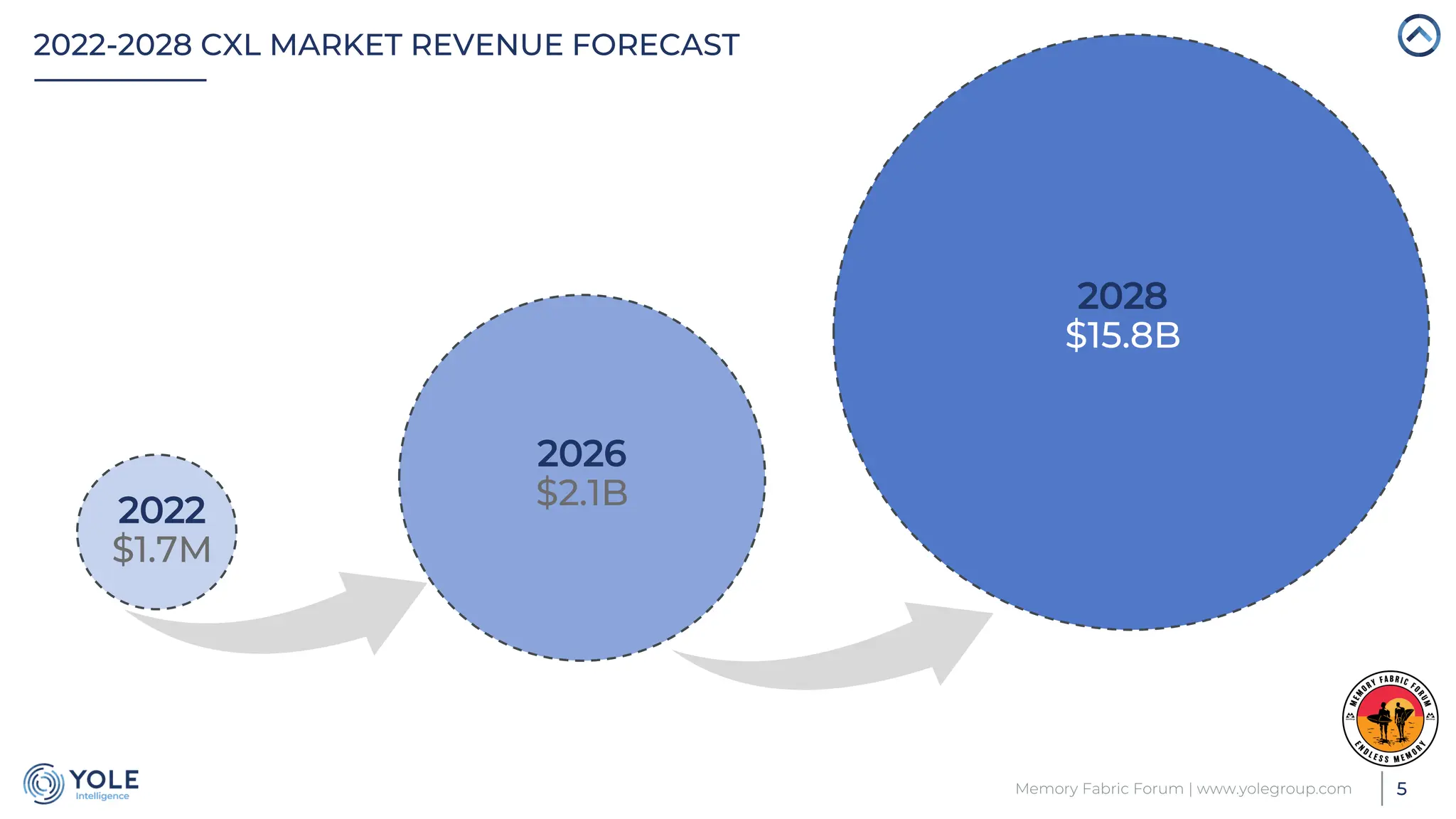
