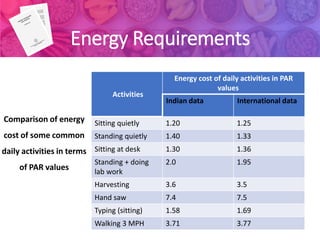
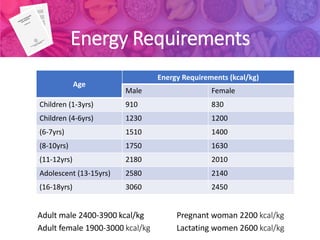
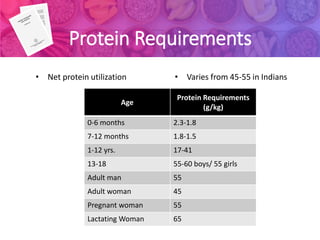
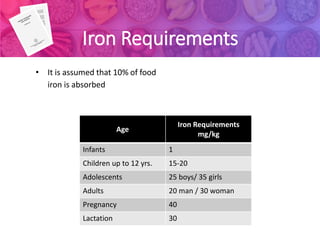
1) Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA) are the daily nutrient intake levels that meet the nutritional needs of nearly all healthy individuals. RDAs are calculated based on estimated nutrient requirements plus a safety factor.
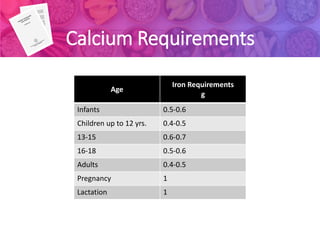
2) Factors like age, sex, activity level, and physiological state affect a person's RDA. For example, pregnant and lactating women have higher RDAs than other adults.
3) The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) defines Reference Men and Women to set RDAs for Indians based on typical activity patterns and body weights.