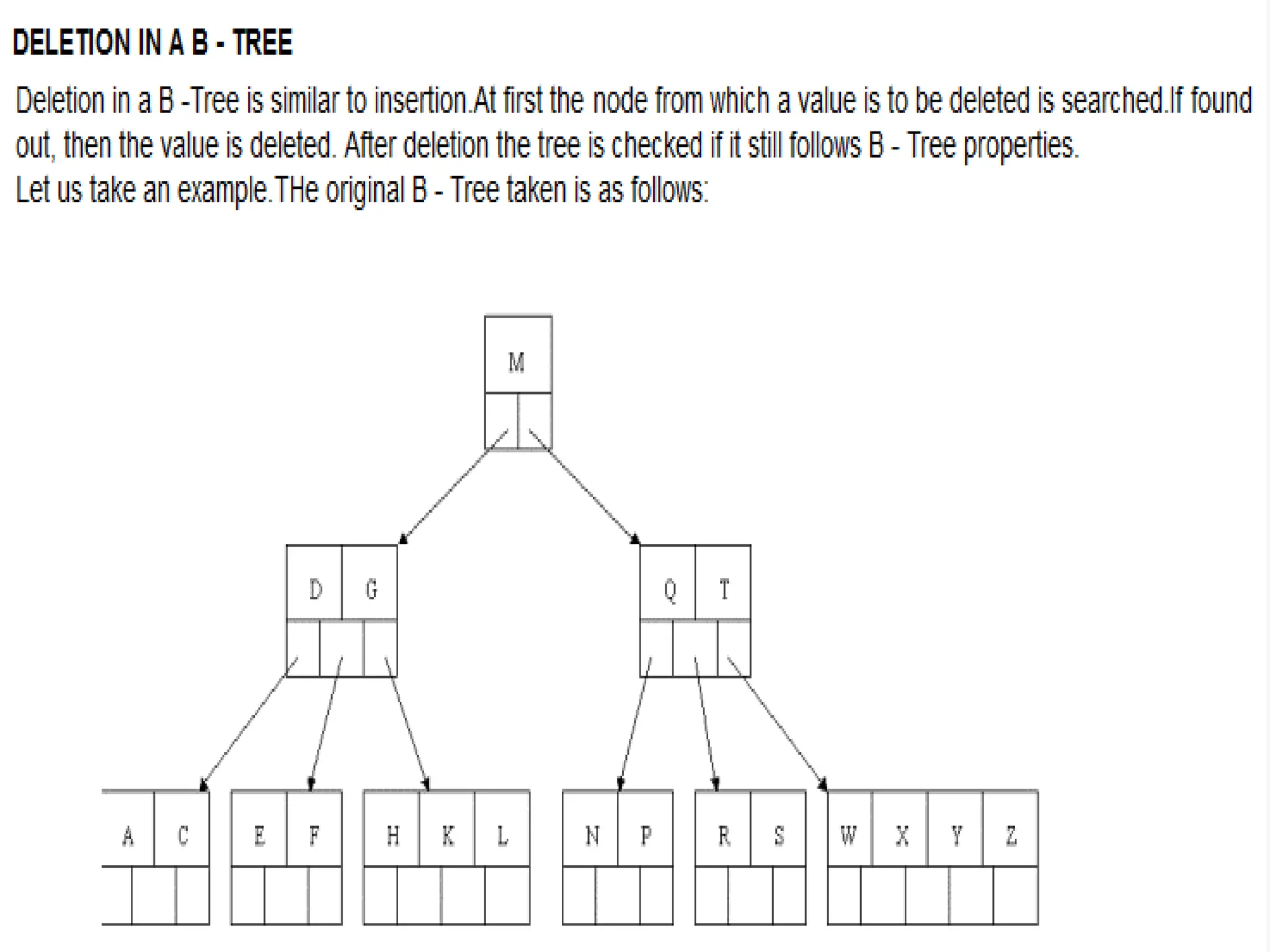
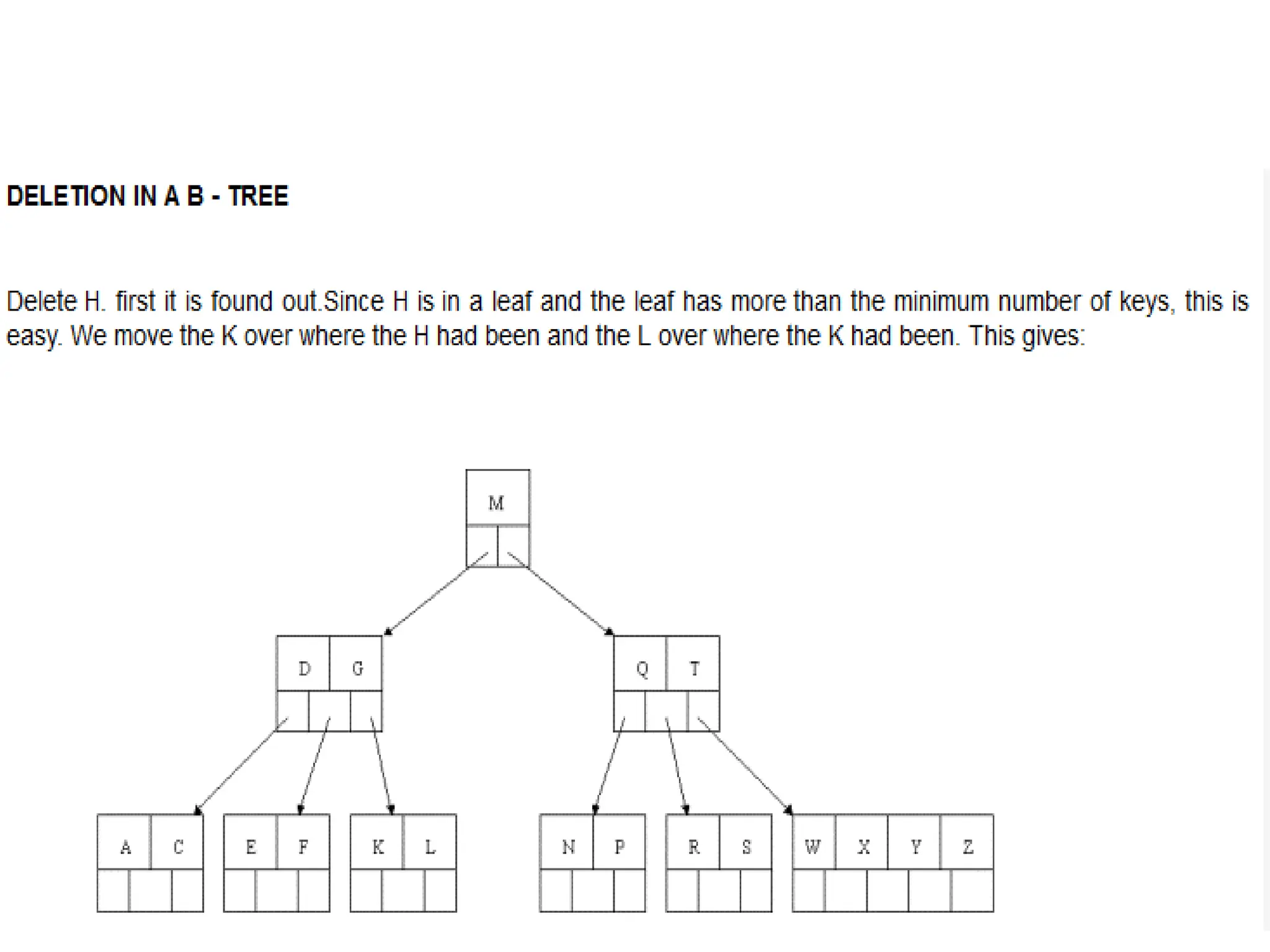
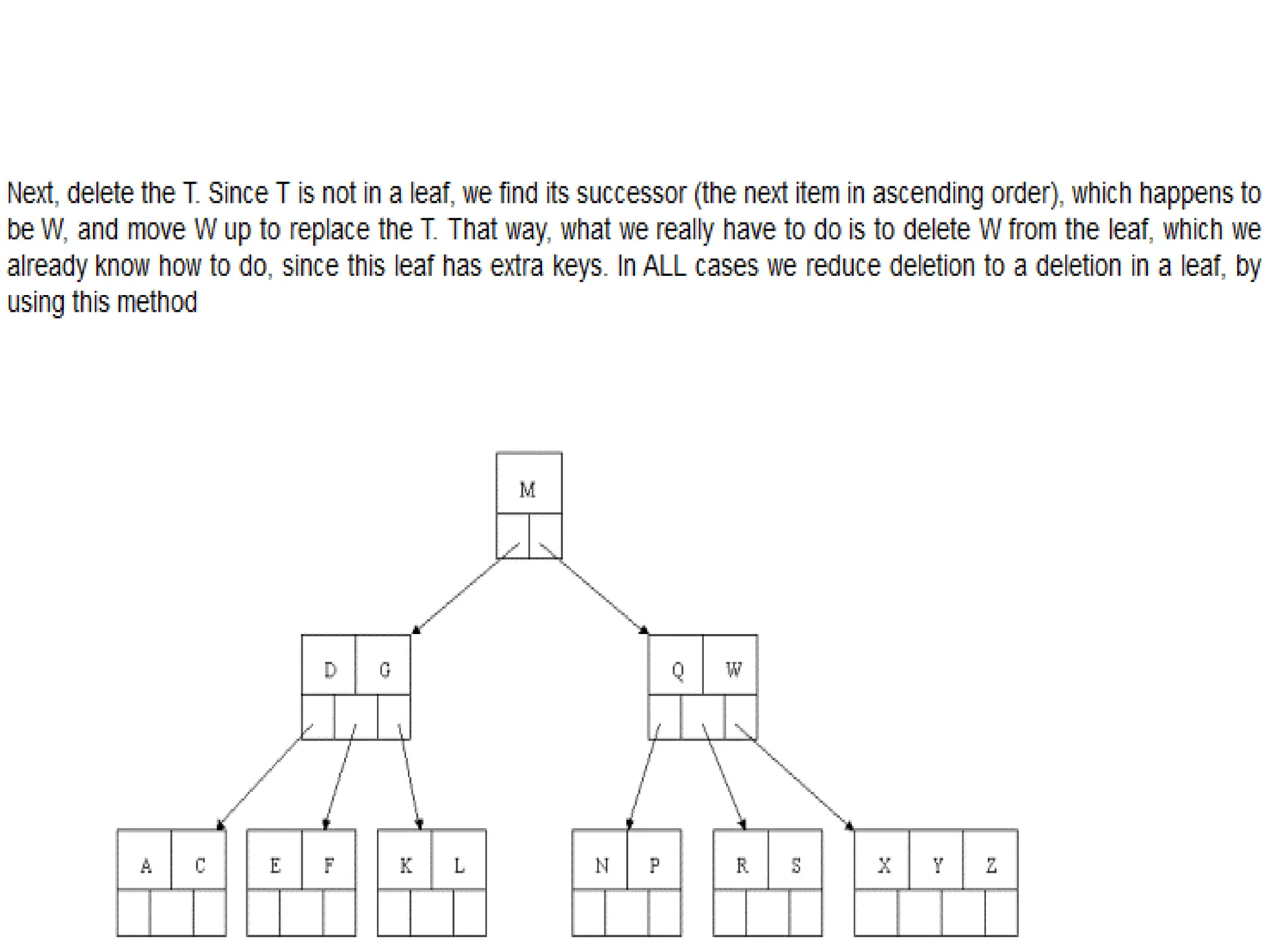