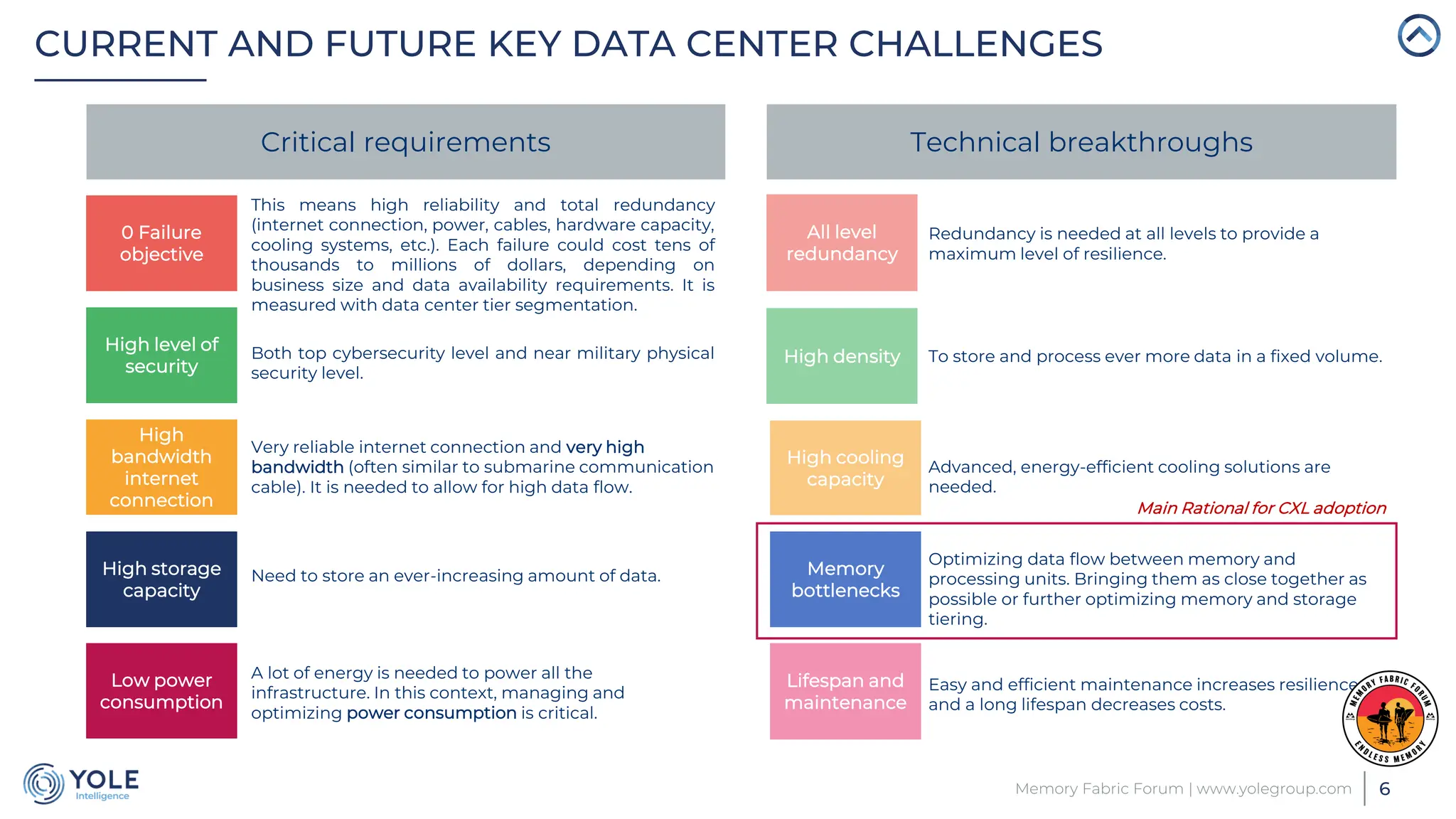
