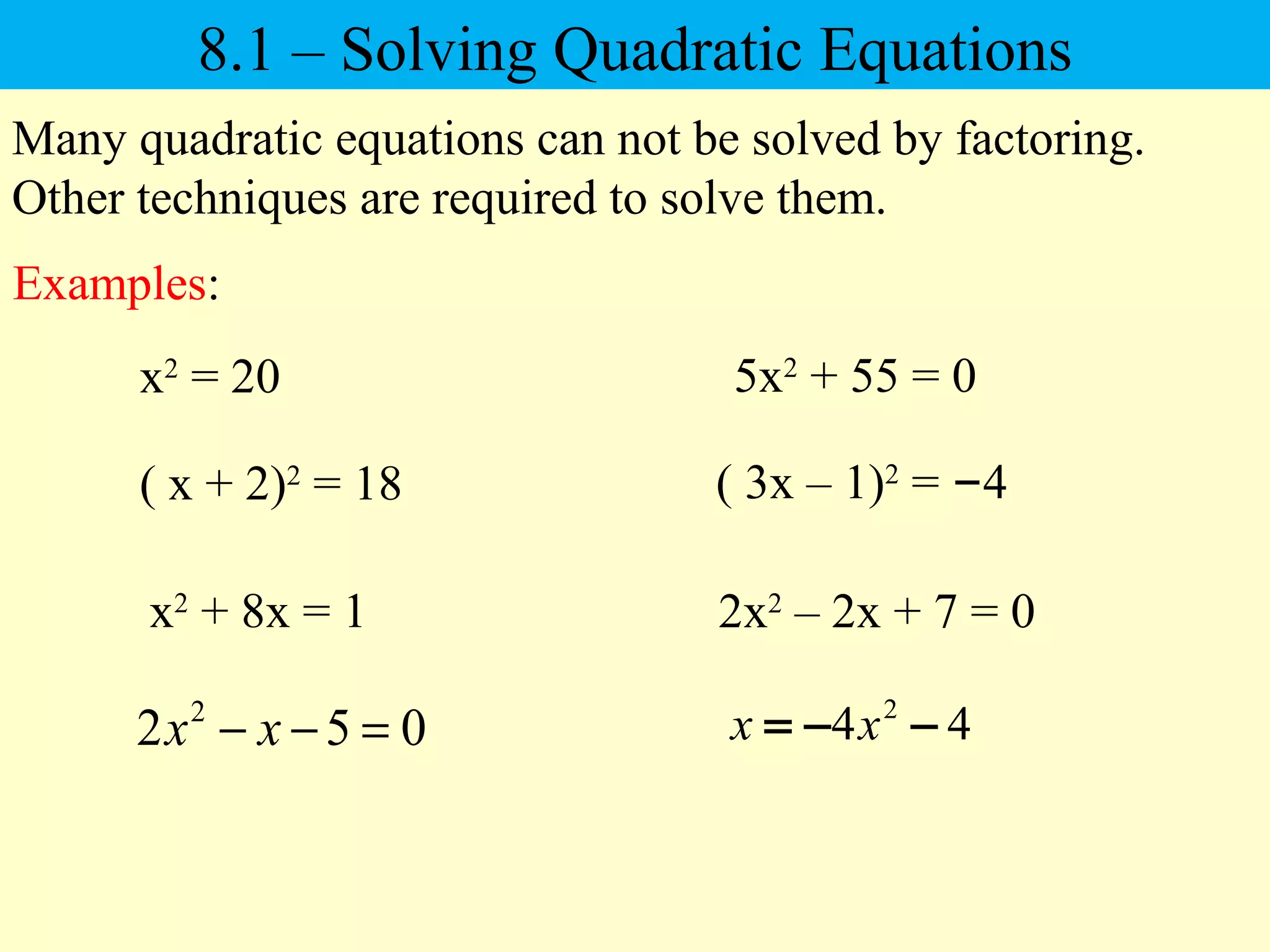
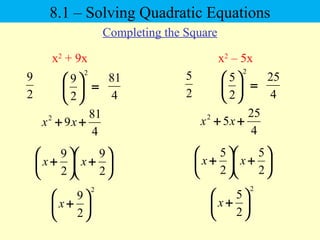
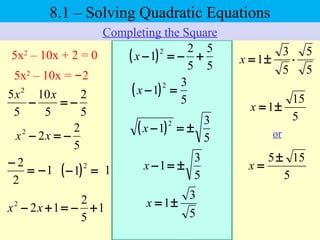
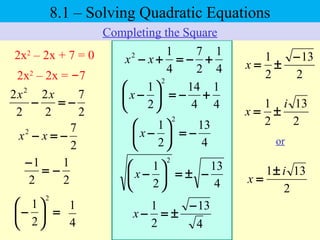
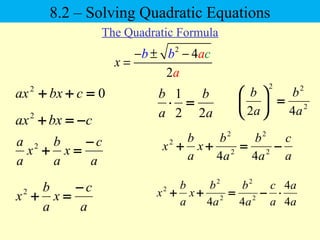
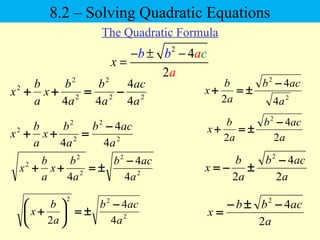
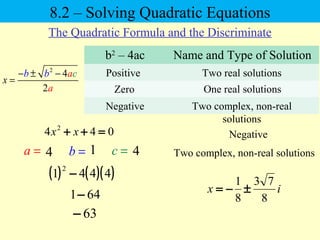
The document discusses solving quadratic equations using various techniques like factoring, completing the square, and the quadratic formula. It provides examples of using these methods to solve equations in standard form. The quadratic formula is derived and explained. The concept of the discriminant is introduced and how it relates to the number and type of solutions. An example problem is worked through applying the Pythagorean theorem and quadratic formula to solve a real world word problem.