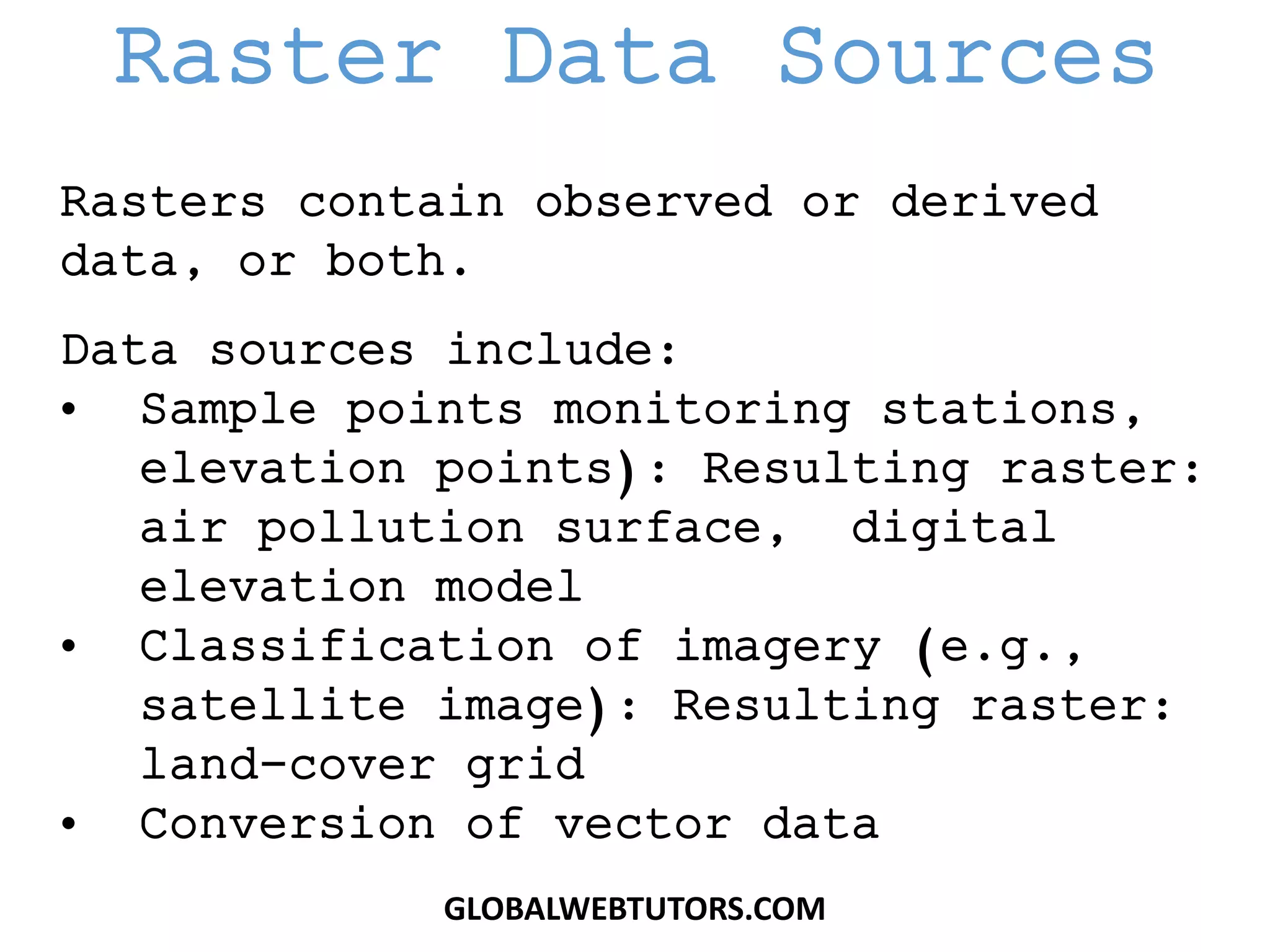
This document discusses key concepts in raster GIS including:
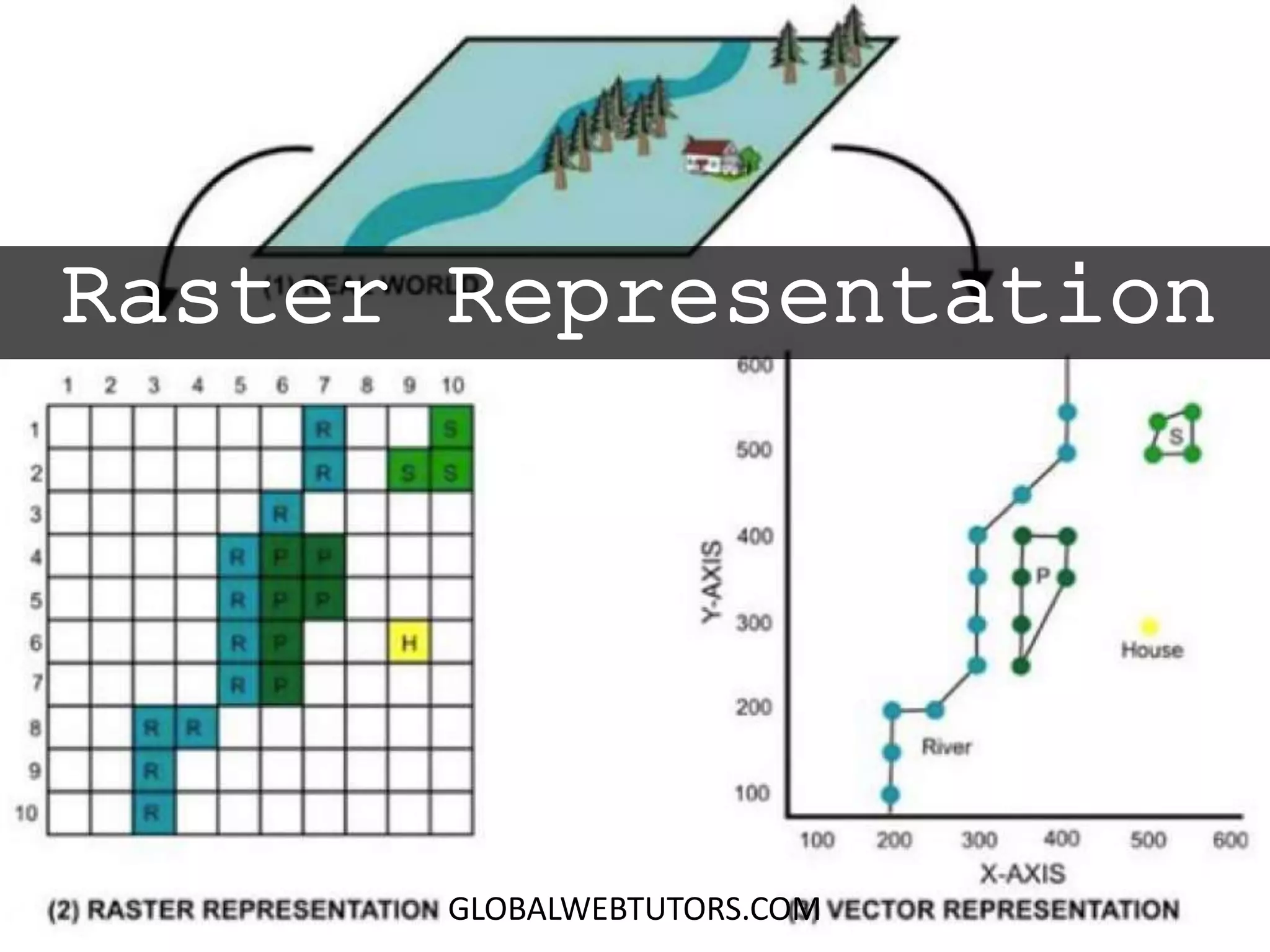