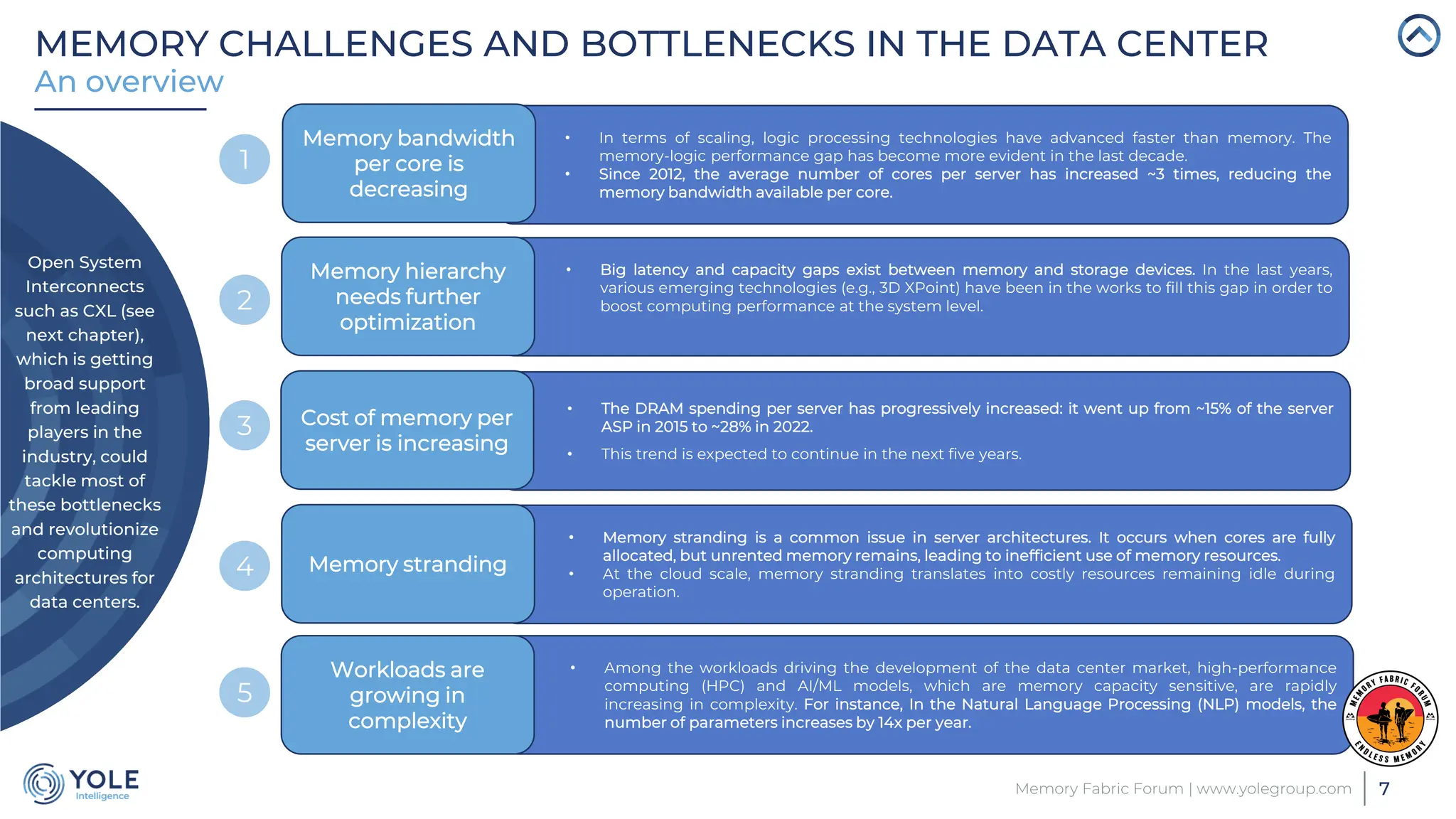
