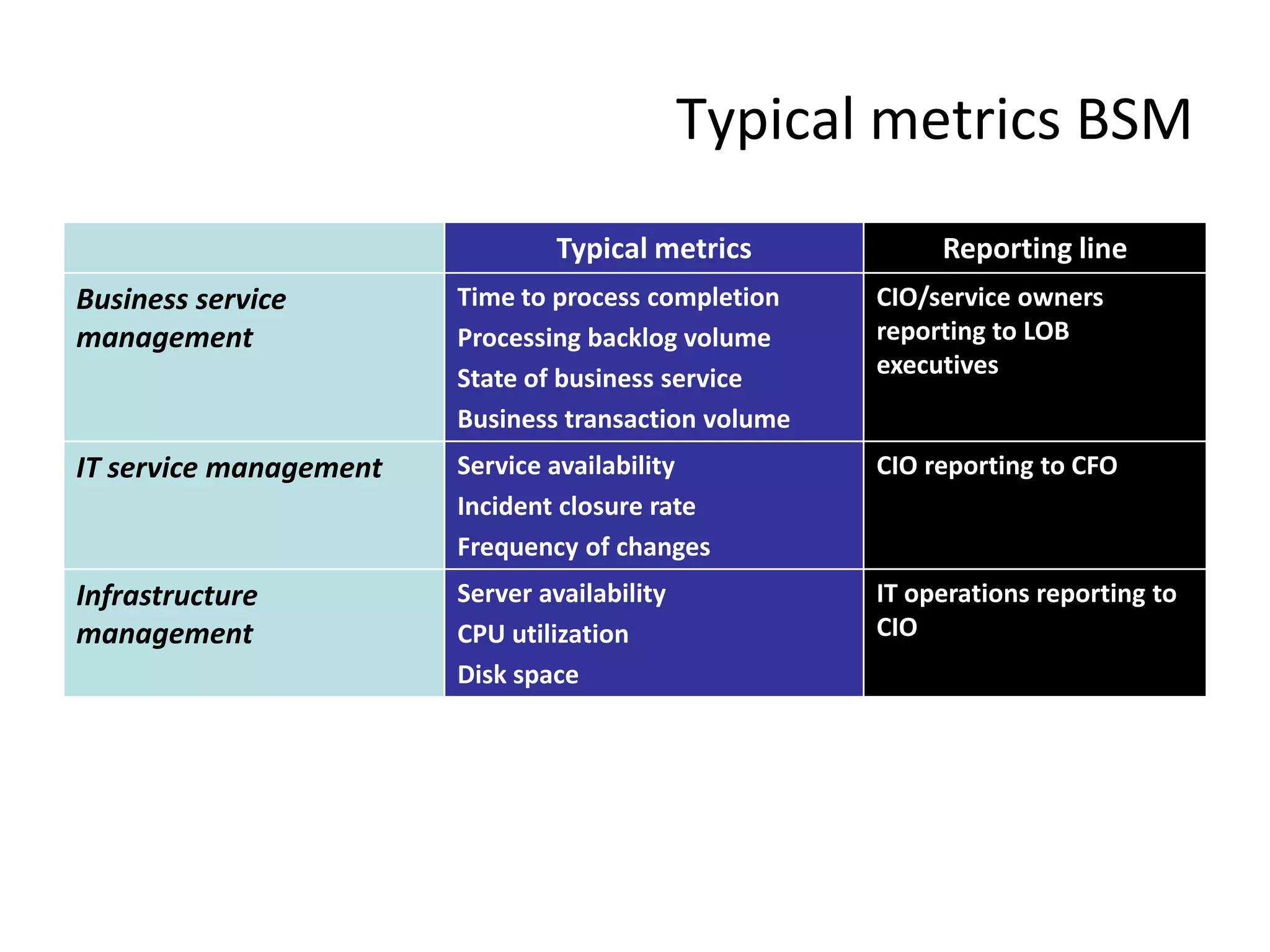
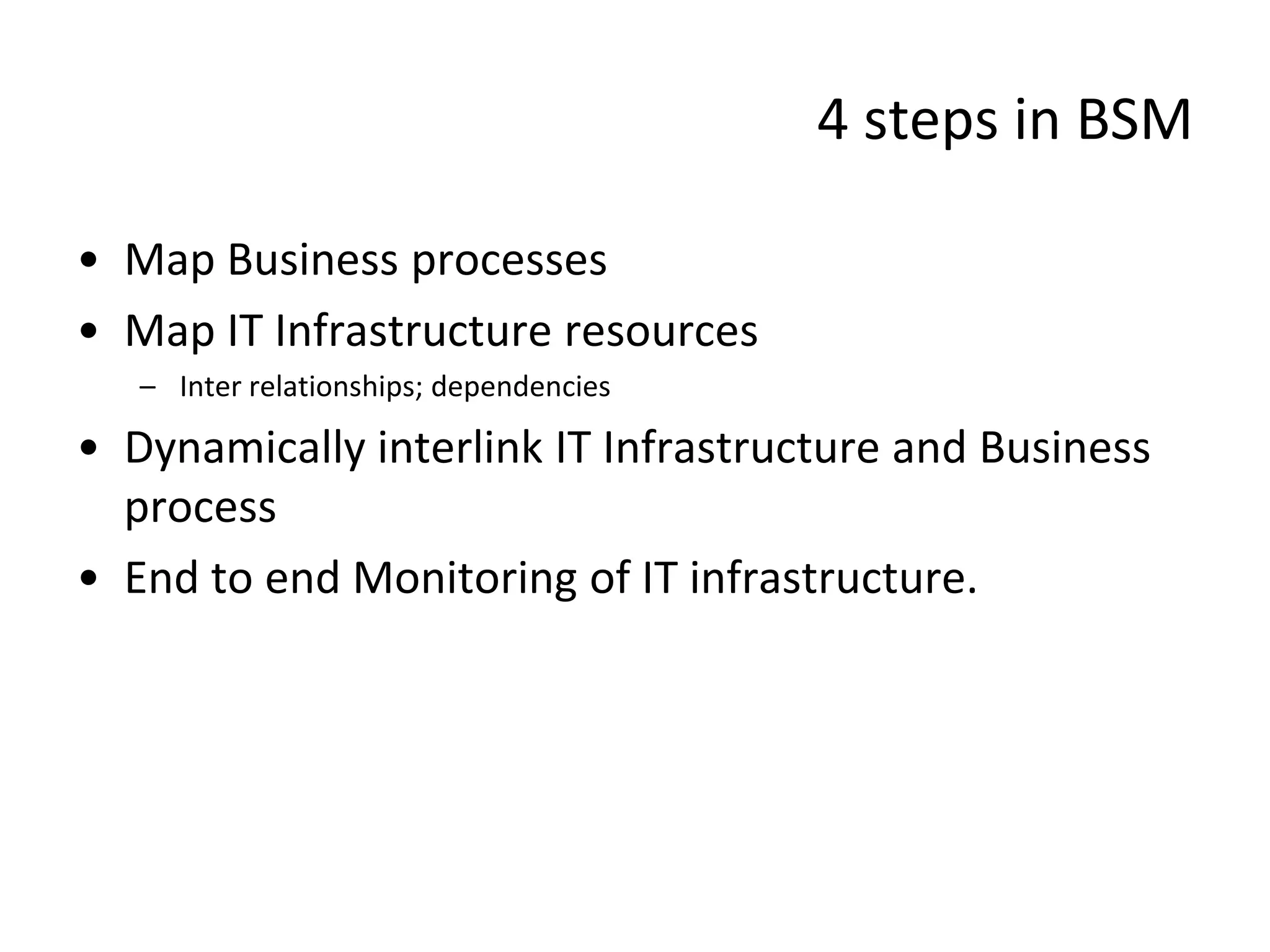
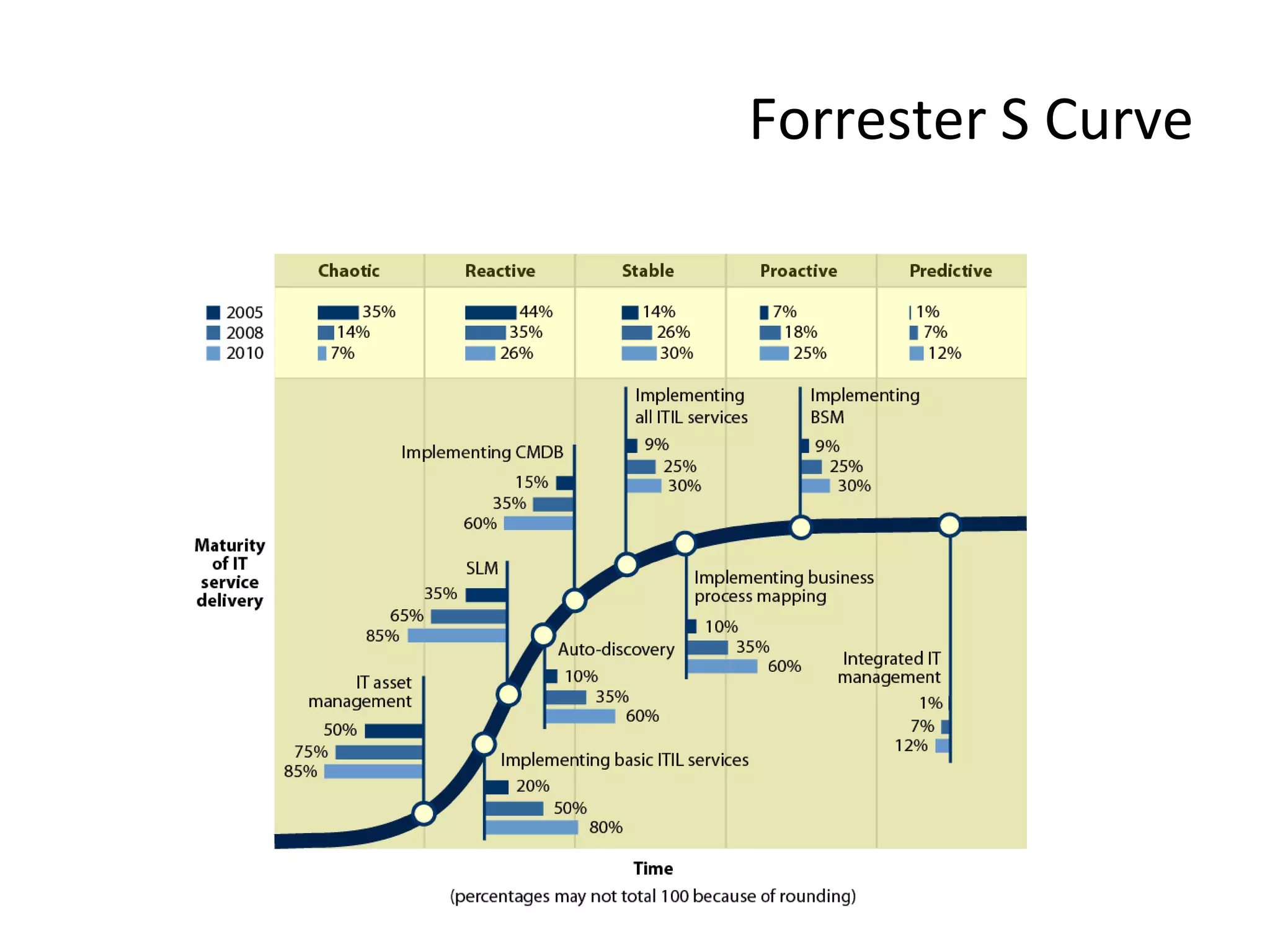
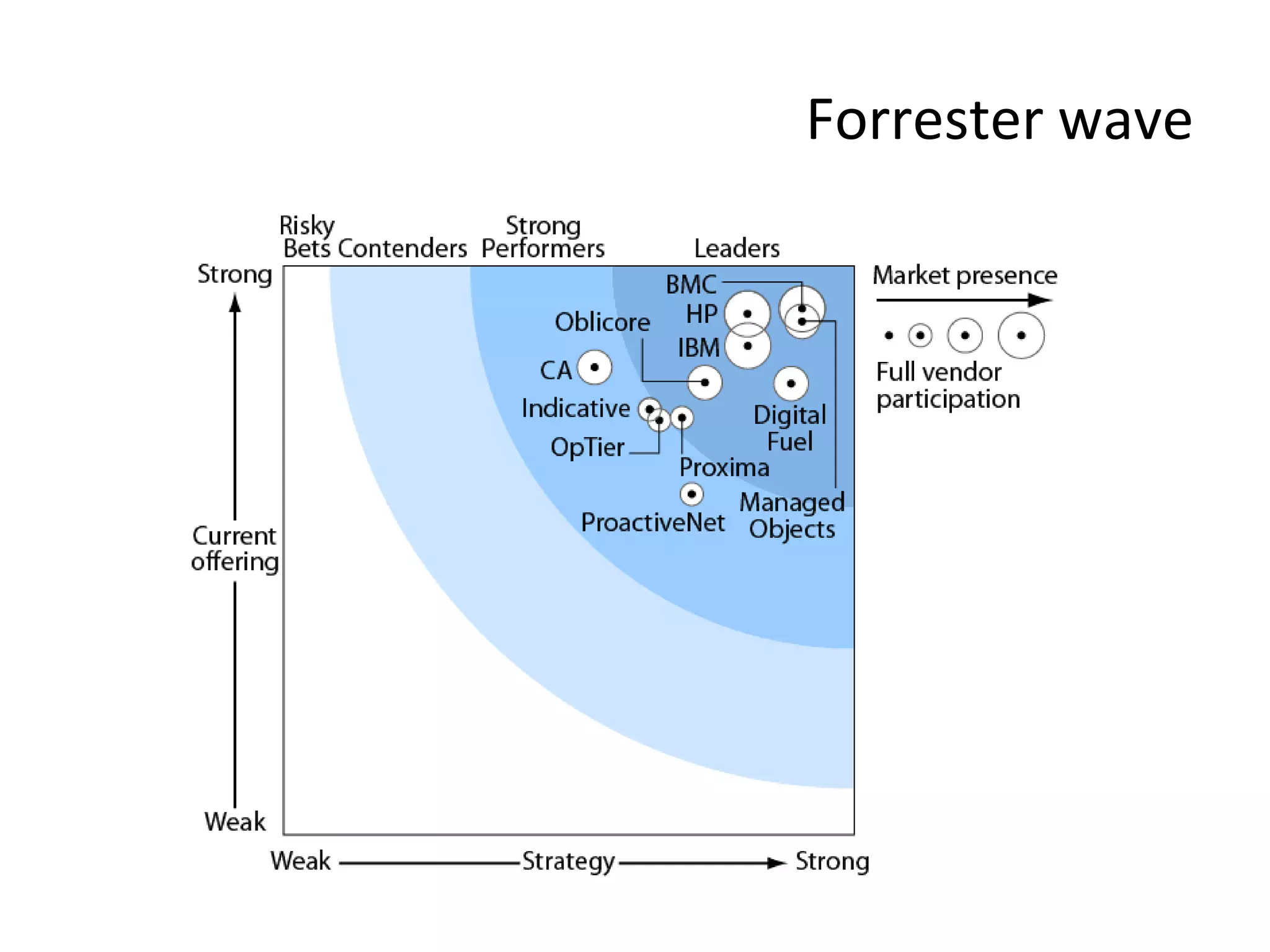
The document discusses best practices for business service management (BSM). It provides typical metrics used for BSM reporting and outlines some key steps in the BSM process. It also discusses challenges of BSM implementation and the vendor landscape. The document emphasizes the importance of mapping business processes and IT infrastructure, dynamically interlinking them, and