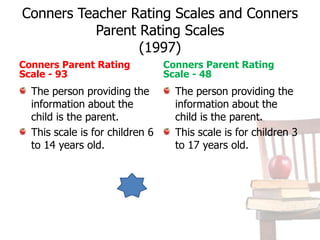
Rating scales are used to evaluate student behavior and can measure the degree to which students exhibit certain behaviors. Descriptors provide detailed information about rating scale levels. Rating scales are useful when combined with other assessments like interval recording. Several commonly used rating forms include the Teacher Report Form, Child Behavior Checklist, Youth Self-Report, Behavior Rating Profile-2, and Conners Teacher and Parent Rating Scales. These forms measure behaviors, adaptive functioning, and problems through ratings from teachers, parents, and students. While rating scales can provide useful information, they also have limitations like subjectivity.