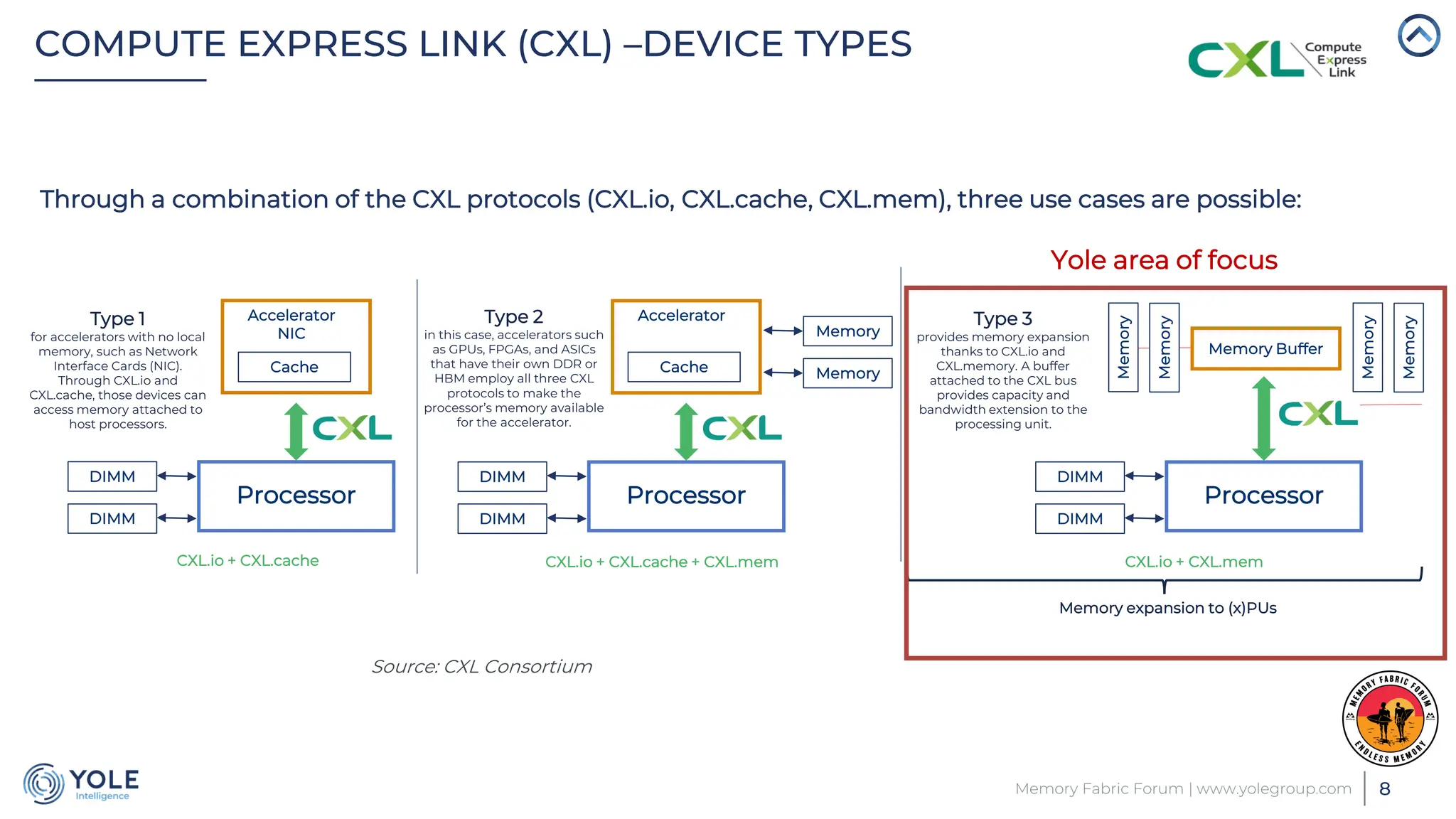
