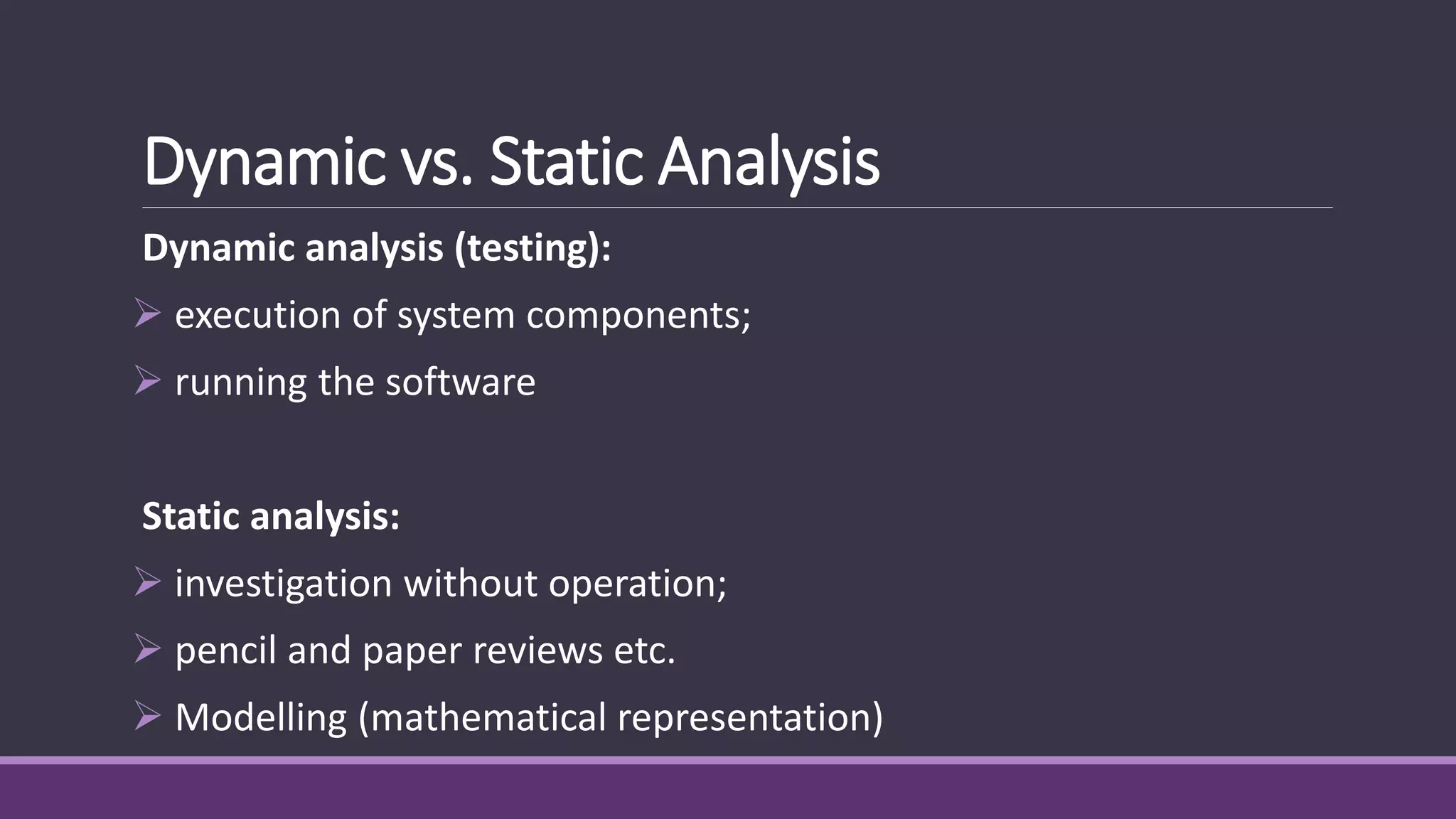
The document discusses quality control and software assurance techniques. It defines quality control as a series of inspections, reviews and tests used throughout development to ensure requirements are met. It distinguishes between verification, ensuring software implements specific functions, and validation, ensuring software meets customer requirements. Static analysis techniques like reviews and inspections are discussed for evaluating software without execution, while dynamic analysis involves software execution. Different review techniques like personal reviews, inspections, walkthroughs and formal reviews are outlined.