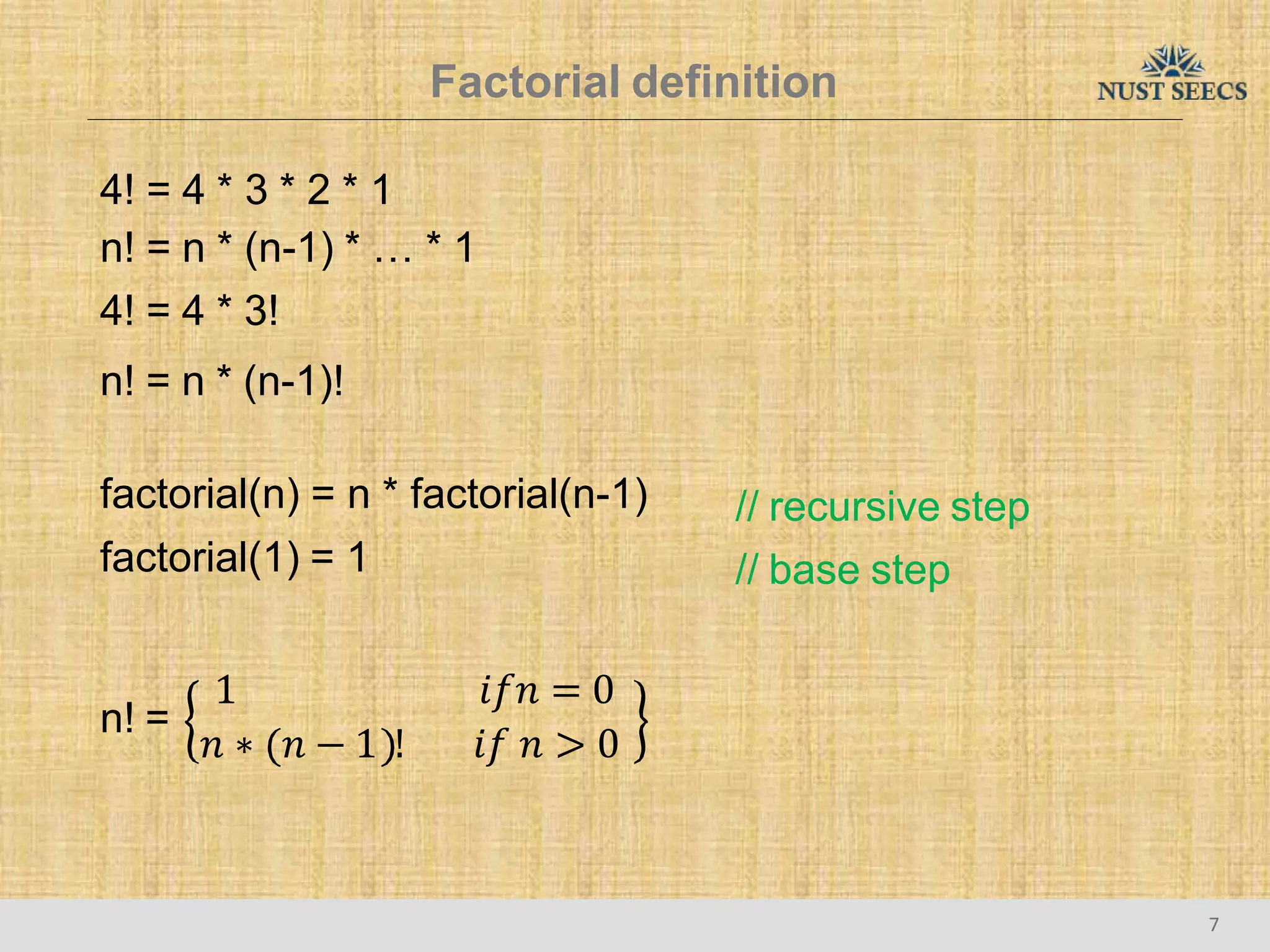
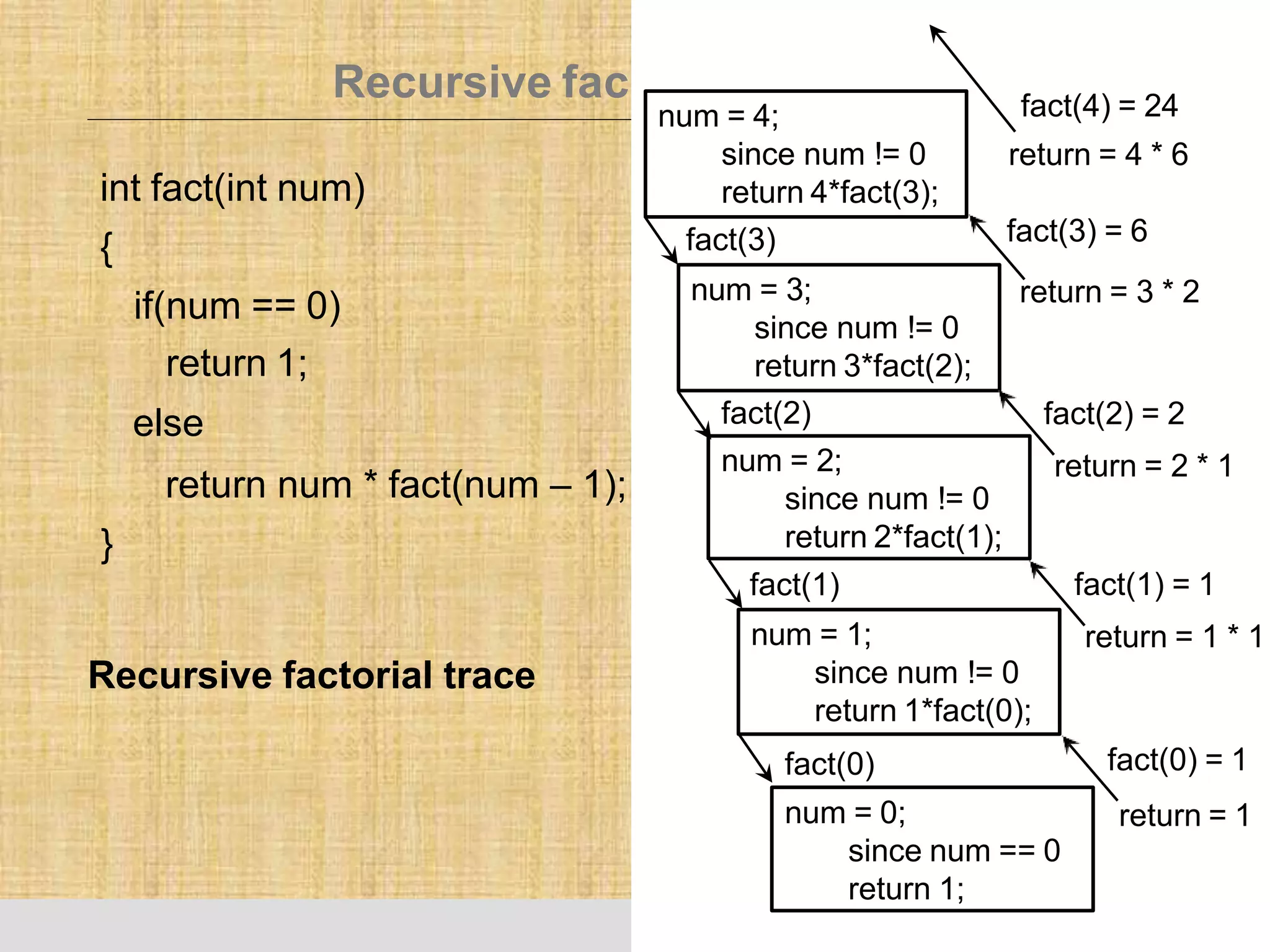
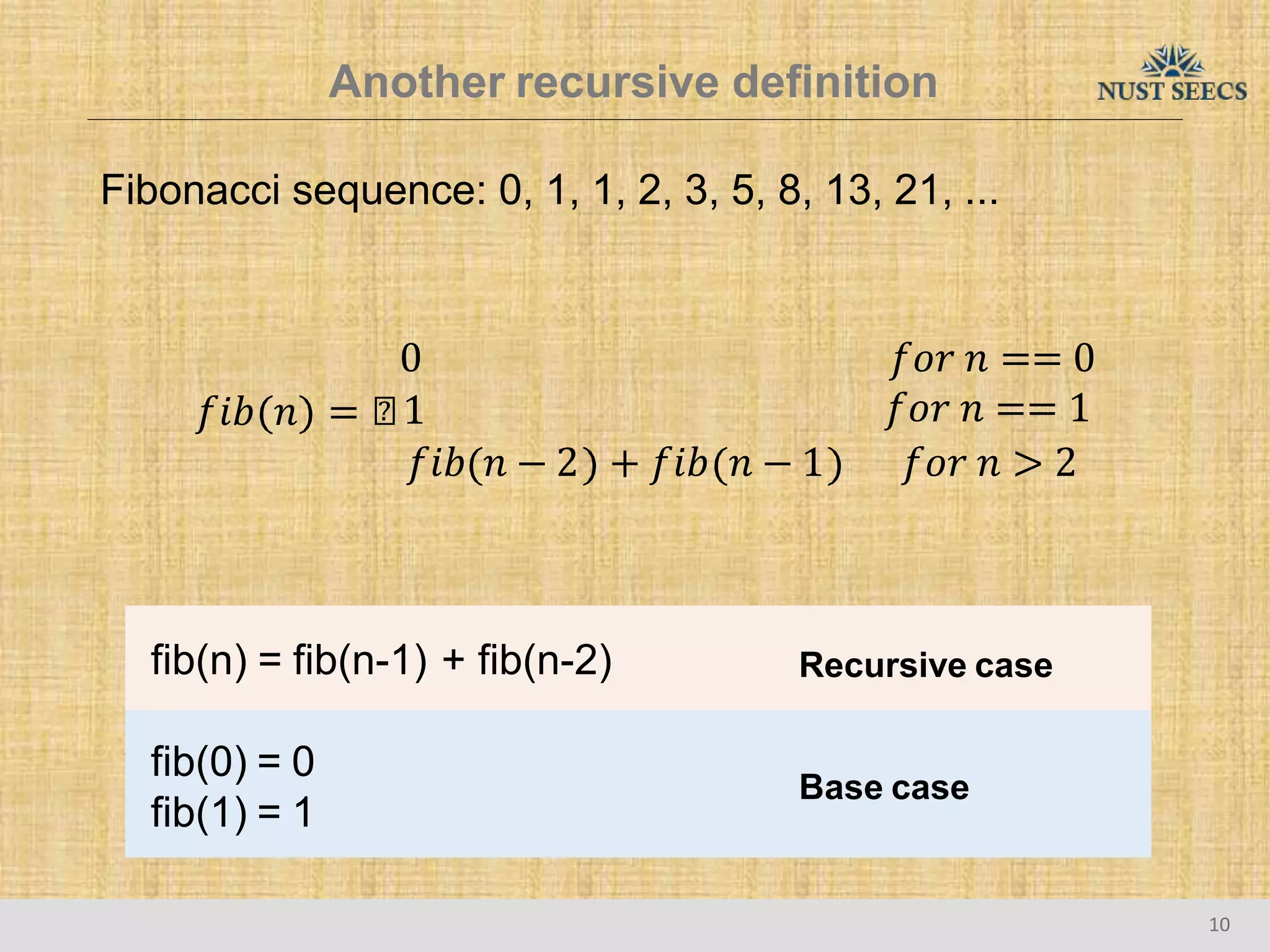
