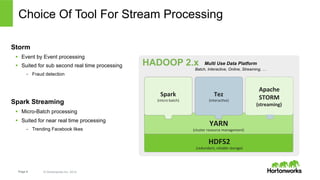
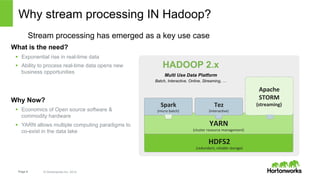
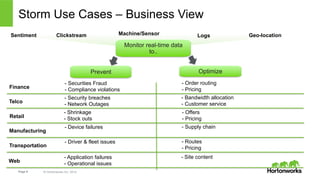
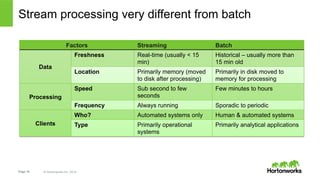
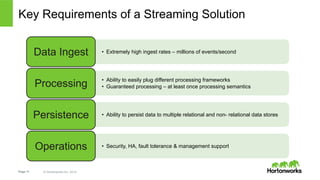
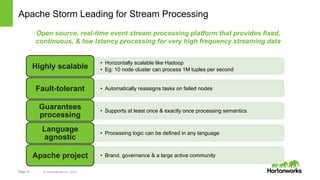
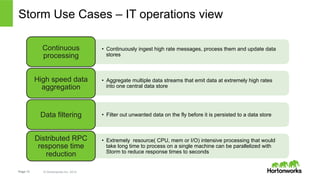
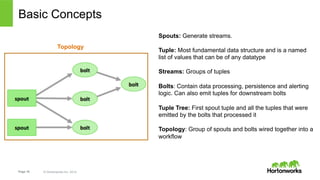
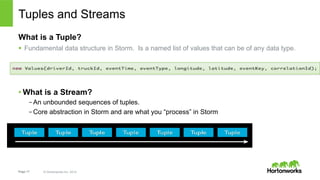
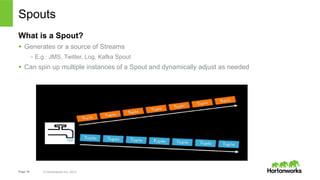
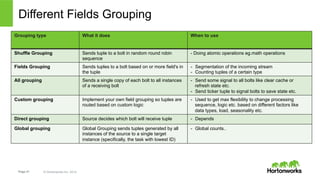
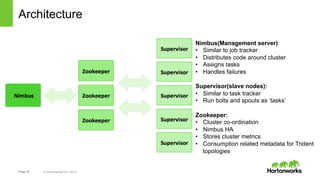
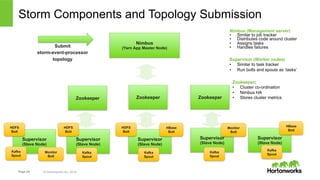
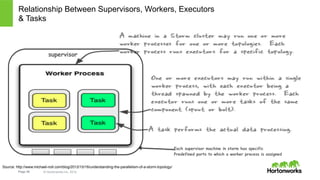
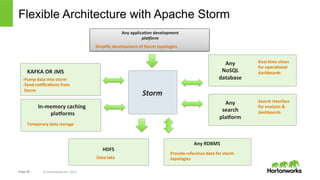
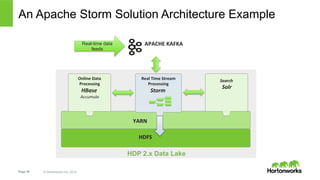
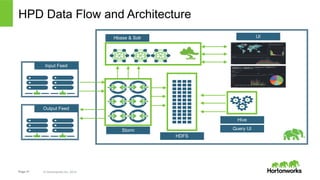
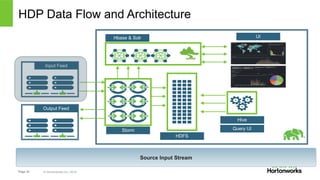
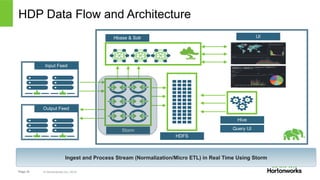
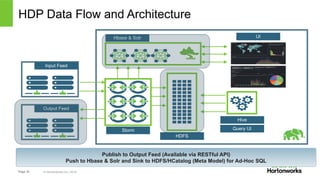
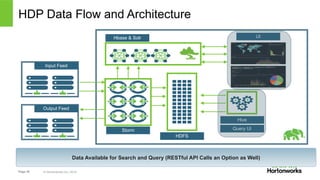
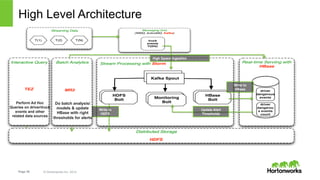
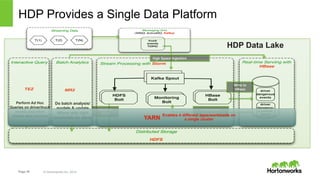
The document discusses real-time processing with Hadoop, focusing on Hortonworks and Apache Storm. It outlines the architecture and key constructs of Apache Storm, including its ability to handle high-volume streaming data, processing guarantees, and various use cases in business and IT operations. The document emphasizes the importance of stream processing in managing real-time data and improving operational efficiency.