end-to-end monitoring to optimize the IT service supply chain aligned to business needs.

















![Chapter 4 Implementing BSM
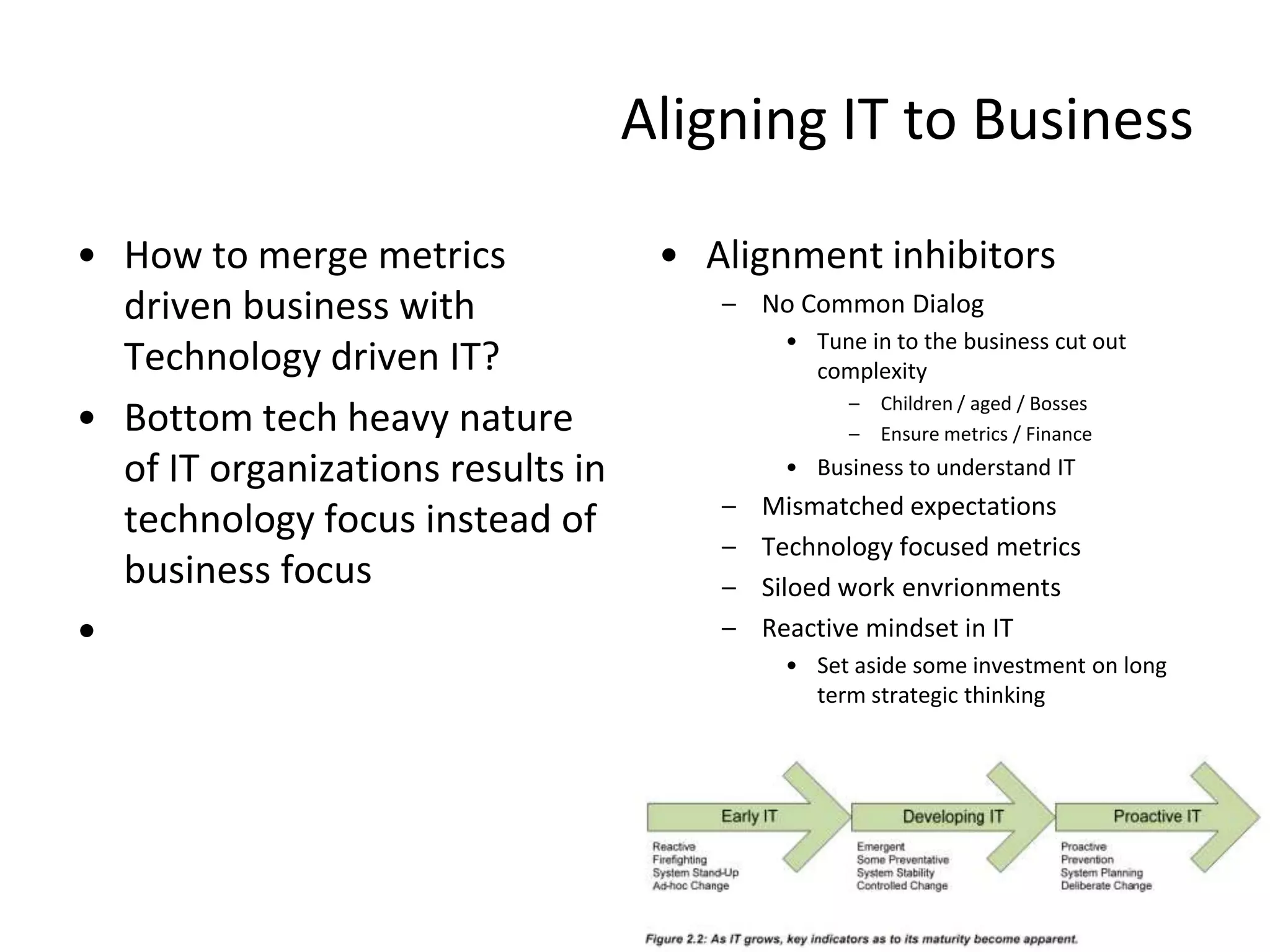
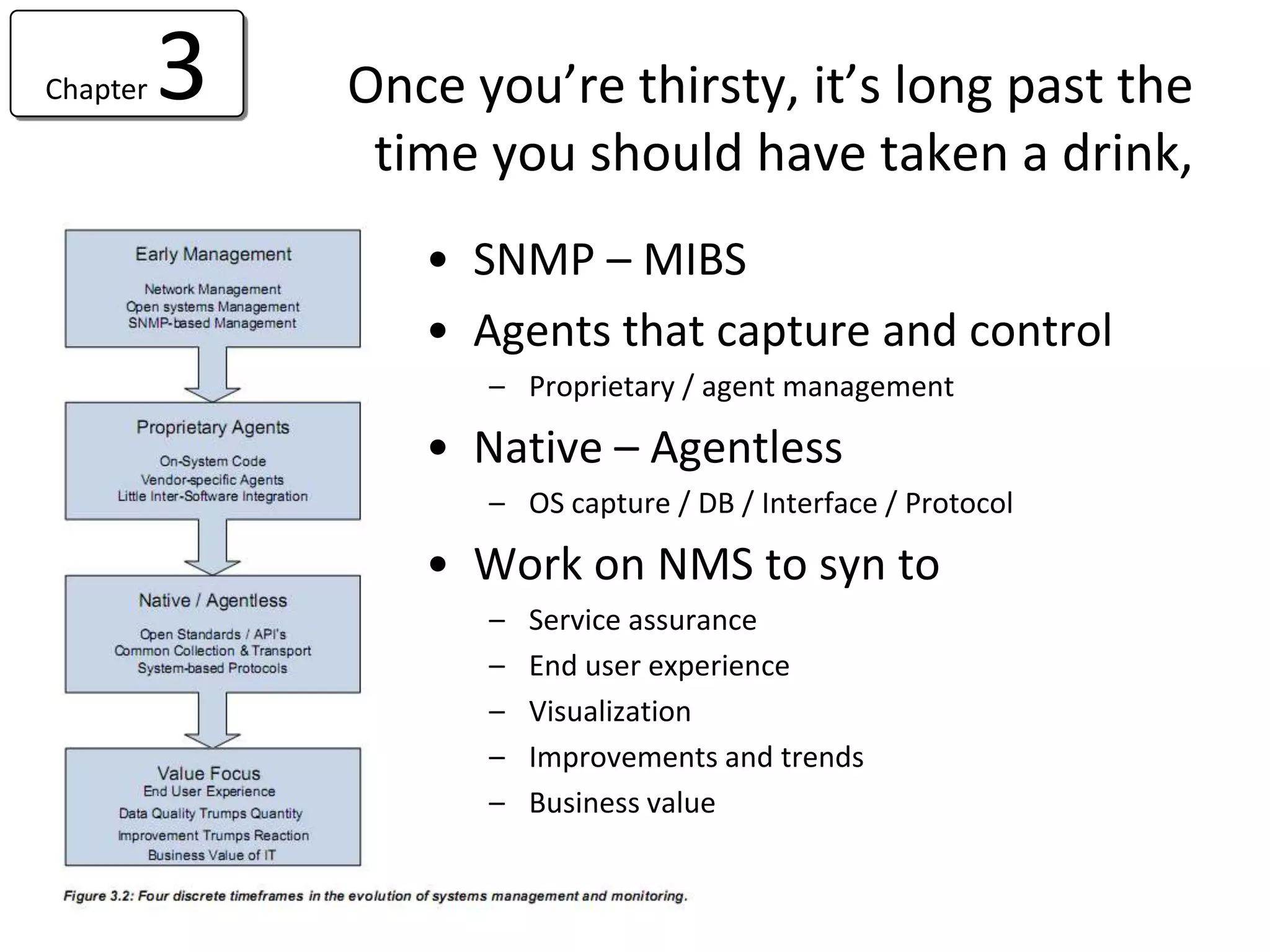
• Value of BSM
– Understand the Critical to Quality Services [ portfolio]
– Manage Daily Risk and Improve Business Decision Making
– Initiate Service Improvement Activities
• 7 steps of BSM Implementation
– These are malleable and need to be fit to a customer
