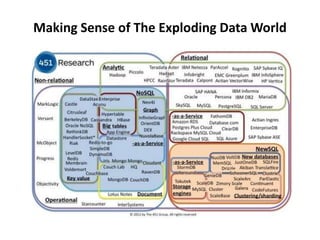
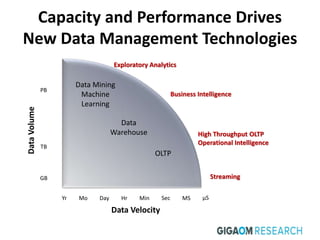
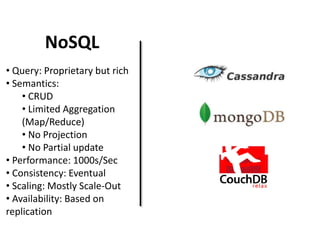
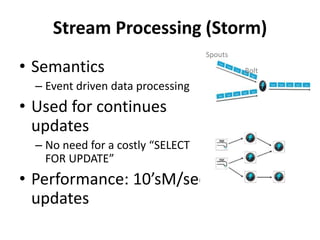
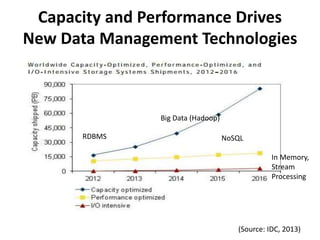
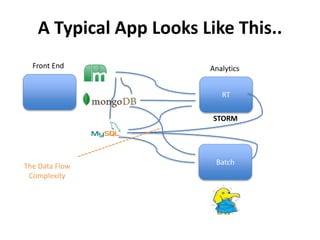
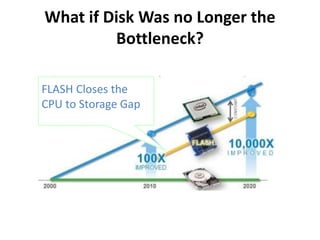
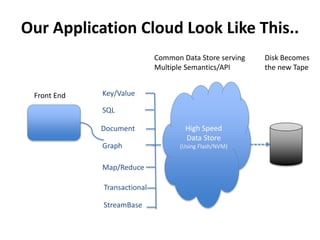
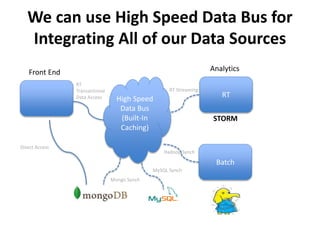
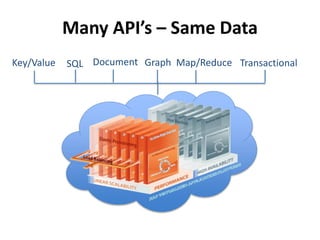
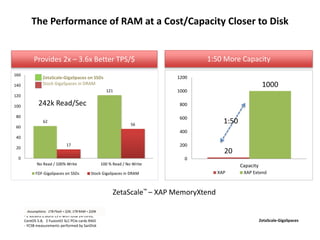
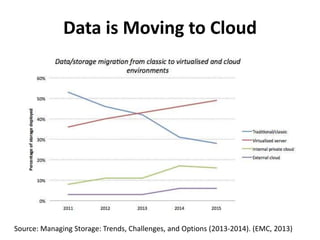
The document discusses advanced data management technologies that leverage NoSQL, in-memory databases, and stream processing to address the challenges of handling vast amounts of data in real time. It highlights the performance capabilities of various database approaches and the importance of integrating orchestration into database solutions for cloud readiness. The content includes a comparative analysis of SQL queries, NoSQL databases, key-value stores, and stream processing with respect to performance, scalability, and data consistency.