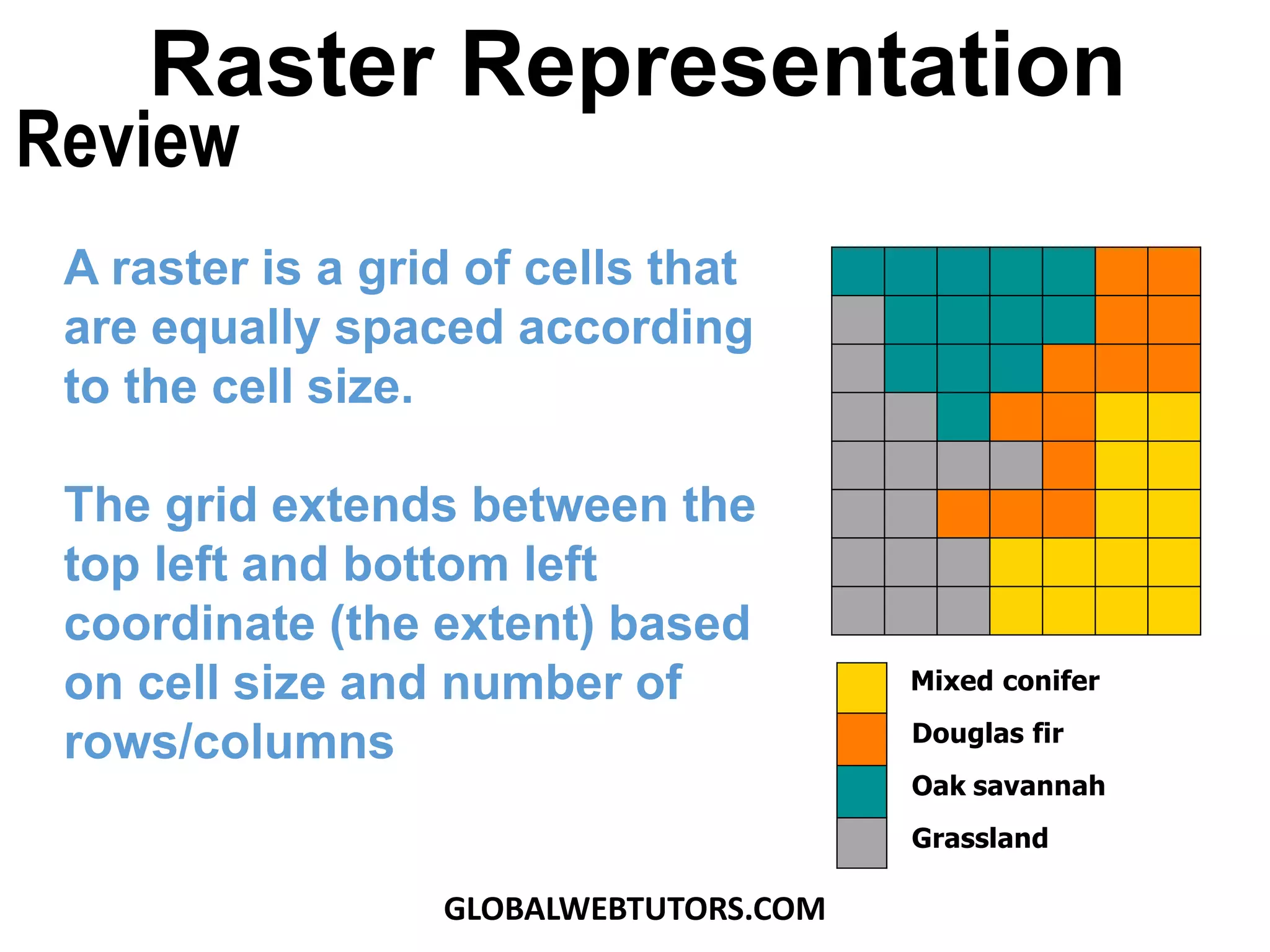
- Raster representation involves organizing geographic data into a grid of