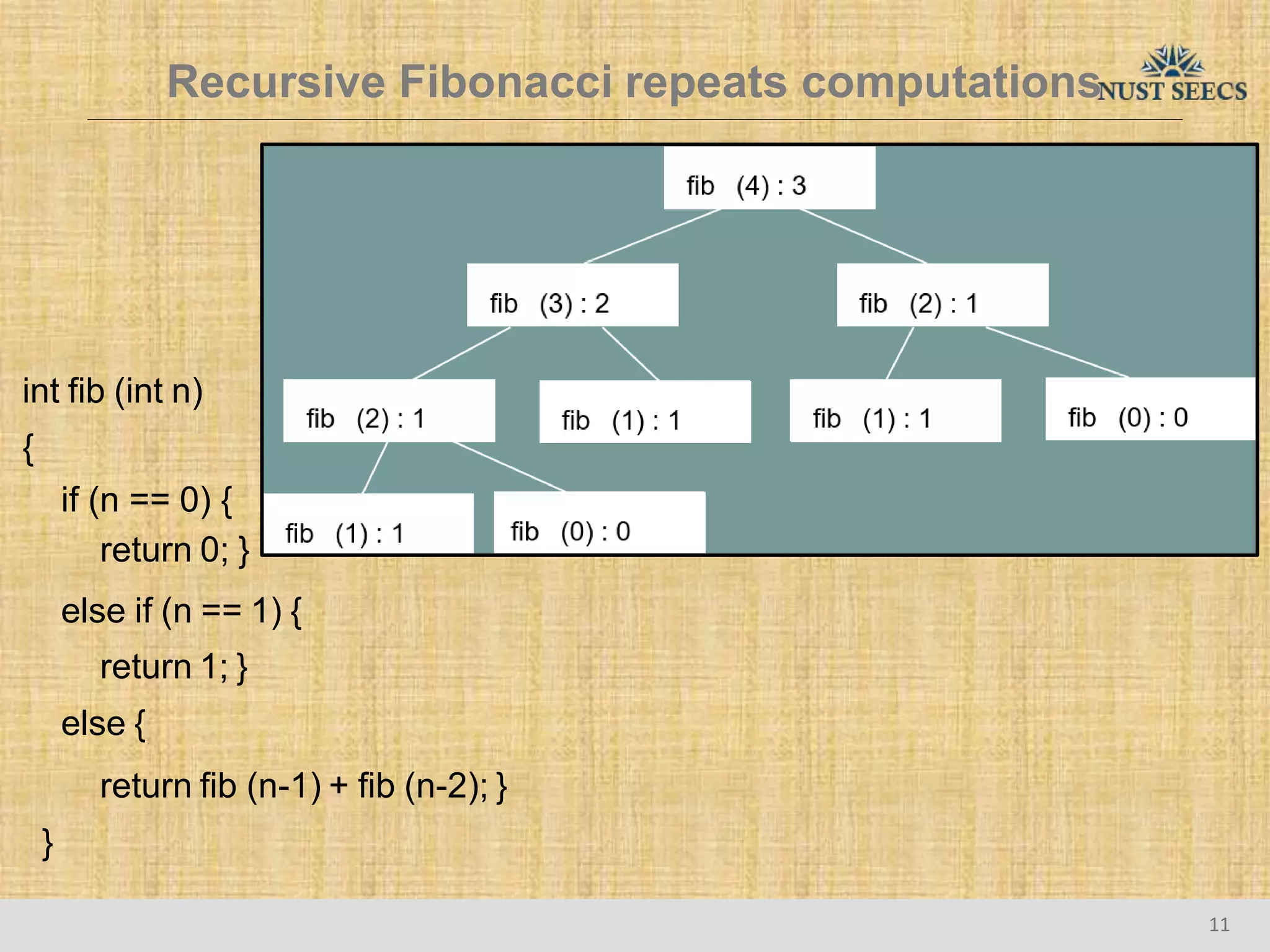
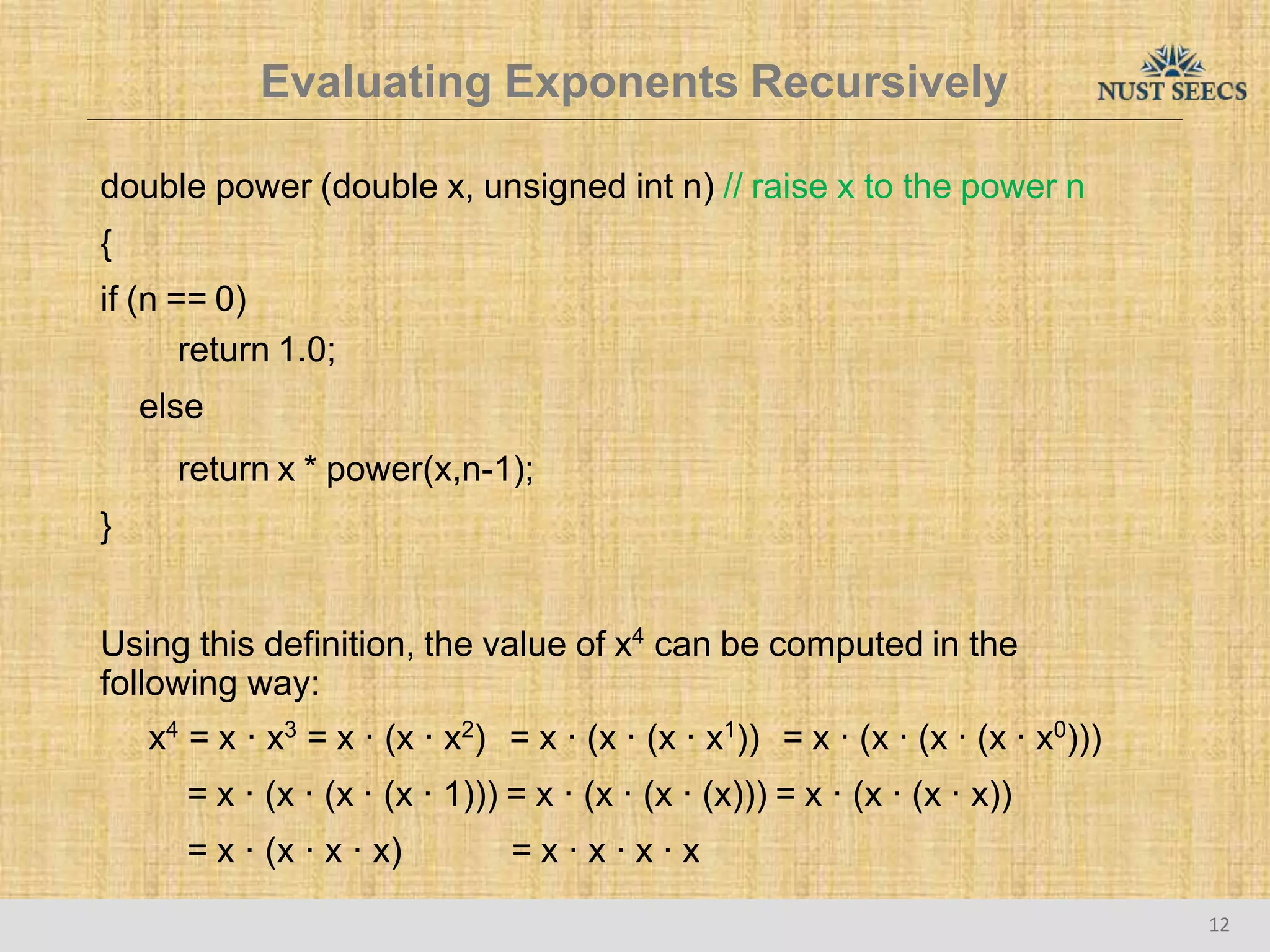
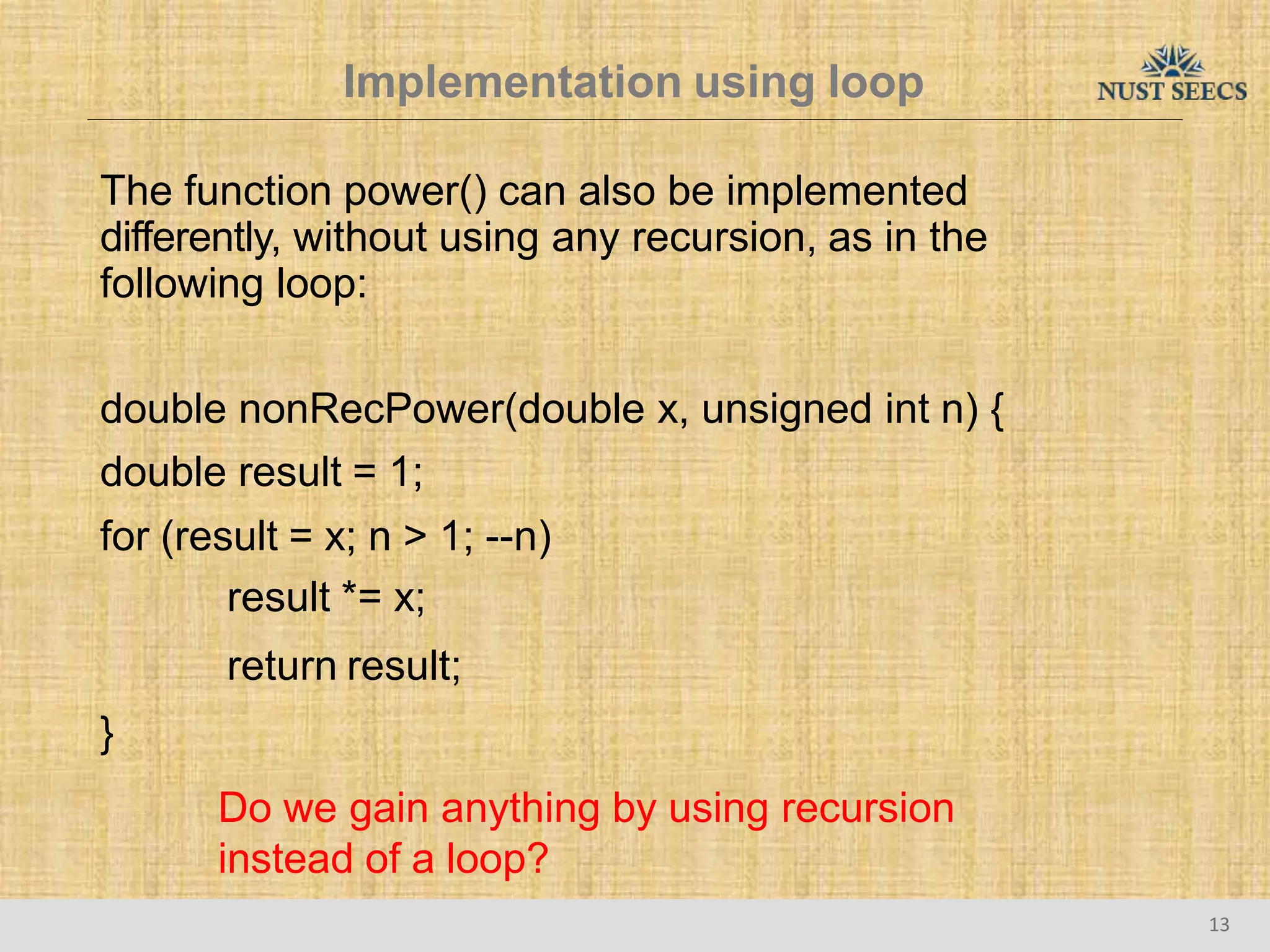
