This document provides an introduction and overview of React Native, including what it is, its prerequisites, core components, and how to set up the development environment. Specifically:
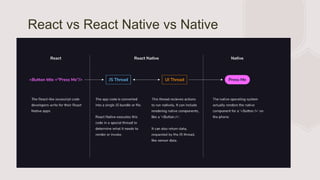
- React Native is a framework for building mobile apps for iOS and Android using React. It allows writing apps once in JavaScript and deploying to both platforms.
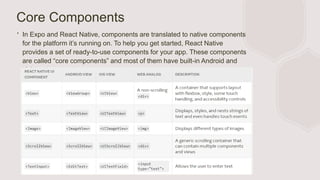
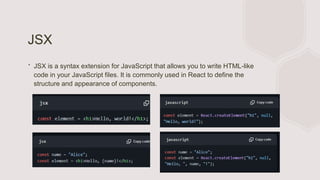
- Basic JavaScript and React knowledge are prerequisites. Core components include common mobile components with built-in native implementations.
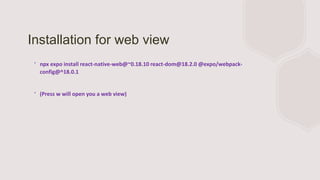
- The entry point file initializes the app and renders the root component. Setting up the environment involves installing Node, Expo, and creating a new project.









![Setting up the development
environment
∙ Download Node.js
∙ Download ExpoGo (iOS or Android)
∙ Download Visual Studio Code
∙ 1. Select folder
∙ 2. Check node.js version node -v
∙ 3. Check the node package manager npm -v
∙ 4. npm install -g expo-cli// add sudo if you’re MacOS]
∙ 5. npx create-expo-app HelloApp
when appear >npm install (Wait to install, if long time no respond, try press enter 1 time)
∙ 6. cd HelloApp (go to the HelloApp Directory)
∙ 7. npx expo start
∙ 8. Make sure connect mobile phone with your PC the same Wifi -- if fail, CTRL+C, go back to step 5
∙ 9. iOS (Scan QR code through camera), Android (Scan using Expo Go App scanner)
(will create a project folder)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture1introductiontoreactnative-230801035630-cacfa066/85/Lecture-1-Introduction-to-React-Native-pptx-17-320.jpg)