– 100% is never reached! [ CSI]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasbsm-120103213430-phpapp01/75/Readings-on-BSM-32-2048.jpg)
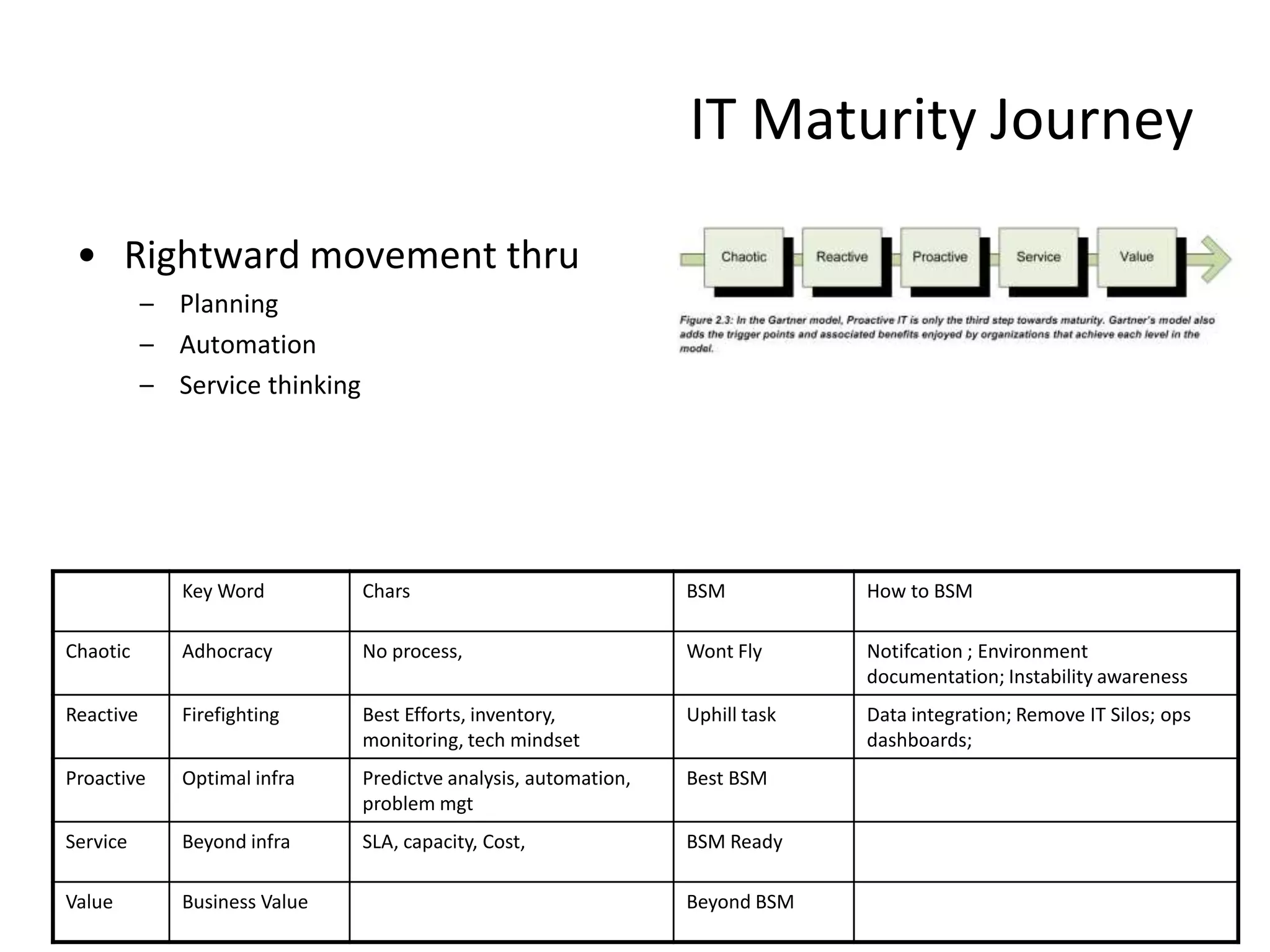
![Chapter 4 7 steps in BSM Implementation
• Step 0 – prepare • Step 2 – Define
– Project Team / Charter – Structure. Behavior. Relevance.
• Ensure that business is involved – Use Case Diagrams
– Stakeholders / Plan – Categorize
• Value / Outage impact / Abnormality
• Step 1 - Selection Impact / RTO – RPO / SLA – OLA /
– Identify services MECE + Business Users / time / Code / Location
– Just Enough | Phases | Low hanging /Dependencies