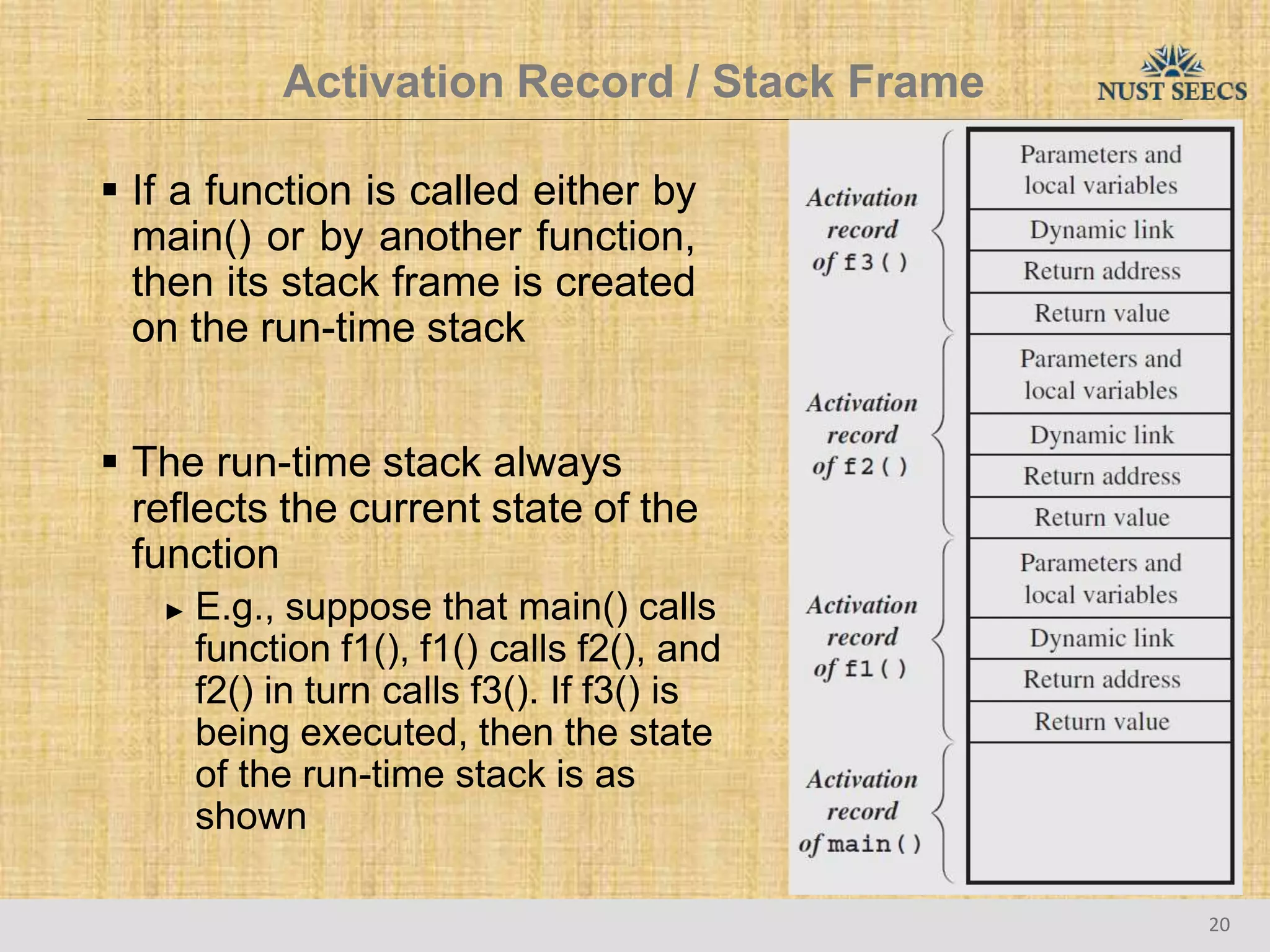
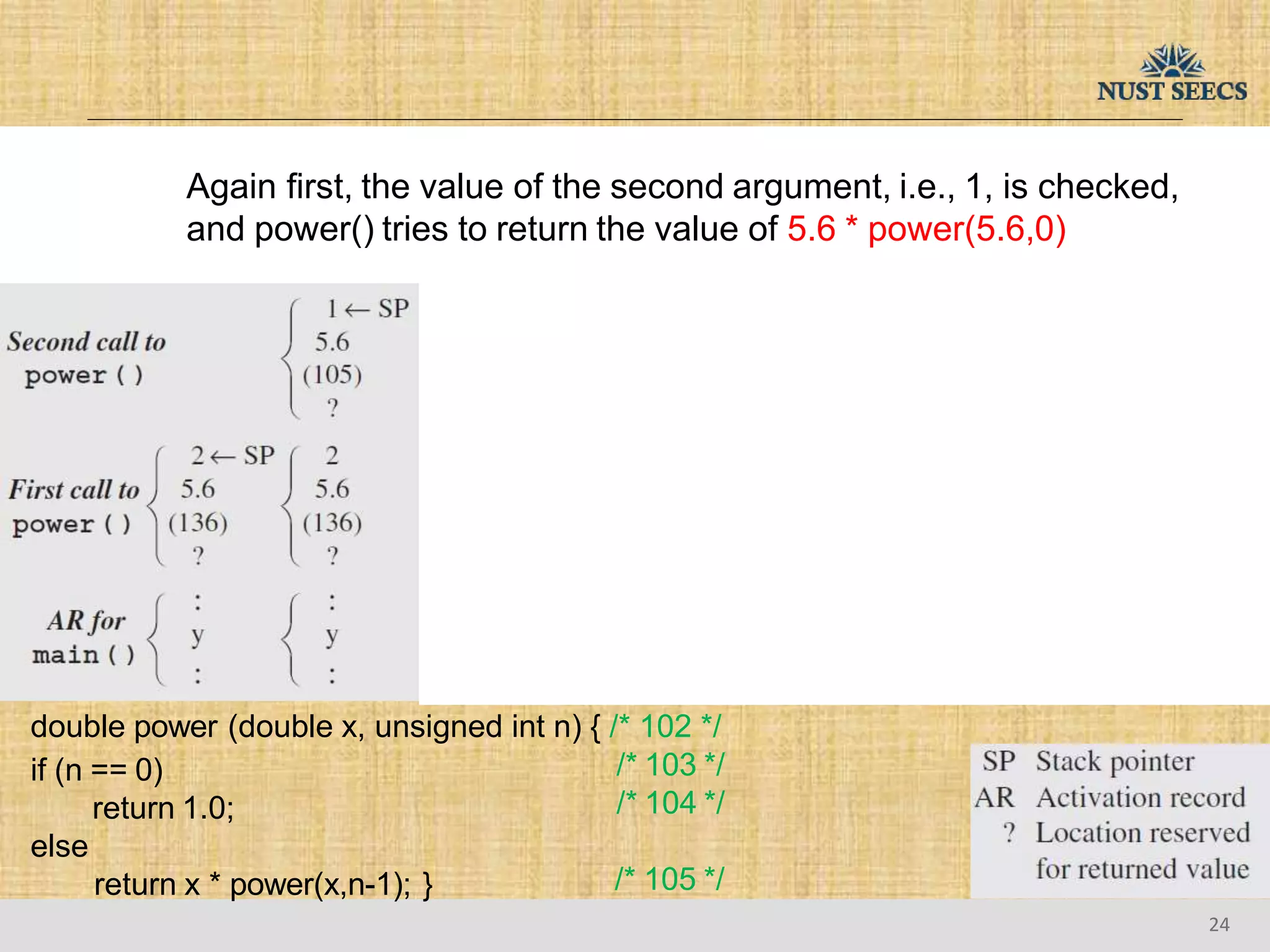
