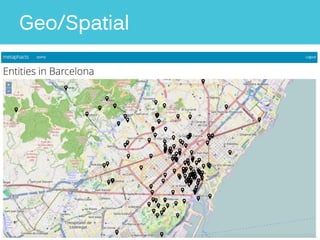
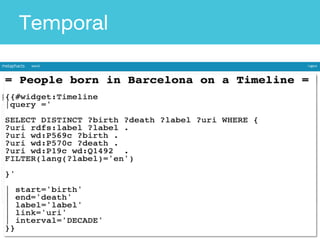
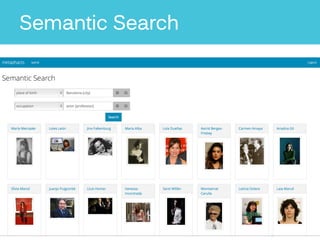
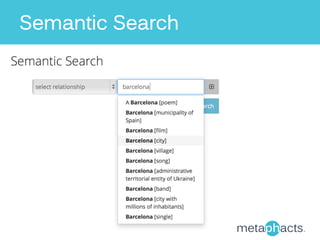
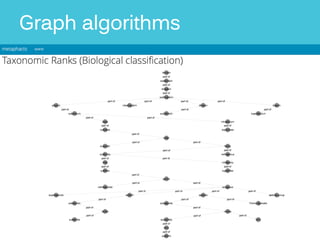
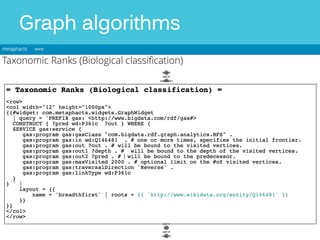
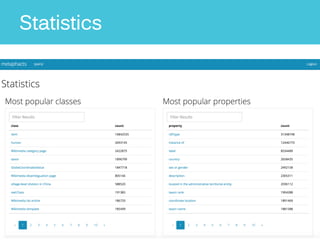
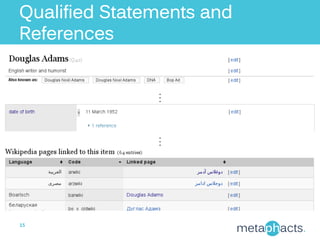
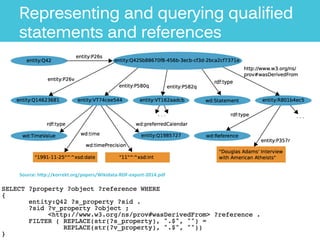
The document discusses Metaphacts GmbH, established in 2014, focusing on solutions for knowledge graphs, including storage, querying, and application development. It highlights Wikidata's structure as a multilingual, collaborative database that integrates with Wikipedia and includes RDF exports. Additionally, the document addresses challenges in representing Wikidata's model in RDF and explores advanced querying capabilities and real-life use cases.