equally-sized cells.
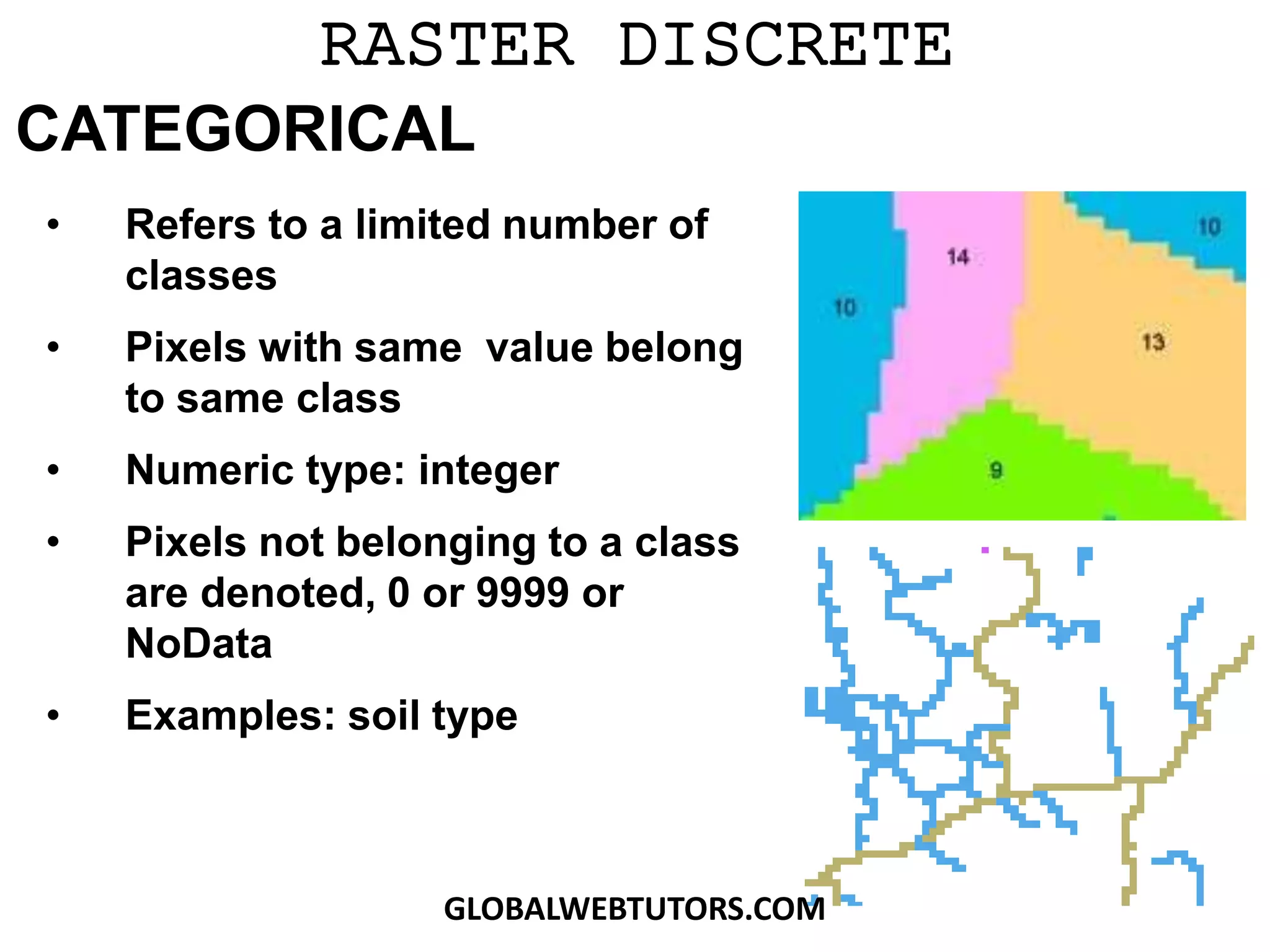
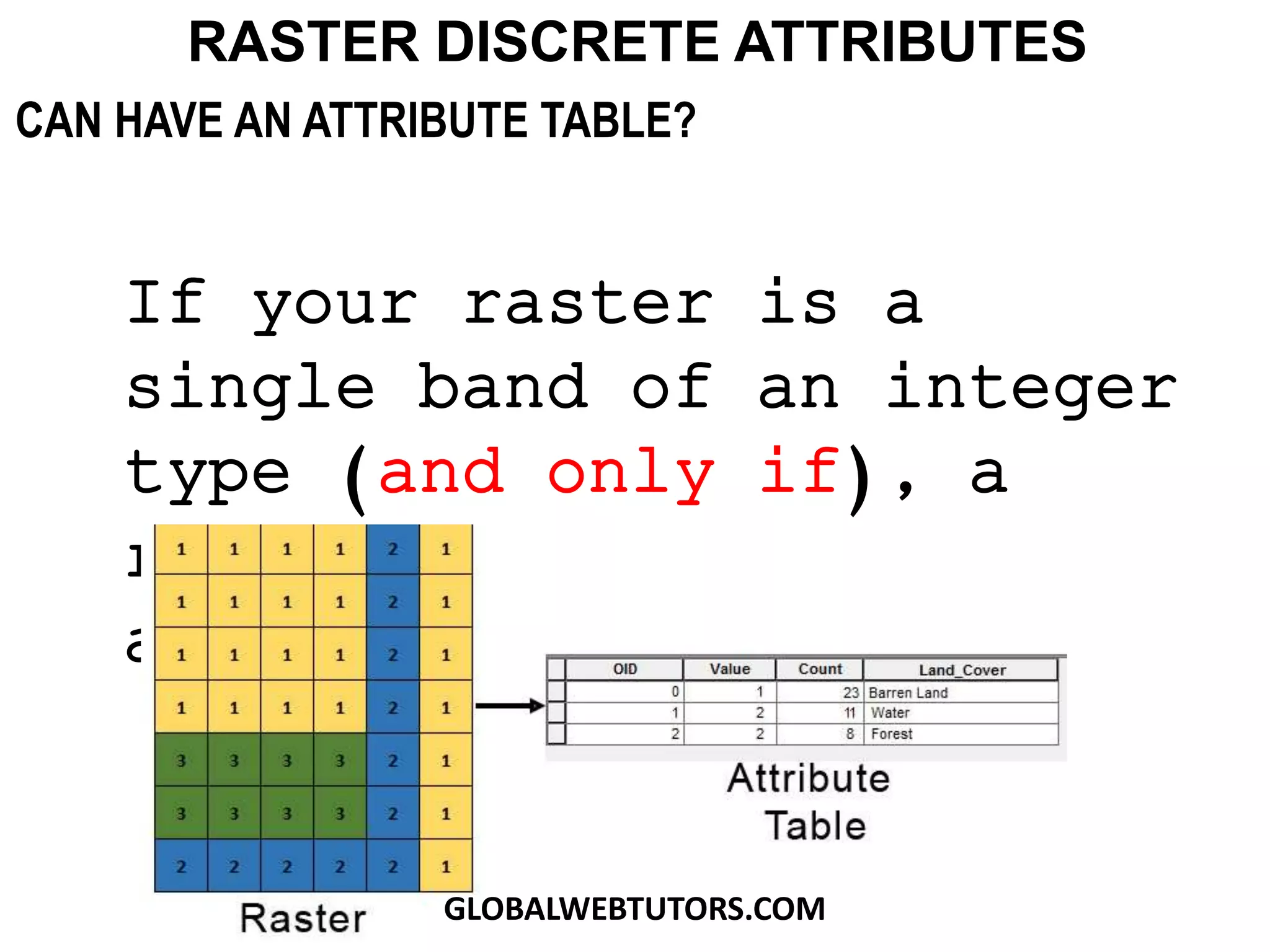
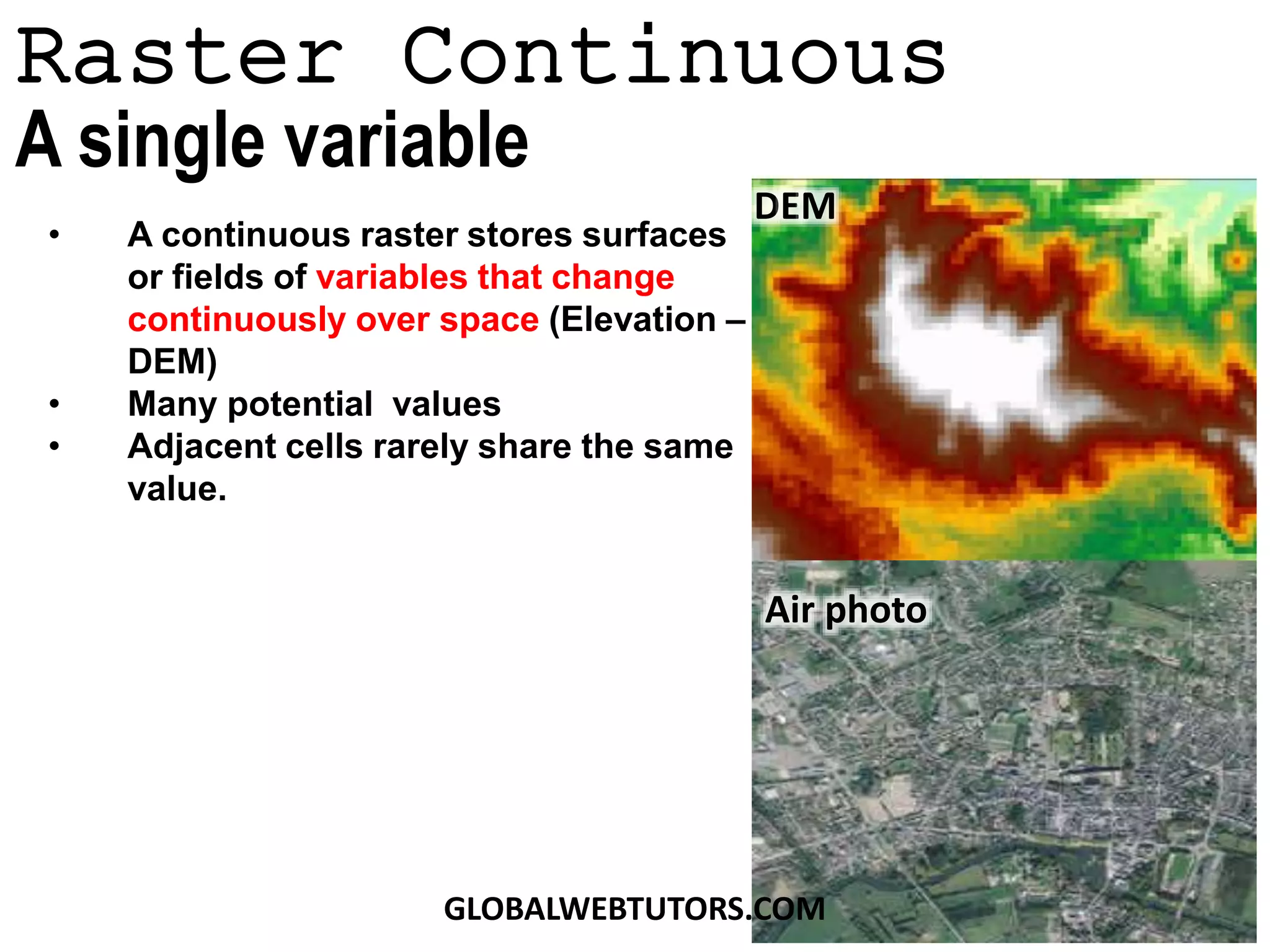
