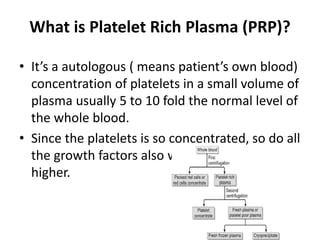
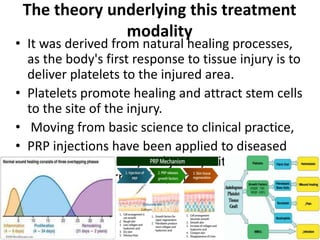
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) involves concentrating the platelets from a patient's own blood, which contain growth factors that promote healing. PRP is being used increasingly in various medical fields as a non-operative treatment. In obstetrics, studies have found PRP may help seal tears in the amniotic membrane in cases of premature rupture of membranes. It may also accelerate wound healing after cesarean sections and episiotomies. The PRP preparation process involves drawing and centrifuging blood to separate out platelets, which are then injected into the target site to stimulate healing. More research is still needed but PRP represents a promising regenerative approach with few risks.