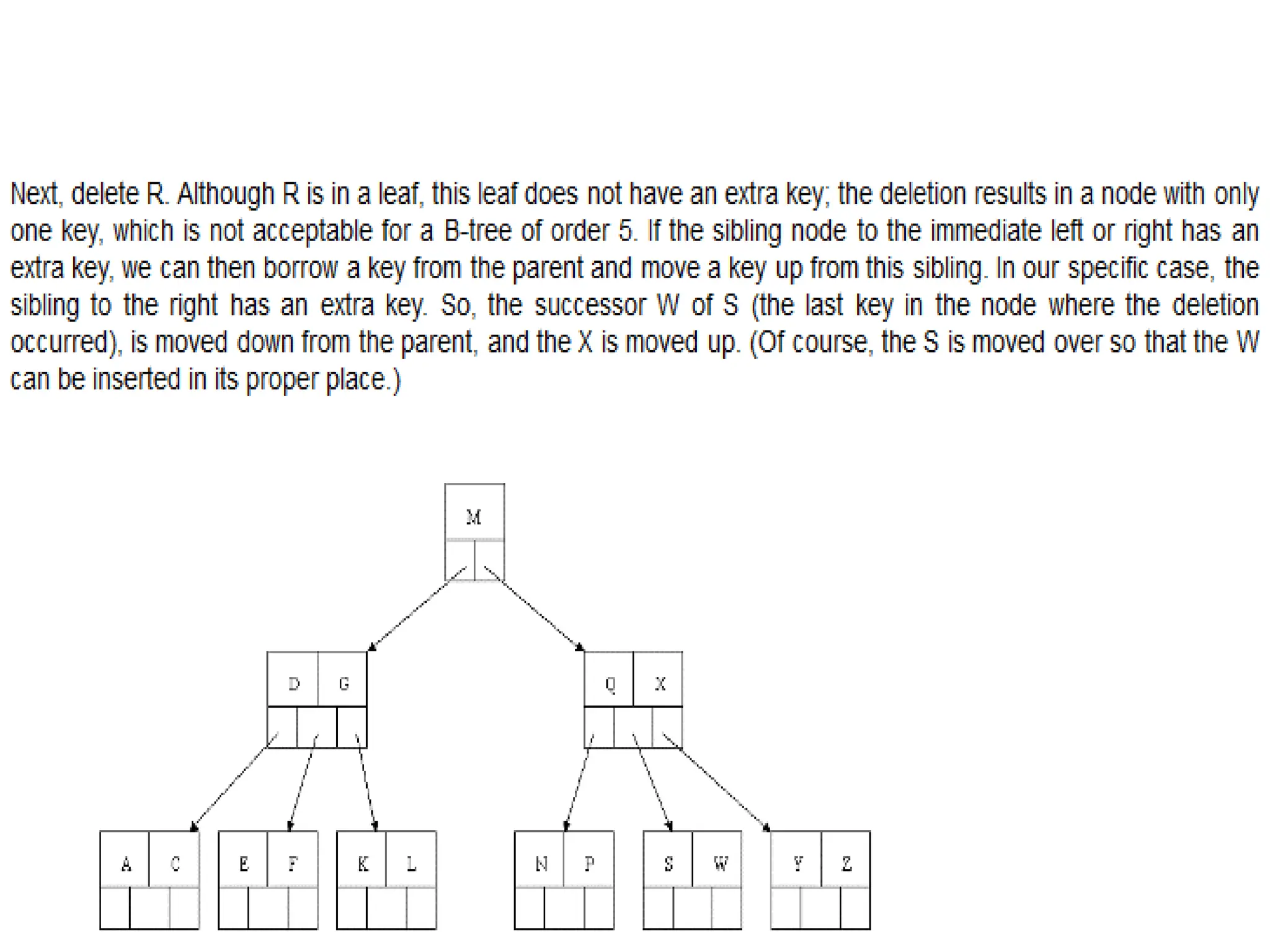
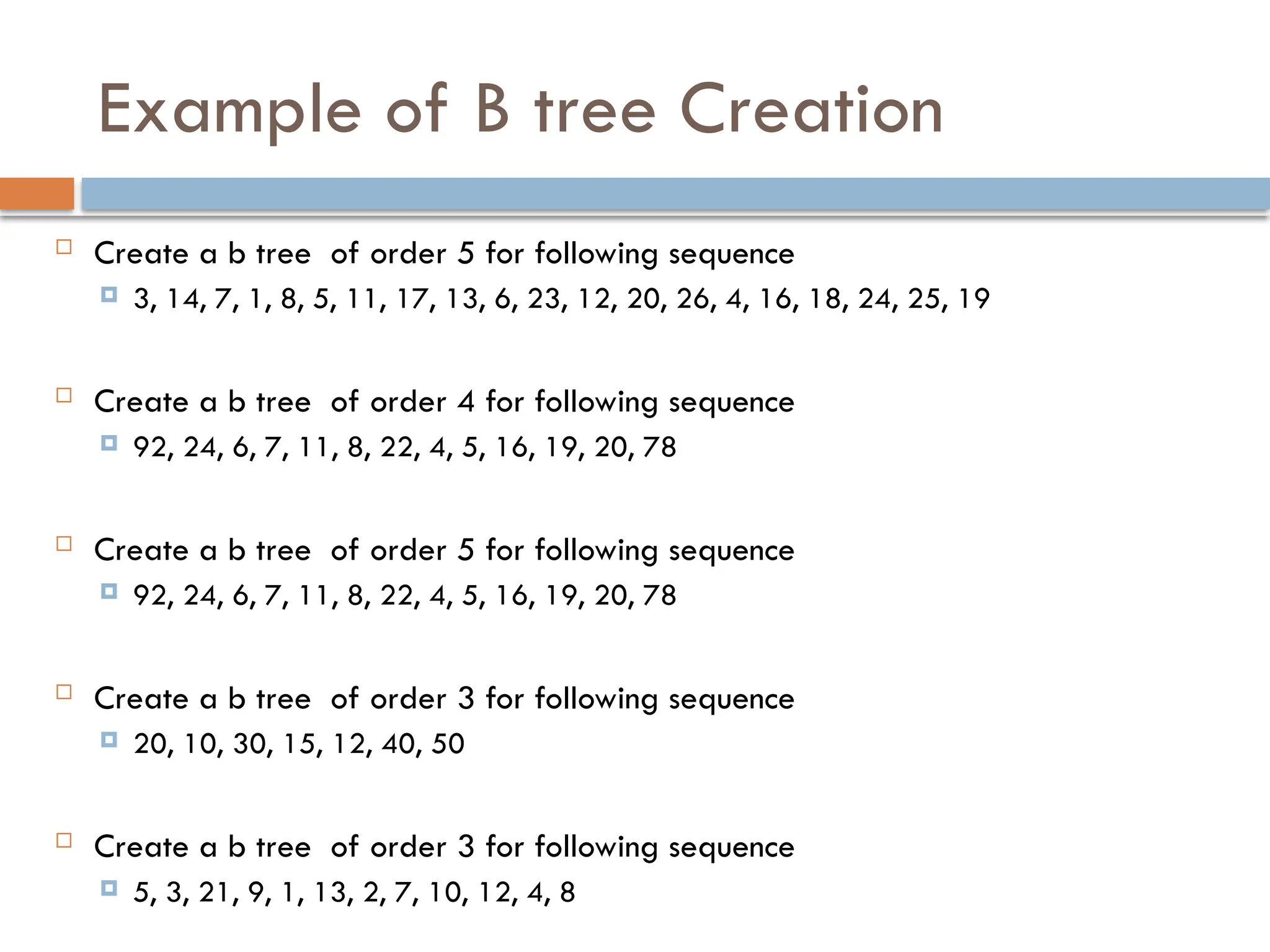
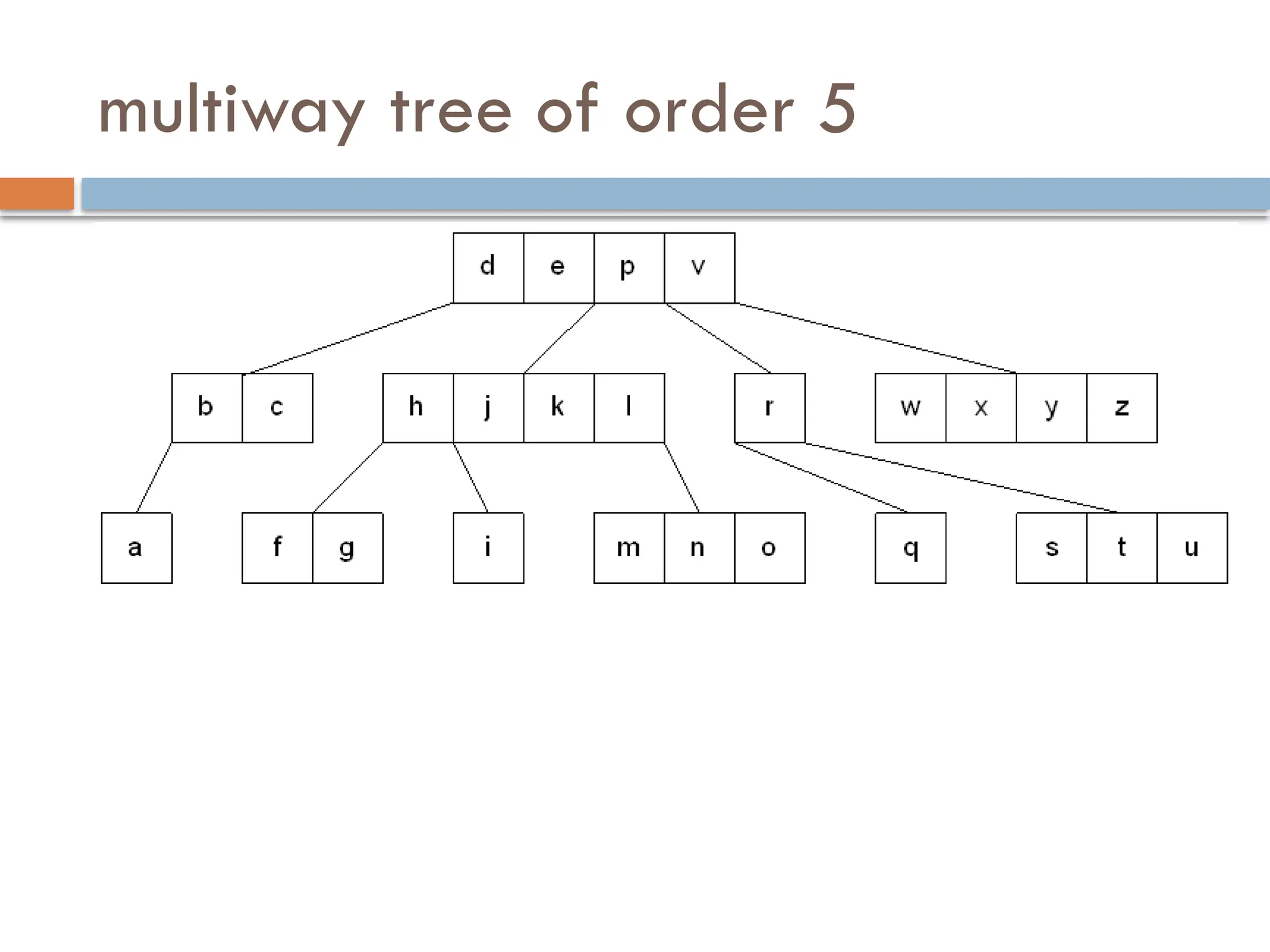
The document explains m-way search trees, which are multiway trees allowing nodes to have multiple children and keys stored in ascending order, enhancing search operations compared to binary trees. It details properties and algorithms for searching within m-way trees and describes B-trees, a type of balanced m-way tree with specific structural rules that optimize data retrieval from secondary storage. Examples of creating B-trees with various orders illustrate the application of these concepts.









