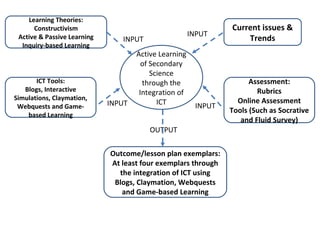
This document outlines an active learning science course that integrates information and communication technologies (ICT). The course aims to teach strategies that promote active learning and critical thinking through ICT tools like blogs, simulations, claymation, webquests and games. Participants will learn about constructivism, active vs. passive learning, inquiry-based learning and how to design lessons, develop assessments and evaluate ICT-integrated science lessons that enhance active learning.