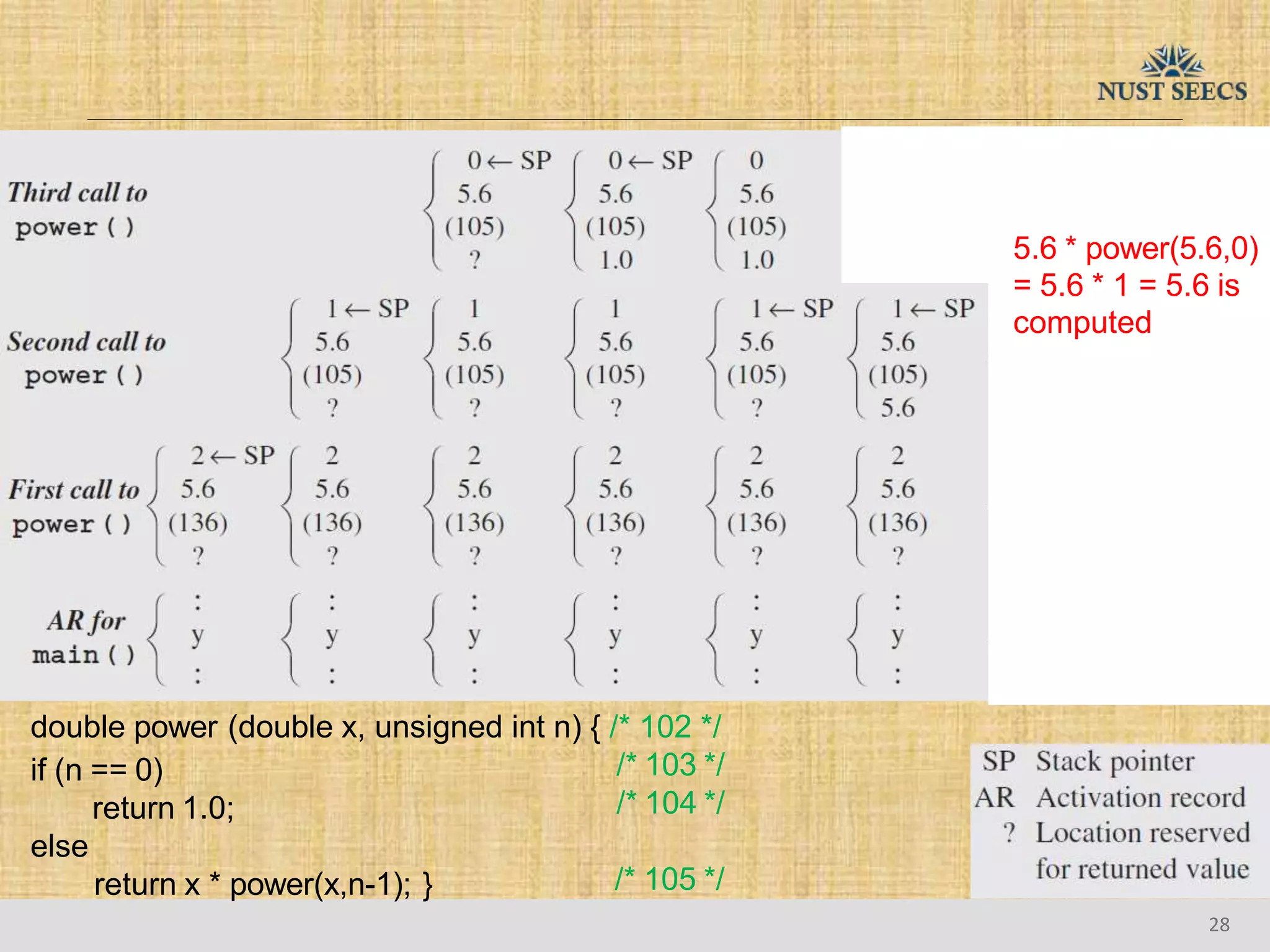
The document provides an overview of recursion, a problem-solving approach that involves breaking a problem into simpler versions and solving them recursively. It explains key concepts such as recursive functions, base cases, and illustrates this with the examples of factorial and Fibonacci calculations, as well as the evaluation of exponents. Additionally, it discusses the advantages and pitfalls of recursion compared to iterative approaches, noting efficiency considerations and the structure of activation records used during recursive calls.