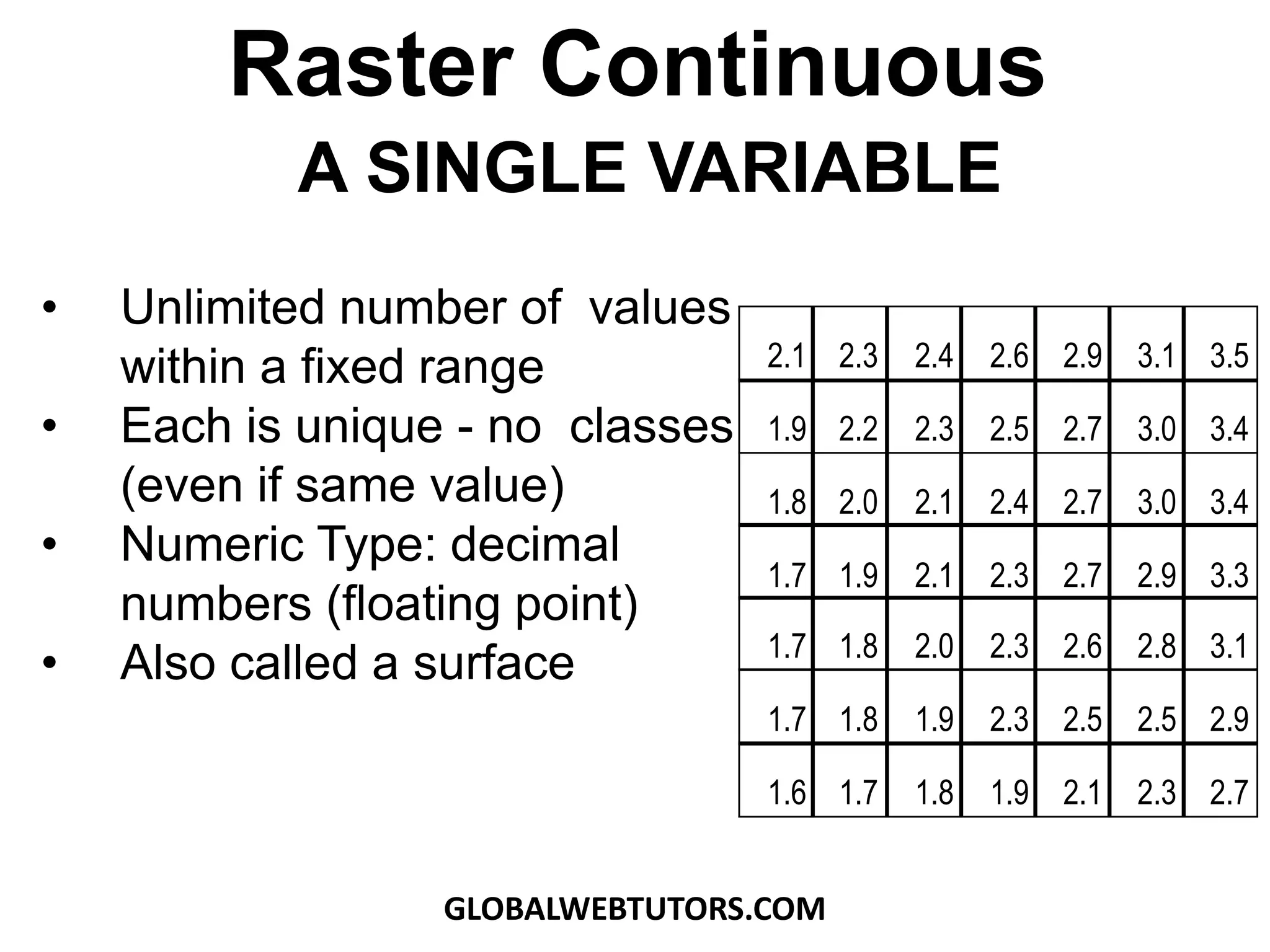
- Raster data can be discrete/categorical with data classified into different