fruit – Define SLR [ Service Assurance ]
– Critical and measurable services • Availability / Reliability /
Performance
– Define Service Breakdown
– Define PIE / Problem & opps - Kano
– Assess [ Value / Cost ]
– Define CSF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasbsm-120103213430-phpapp01/75/Readings-on-BSM-33-2048.jpg)
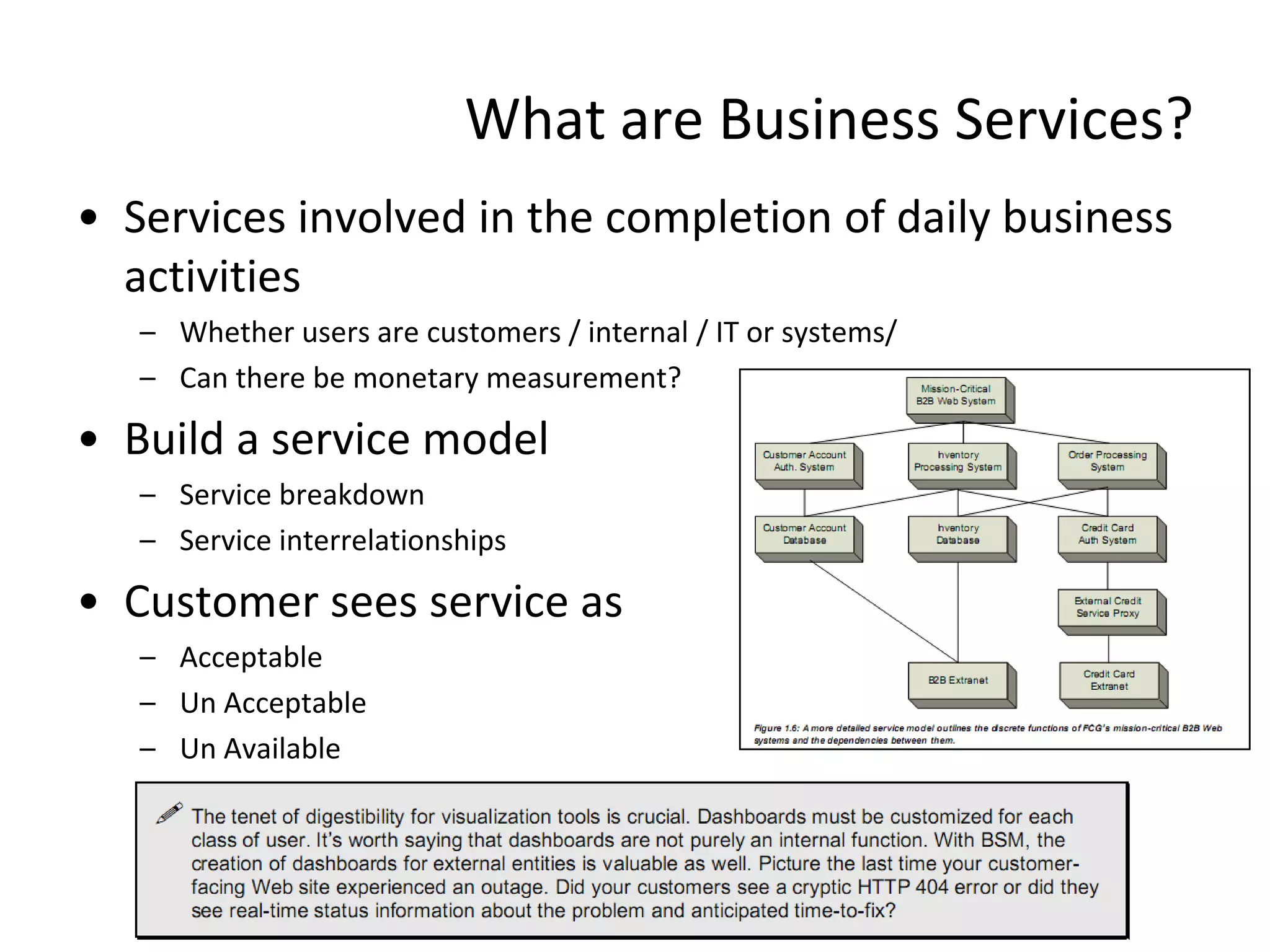
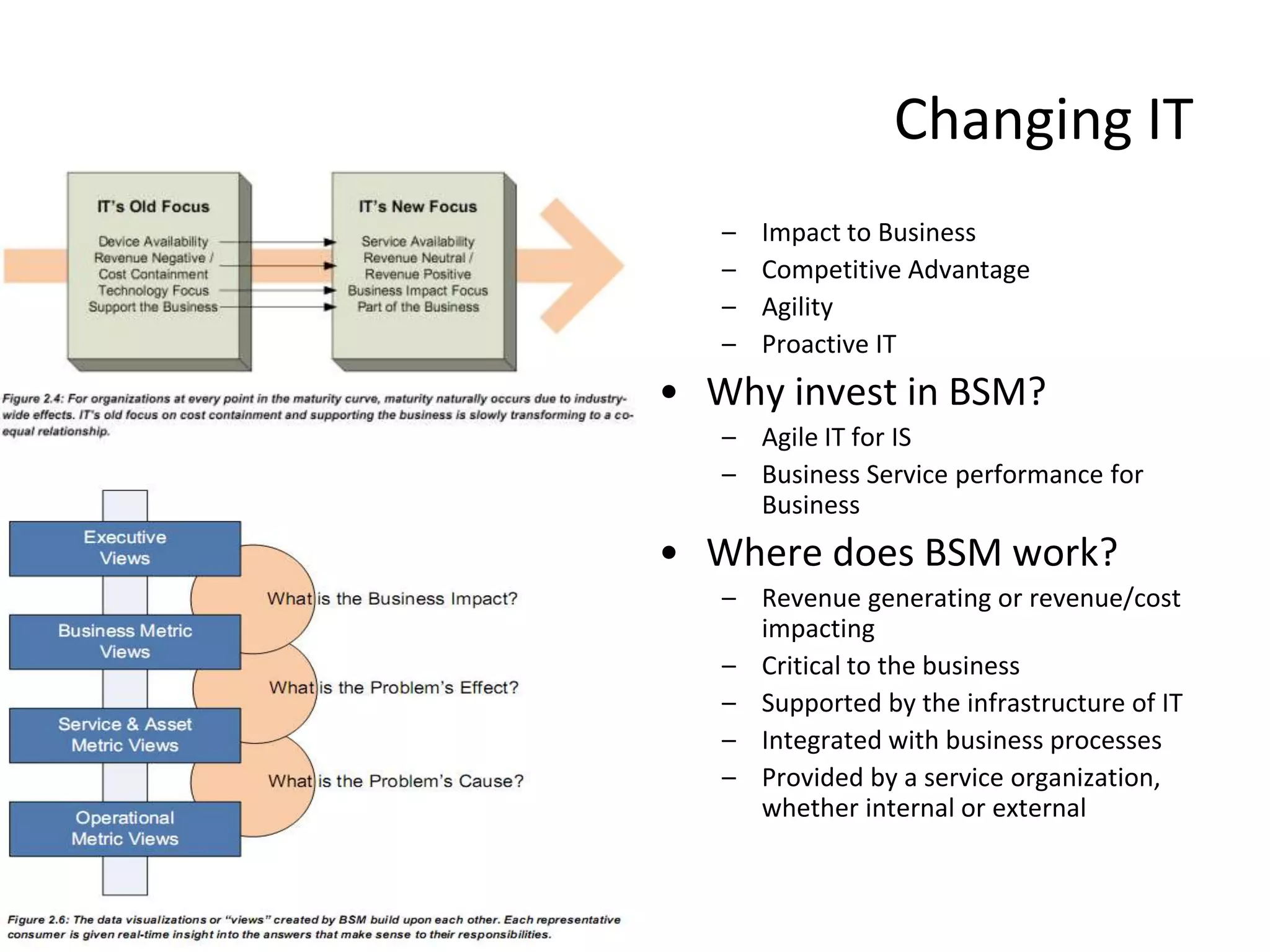
![Chapter 4 7 steps in BSM Implementation
• Step 3 – Model • Step 5 – Data Analysis
– Hierarchical diagrams with business – Where are the gaps
