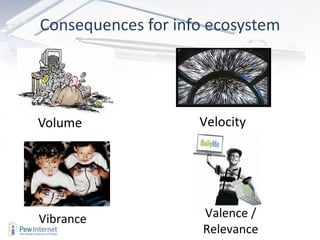
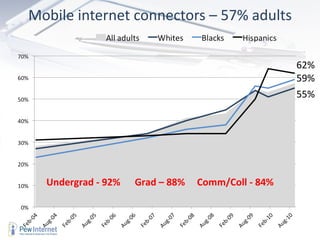
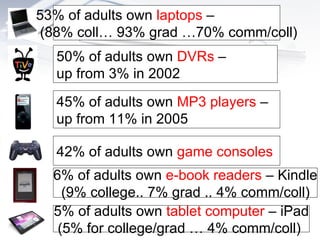
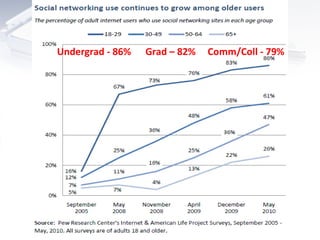
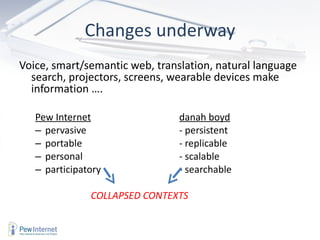
The document discusses how technology will transform universities by 2020. It outlines several major shifts including (1) changing information ecosystems for networked learners due to ubiquitous connectivity and social media, (2) new literacies becoming required to navigate these environments, and (3) big data and the "internet of things" leading to an "exaflood" of information. It suggests universities will need to adapt to students being more self-directed learners who capture diverse inputs and rely on feedback from their networks.
![Universities in 2020: A technology perspective Virginia Tech Task Force January 28, 2011 Lee Rainie: Director, Pew Internet Project Email: [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rainiepresentation-110420165531-phpapp01/75/Universities-in-2020-A-Technology-Perspective-by-Lee-Rainie-1-2048.jpg)



















![Thank you! Lee Rainie Director – Pew Internet Project [email_address] Twitter - @lrainie 202-419-4500](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rainiepresentation-110420165531-phpapp01/85/Universities-in-2020-A-Technology-Perspective-by-Lee-Rainie-30-320.jpg)