land cover types or continuous, storing surfaces like elevation as unique values.
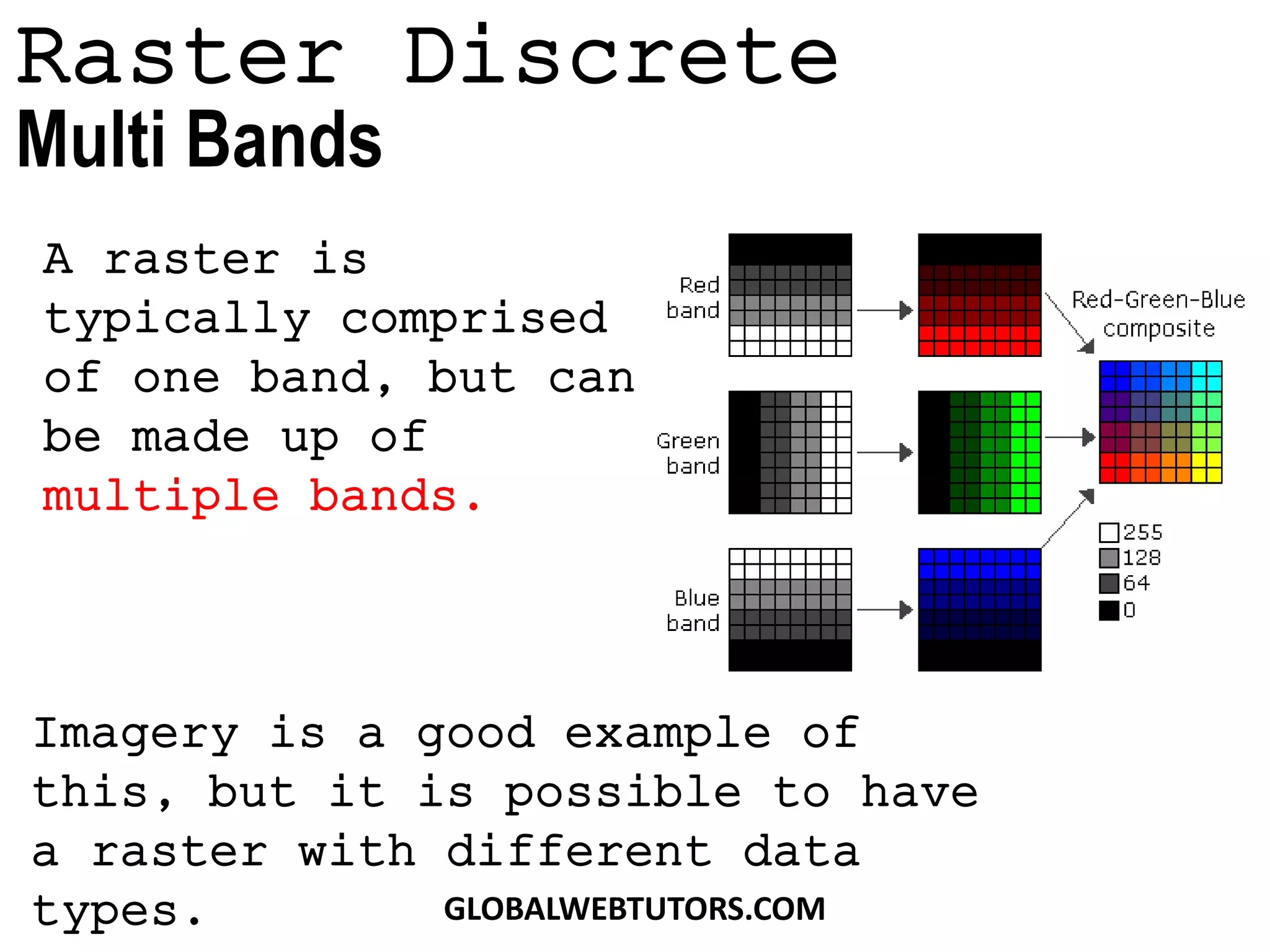
