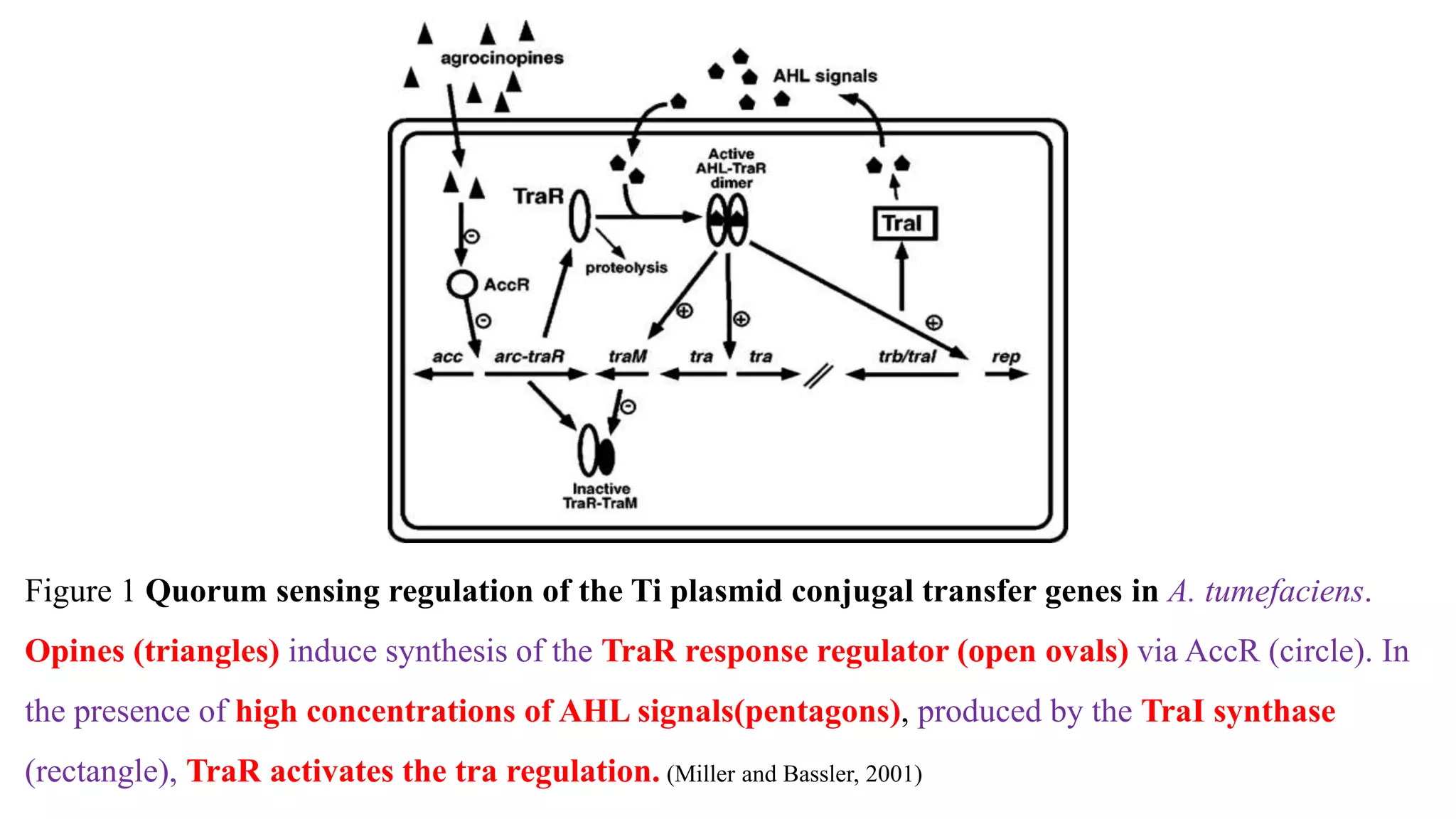
Quorum sensing allows bacteria to coordinate behaviors in response to cell population density. As bacteria increase in number, they produce and detect signaling molecules called autoinducers. This allows them to behave collectively and regulate behaviors like virulence factor production, biofilm formation, and conjugation. Quorum sensing is important for pathogenic bacteria to coordinate virulence and successfully infect hosts. It controls behaviors in both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria through different autoinducer molecules and systems. Understanding quorum sensing provides opportunities to develop new antimicrobial strategies that target bacterial communication rather than growth.







![Other Examples of AIs in Bacteria
Gram Negative Bacteria Gram Positive Bacteria
• Non-AHL unknown signals in Xyllela,
Xanthomonas (water-, air-, soil- borne pathogens of
citrus and grapes)
• Volatile esters of fatty acids[3-hydroxy palmitic
acid methyl ester (3OH-PAME)] in Ralstonia, a
pathogen that causes wilt in tomato.
• Gamma-butyrolactone in Streptomyces controls
production of aerial hyphae and antibiotics.
• Myxococcus uses a mixture of aminoacids to
initiate sporulation (more later).
• Peptide signals in Bacillus, control competence,
virulence.
Bodman et al.,2003](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/quorumsensinginplantpathogenicbacteria-230517062953-b22f02e7/75/Quorum-sensing-in-plant-pathogenic-bacteria-Maruthi-pptx-9-2048.jpg)