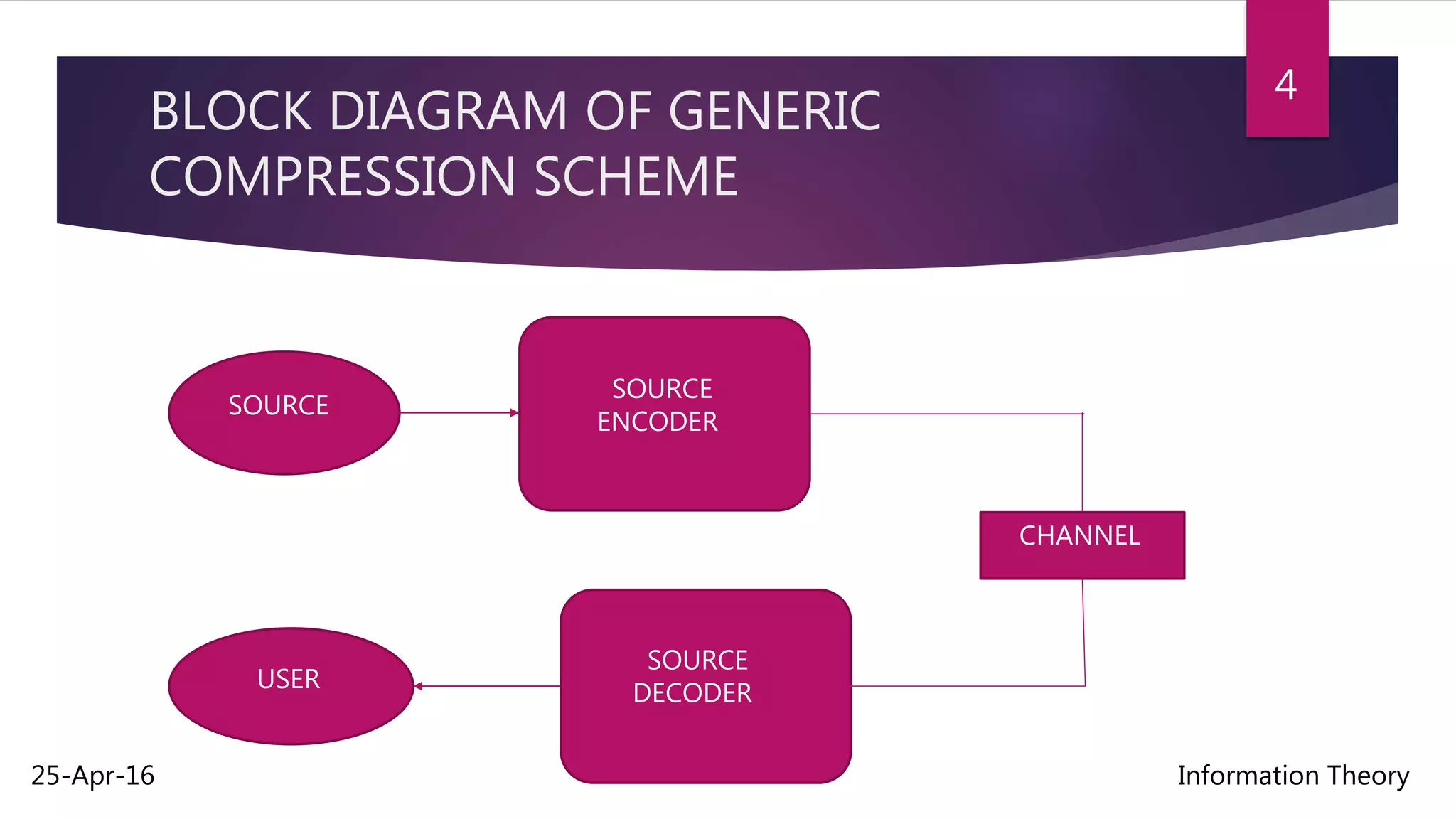
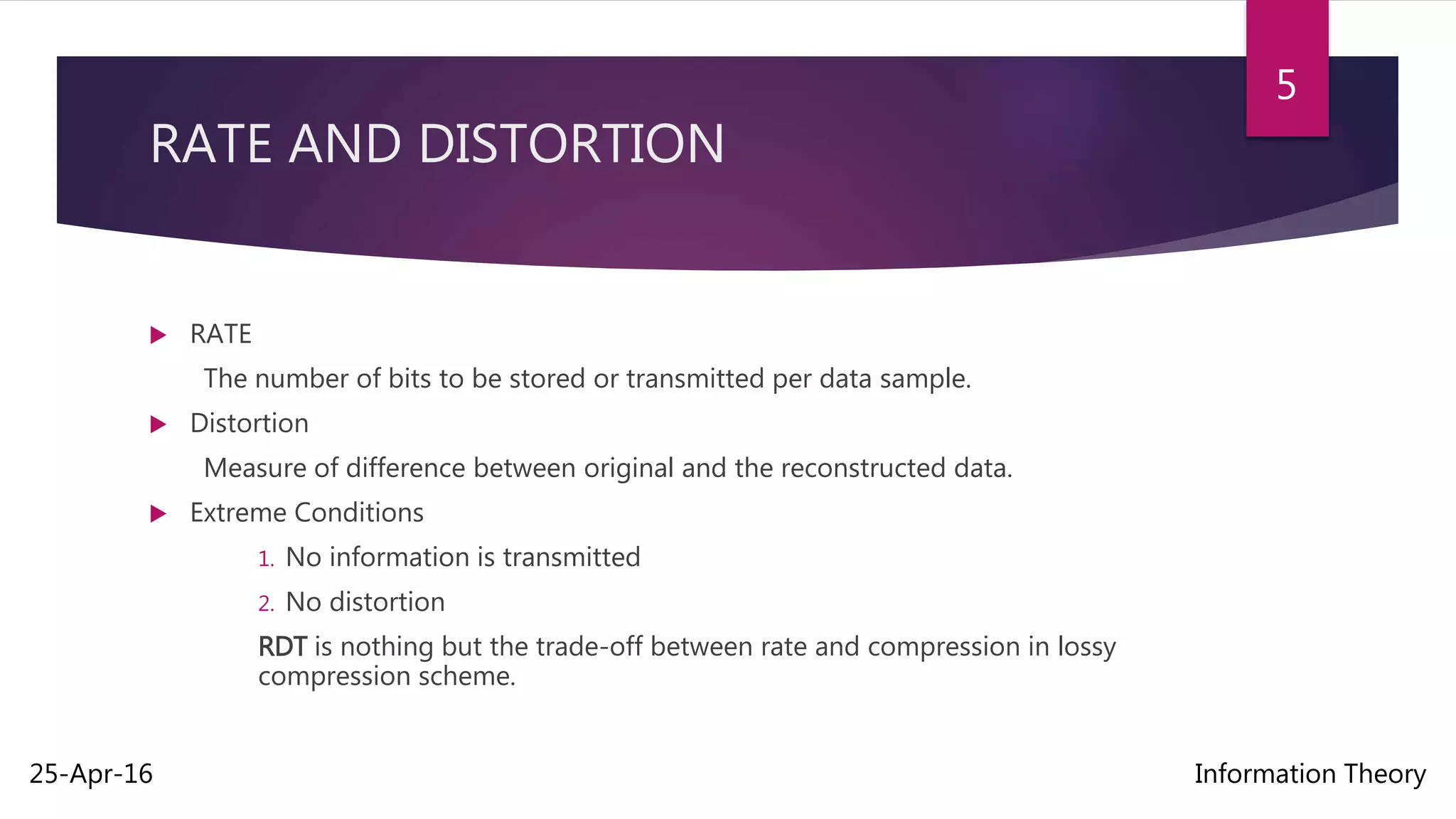
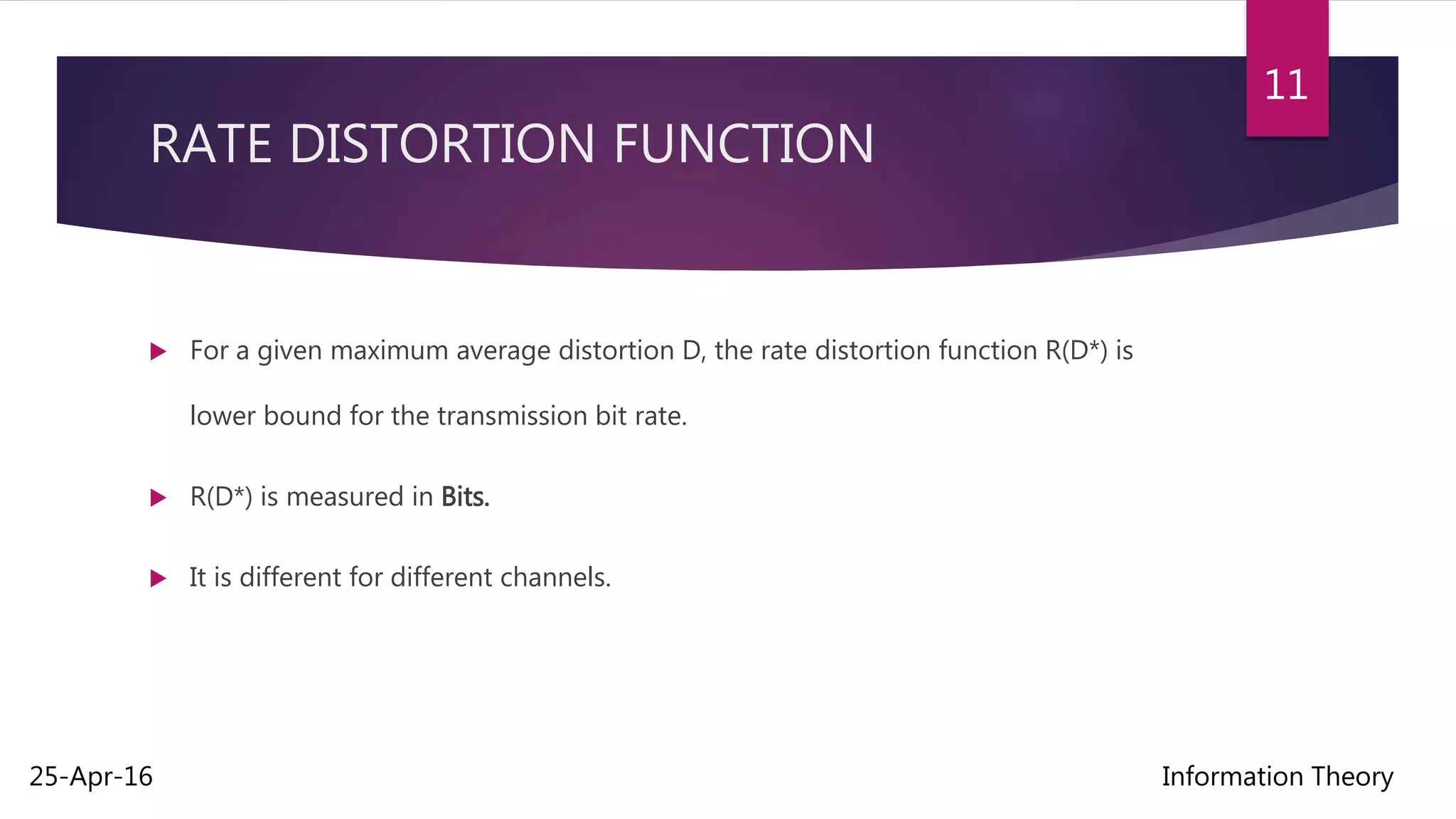
Rate distortion theory is a major branch of information theory that provides the theoretical foundations for lossy data compression schemes. It gives an analytical expression for how much compression can be achieved using lossy compression methods by establishing a tradeoff between the rate of compression and the resulting distortion. The theory aims to minimize the amount of distortion for the lowest possible compression rate given a source distribution and distortion measure. The rate distortion function specifies the lowest rate at which an output can be encoded while keeping distortion below a given level.