- Rasters can have multiple bands of data and discrete rasters can include attribute tables.
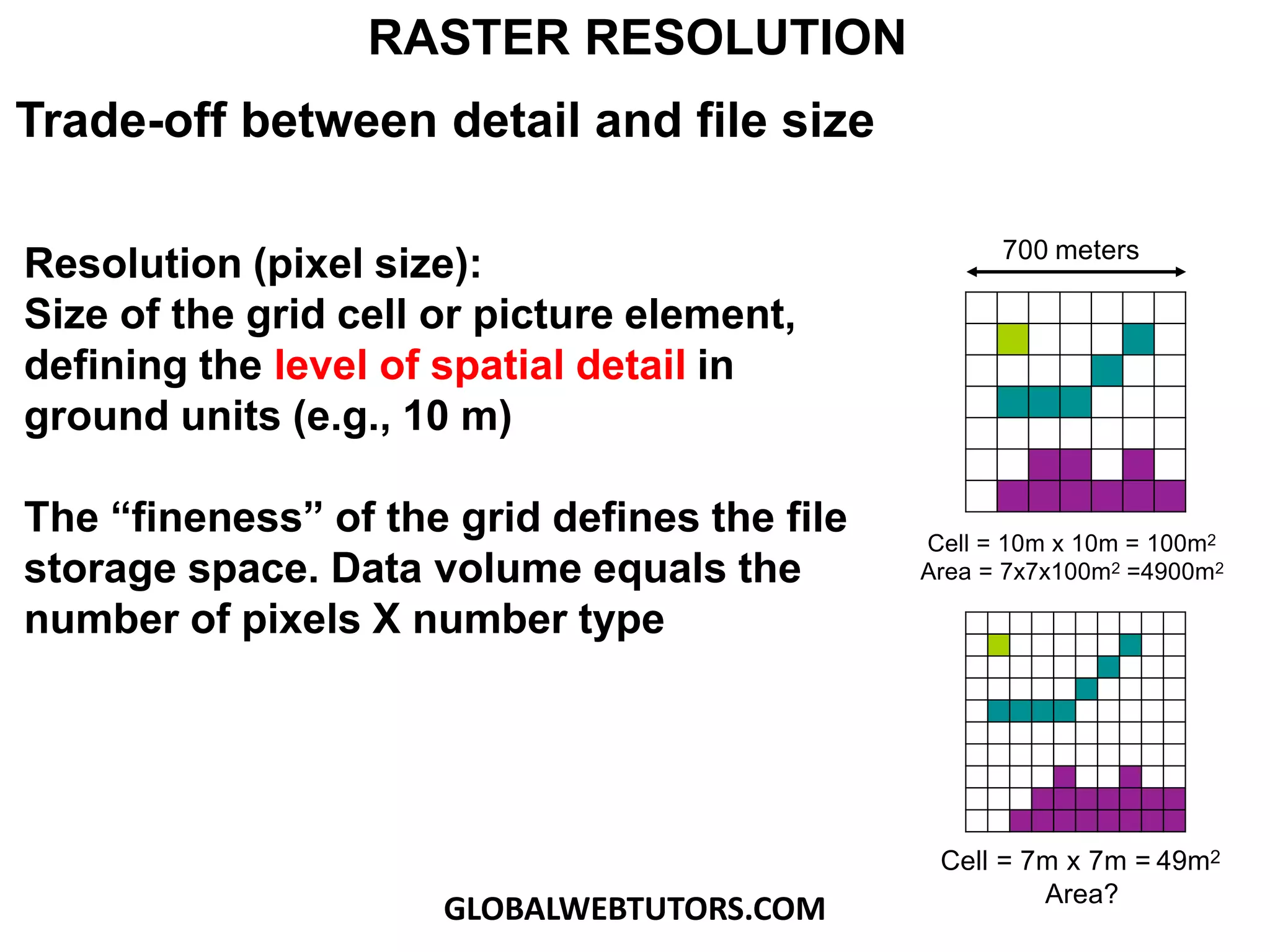
- Resolution refers to the size of grid cells, with higher resolution meaning smaller cells and more detail but larger file sizes.
