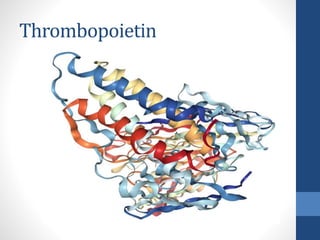
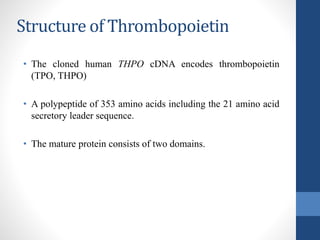
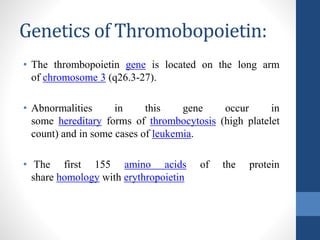
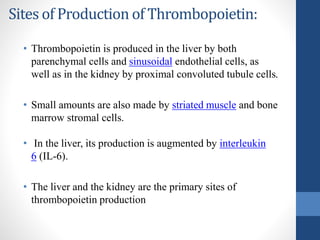
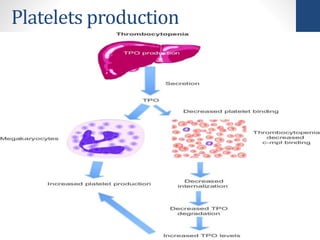
Thrombopoietin is a glycoprotein hormone that regulates platelet production. It is produced in the liver and kidneys and stimulates the production and differentiation of megakaryocytes in the bone marrow, which then release platelets. Low platelet counts (thrombocytopenia) can increase bleeding risk and are caused by conditions like cancer treatments, bone marrow diseases, and immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Thrombopoietin receptor agonists like romiplostim are used to treat thrombocytopenia by stimulating platelet production.