processes in relation to IT resources • bad service quality, customer ratings,
– FMEA / CRAMM / CFIA / FTA system overload, element response
time, or transaction throughput
– Model Associated Metrics [KPI]
– What are the trends
• user wait time, business metrics,
systems & transaction performance – Visualize the Data
– Build the service model – Validate Data – Assumptions
• Link metrics to actual data – Realize the Fault tree paths
– Define the Data model [ERD] • Derive Impact analyses
•
• Step 4 – Measure
– Ensure enough time for this step
– Tie BSM to infra monitoring
– Also attache End user monitoring
– Tie into SM systems, SD, CMDB
Remember too that BSM is not intended to “rip and replace” existing monitoring systems](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasbsm-120103213430-phpapp01/75/Readings-on-BSM-34-2048.jpg)
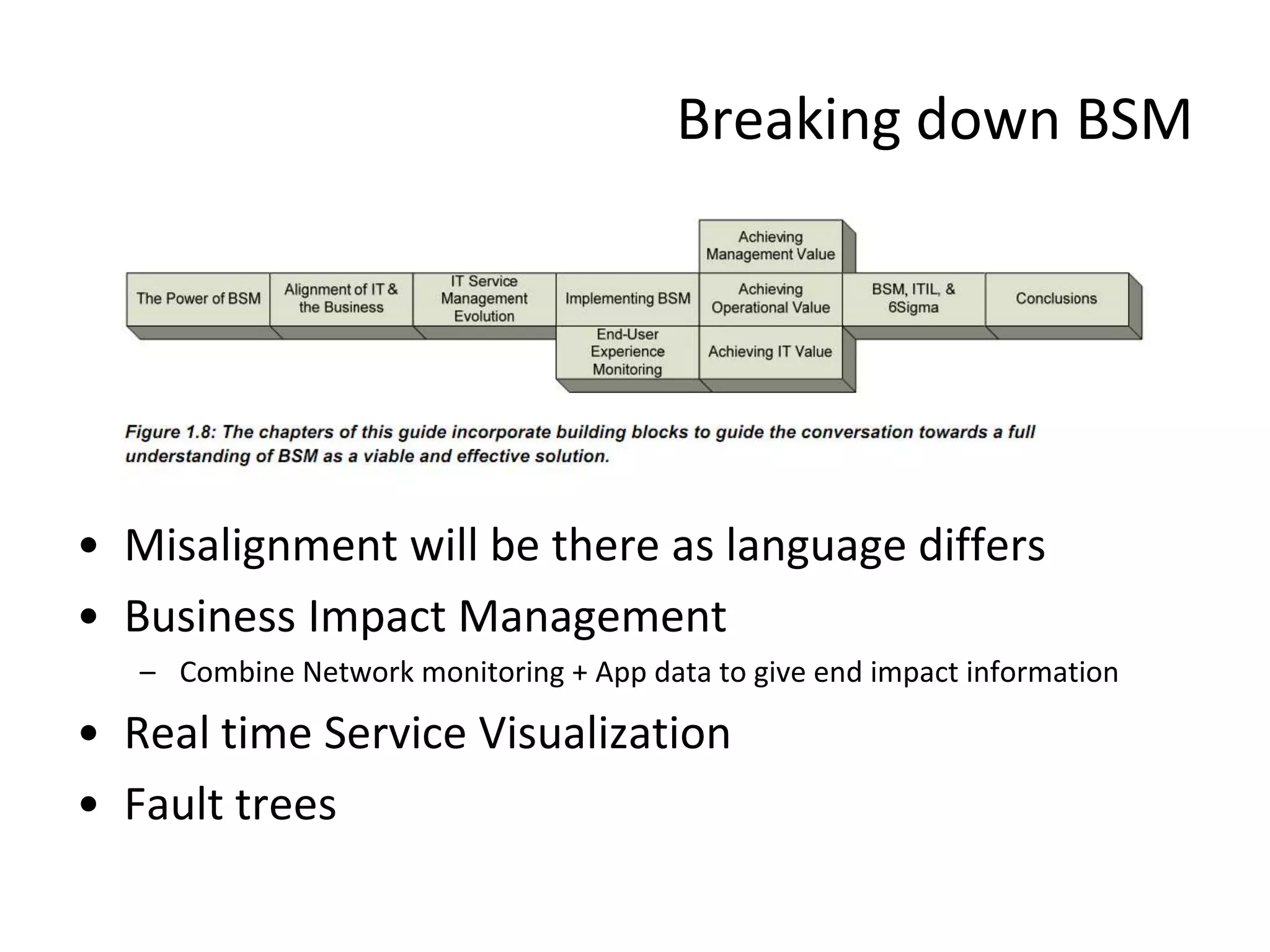
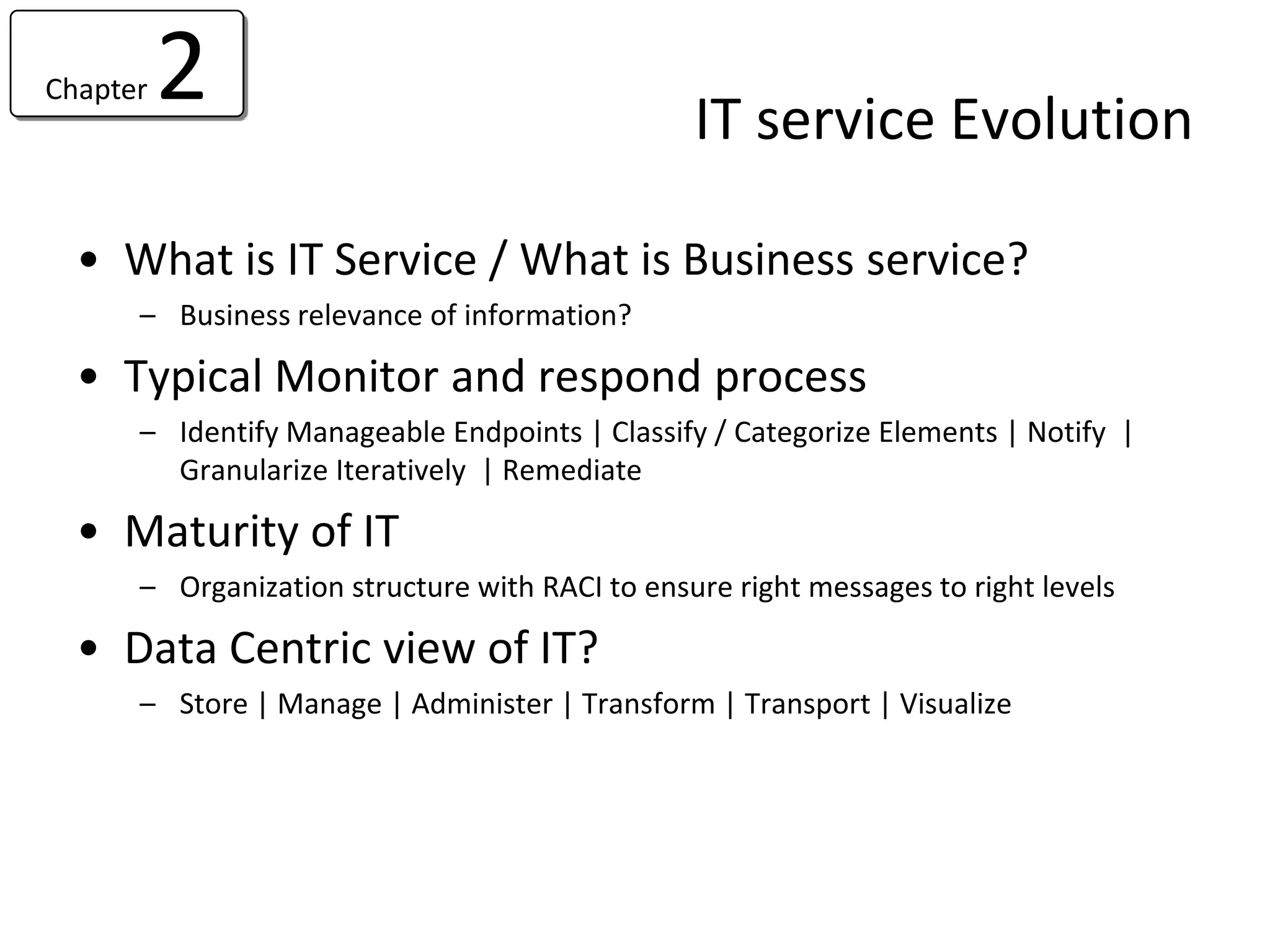
![Chapter 4 7 steps in BSM Implementation
• Step 6 – Improve • Step – 7 – Reporting
– What are the problem domains – Ensure that reporting model does not
