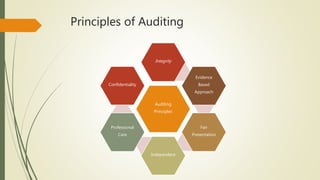
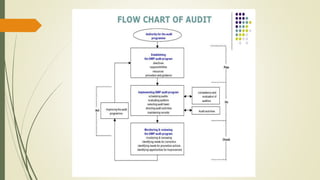
This document defines quality audits and describes the different types, methods, principles, and steps for performing a quality audit. It defines an audit as a systematic, independent process for evaluating the extent to which audit criteria are fulfilled. The types of audits described are first, second, and third party audits. Audit methods include system audits, process audits, compliance audits, and product audits. Principles of auditing include integrity, evidence-based approach, fair presentation, independence, professional care, and confidentiality. The document outlines steps to perform a quality audit and provides tips for an effective internal quality audit program.