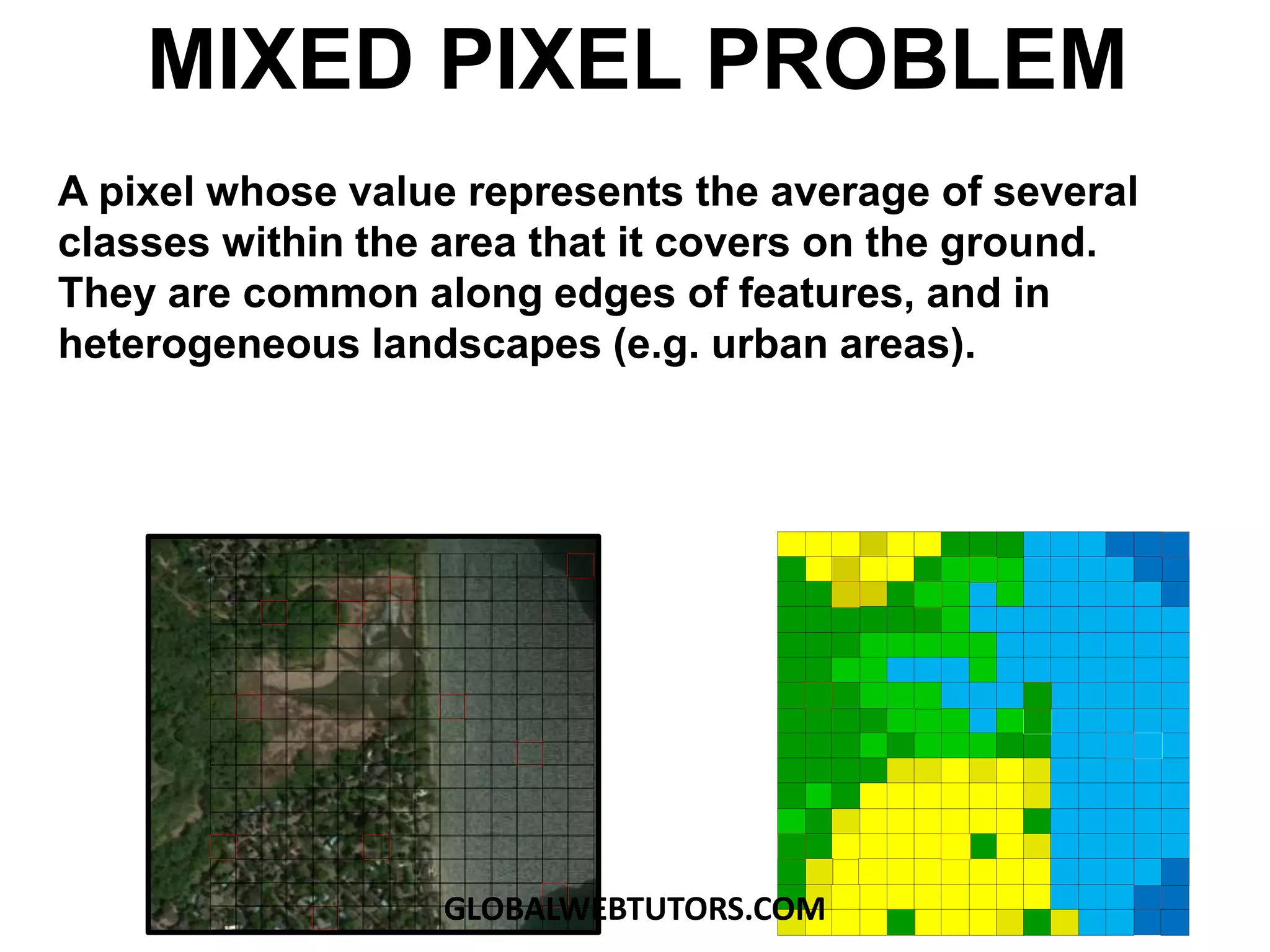
- Mixed pixels can occur along feature edges where a cell value averages multiple land cover types.