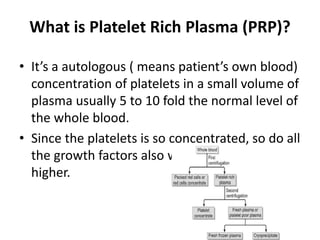
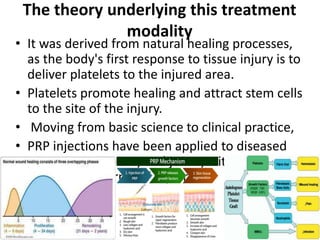
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is an autologous concentration of platelets in plasma. PRP contains high concentrations of growth factors that promote healing. It is prepared by drawing a patient's blood, centrifuging it to separate platelets from other blood components, and collecting the platelet-rich plasma. PRP is being used increasingly in regenerative medicine due to its ability to promote natural healing responses. In reproductive medicine, PRP is being used for endometrial rejuvenation, ovarian rejuvenation, treatment of ovarian torsion, and treatment of azoospermia. PRP injections are generally well-tolerated with minimal side effects.