– Identify and resolve the gap stagnate [ users get reliant]
• De Bono – Simplicity – Dashboards
• TRIZ – 40 Principles – Notifications
• Lean – 3M 5S 7W – Configuration control & handoff to
– Recheck the model continually operations
Remember too that BSM is not intended to “rip and replace” existing monitoring systems](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasbsm-120103213430-phpapp01/75/Readings-on-BSM-35-2048.jpg)
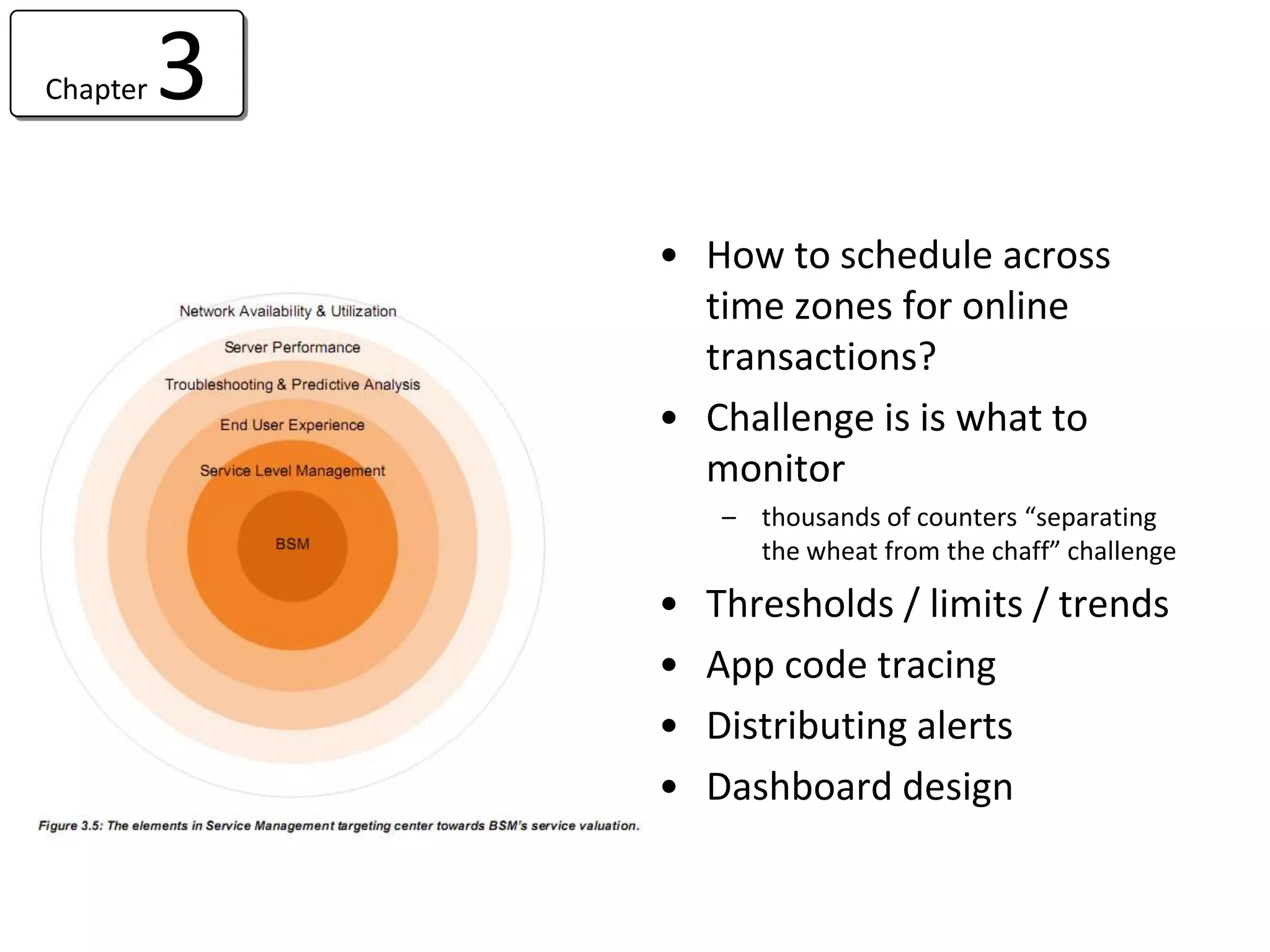
![Chapter 5 End user Experience Monitoring
• “Egg Timer” Problem
– times but does not reflect the quality of the eggs
• Flow Analysis
– Single flow analysis [End user monitoring]
• Understand the Client Network Server [CNS] Spread
• Agent / Agentless || Server / Client || Service / Transaction
– Aggregate flow analysis [ flood monitoring]
– Usage / Feature Profiling
• Visualize & Prioritize problems before the impact
– Interface tracing / data channel sniffing /](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/readviramdasbsm-120103213430-phpapp01/75/Readings-on-BSM-36-2048.jpg)
