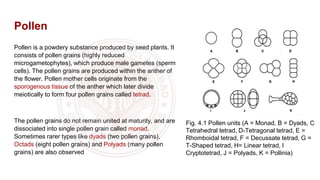
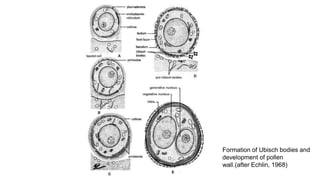
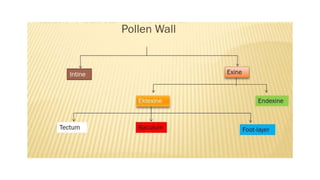
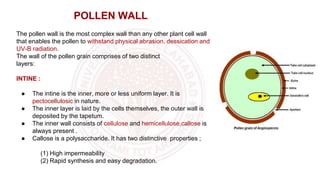
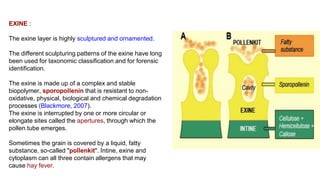
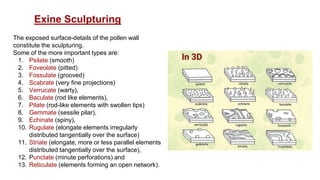
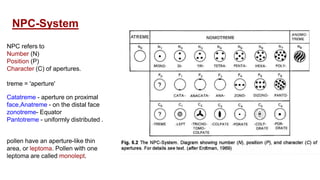
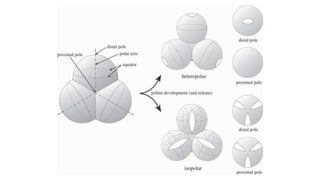
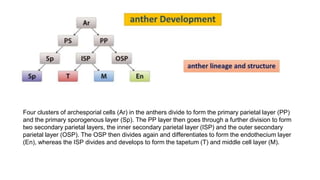
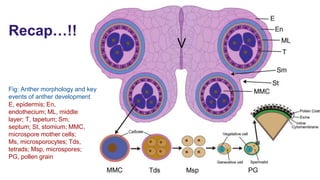
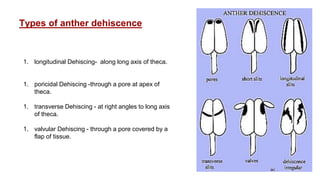
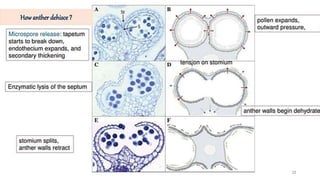
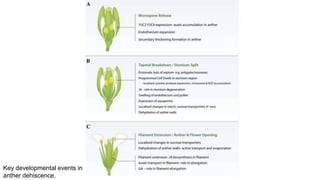
The document discusses pollen wall morphogenesis and anther dehiscence, detailing the development of pollen grains from pollen mother cells and the construction of complex pollen walls comprising intine and exine layers. It elaborates on the process of anther dehiscence, which involves specialized cells and various types of dehiscing mechanisms for pollen release. Additionally, it highlights the significance of pollen structure for taxonomic classification and the interaction of allergens present in pollen.