![SEARCHING OF A VALUE IN A B-TREE
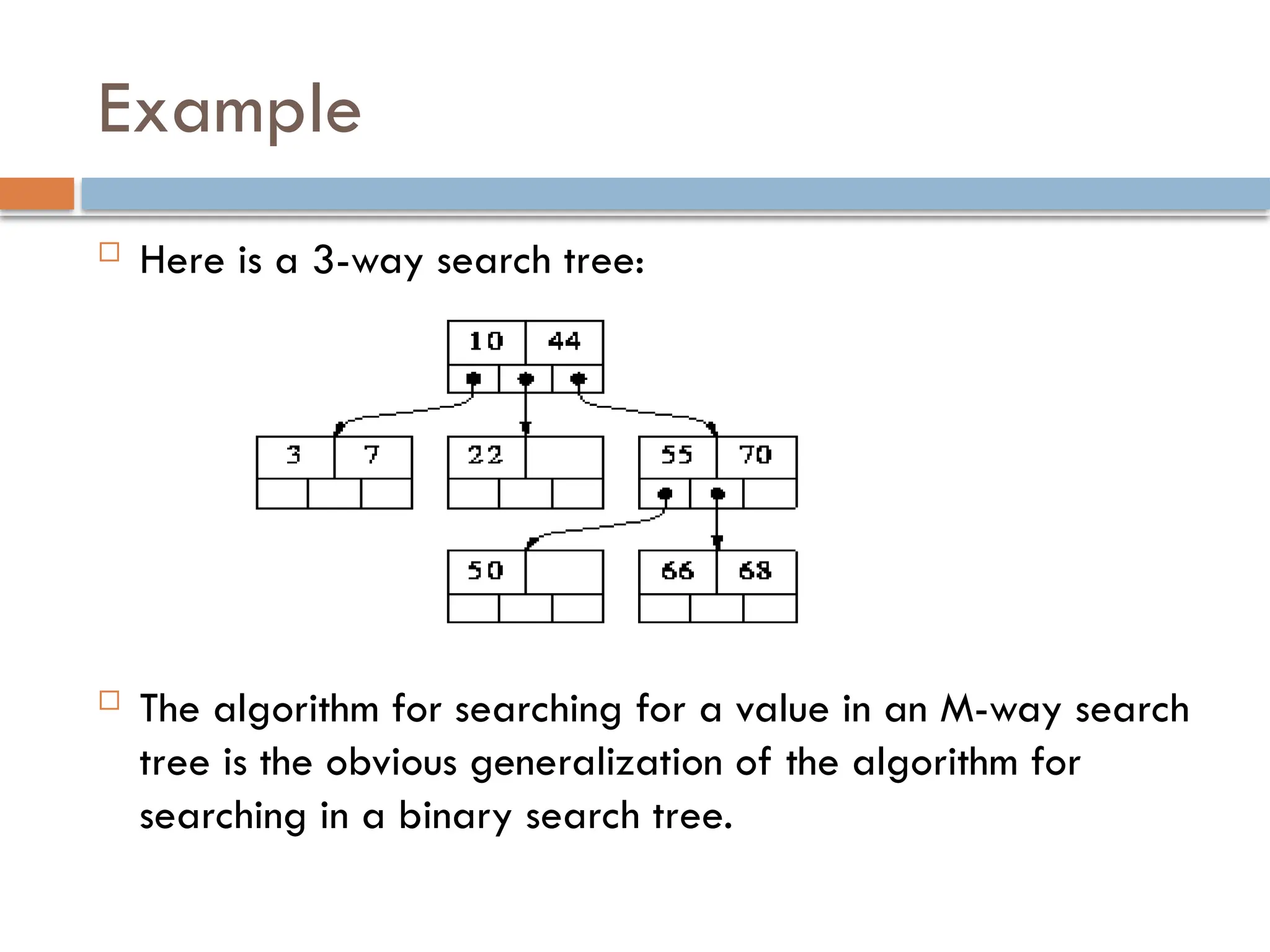
Searching of a value k in a B-Tree is exactly similar to
searching for values in a 2-3 tree.
To begin with the value k is compared with the first
value key [0] of the root node.
If they are similar then the search is complete.
