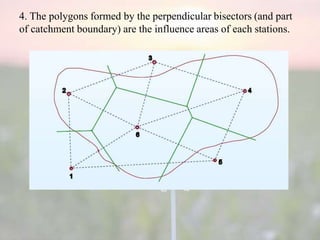
Rainfall is measured as the depth of water that would collect on an area from the rain. Raingauges are used to collect and measure rainfall. There are several methods to calculate the average rainfall over a catchment area from point measurements at raingauge stations, including the arithmetic mean method, Thiessen polygon method, and isohyet method. The Thiessen polygon method assigns an area of influence to each station based on perpendicular bisectors and calculates a weighted average.