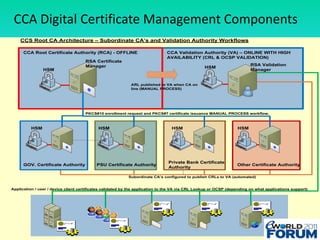
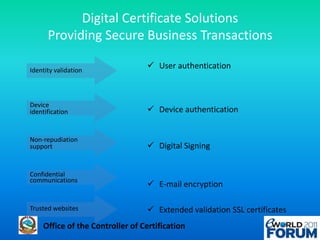
The document discusses a national authentication framework in Nepal that integrates digital certificates and one-time passwords (OTPs) for stronger user authentication. It emphasizes the transition from traditional password-based systems to hybrid authentication methods, enabling citizen-centric services while minimizing costs and enhancing security. The framework is designed to simplify the user experience and is supported by the government to facilitate access across public and private sectors.