If k is less than key [0] then the search is done in the
first child node or the sub-tree of the root node.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5mwaytree-241224162811-18f08d5e/75/Unit-5-m-way-tree-pptxMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMM-13-2048.jpg)
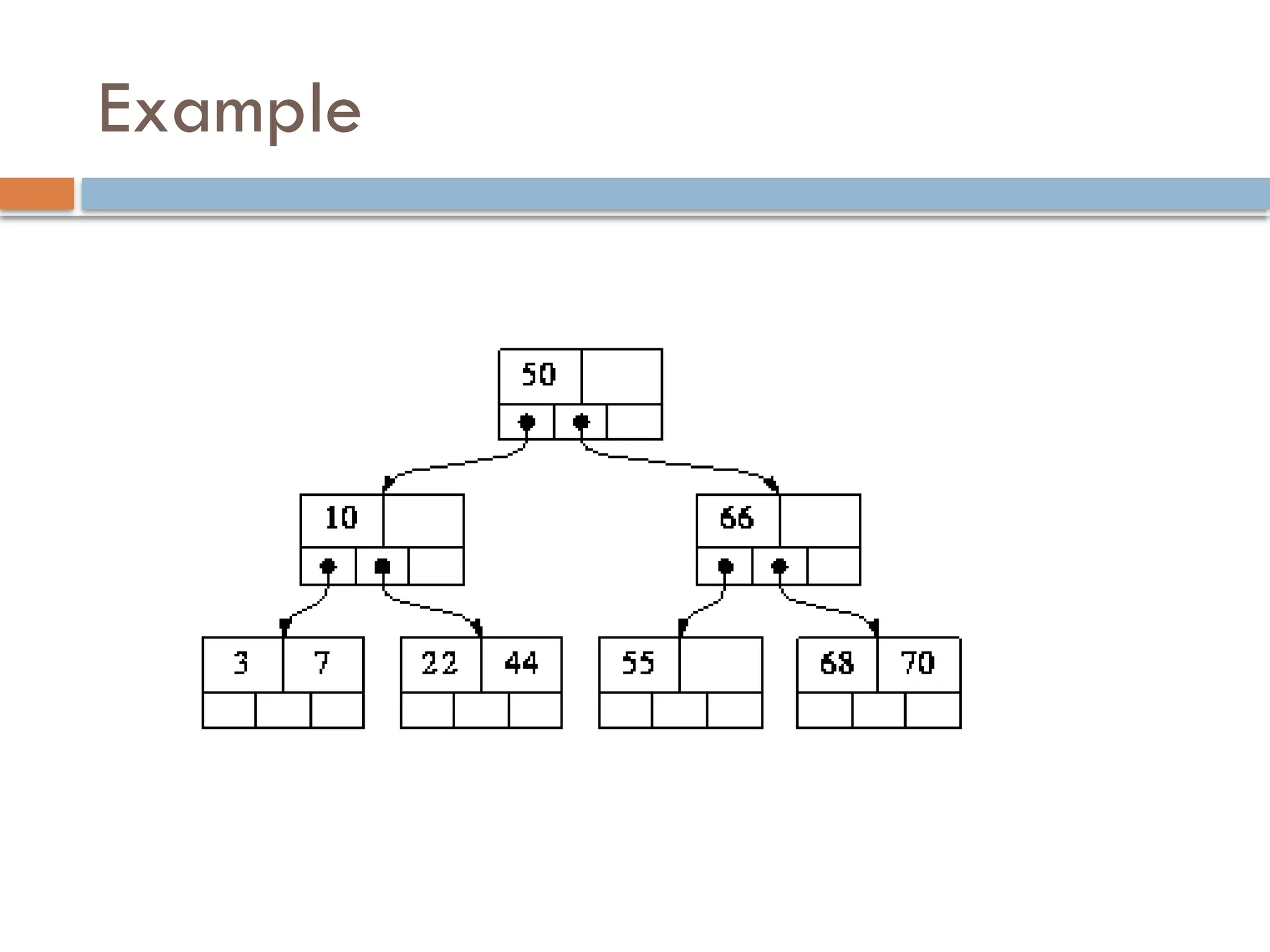
![Cont..
If k is greater than key [0] then it is compared with key [1]. If k
is greater than key [0] and smaller than key [1] then k is
searched in the second child node or sub-tree of the root node.
If k is greater than the last value key [i] of the root node then
searching is done in the last child node or sub-tree of the root
node.
If k is searched in any of the child nodes or sub-tree of the
root node then the same procedure of searching is repeated
for that particular node or sub-tree.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5mwaytree-241224162811-18f08d5e/75/Unit-5-m-way-tree-pptxMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMMM-14-2048.jpg)