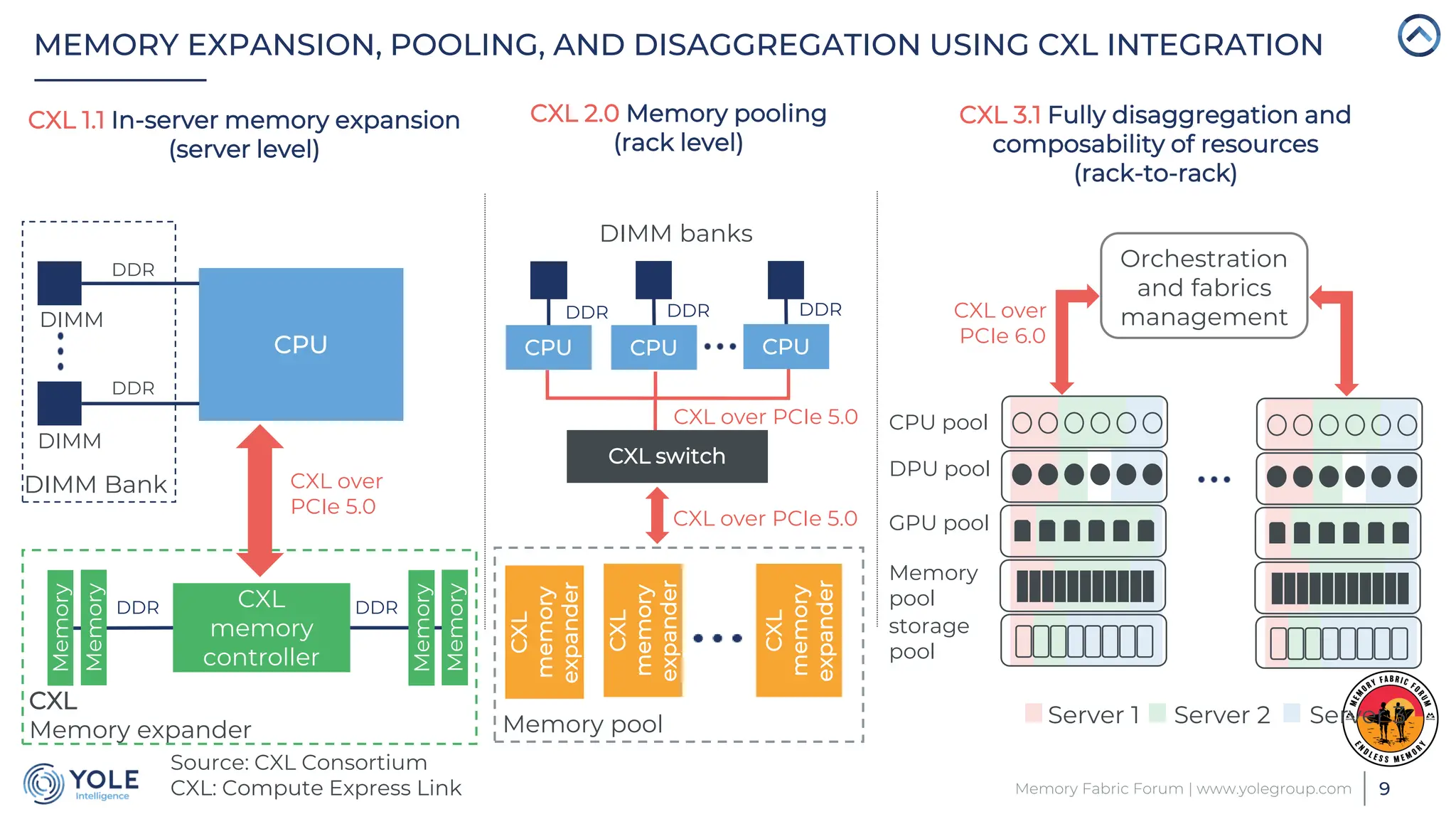
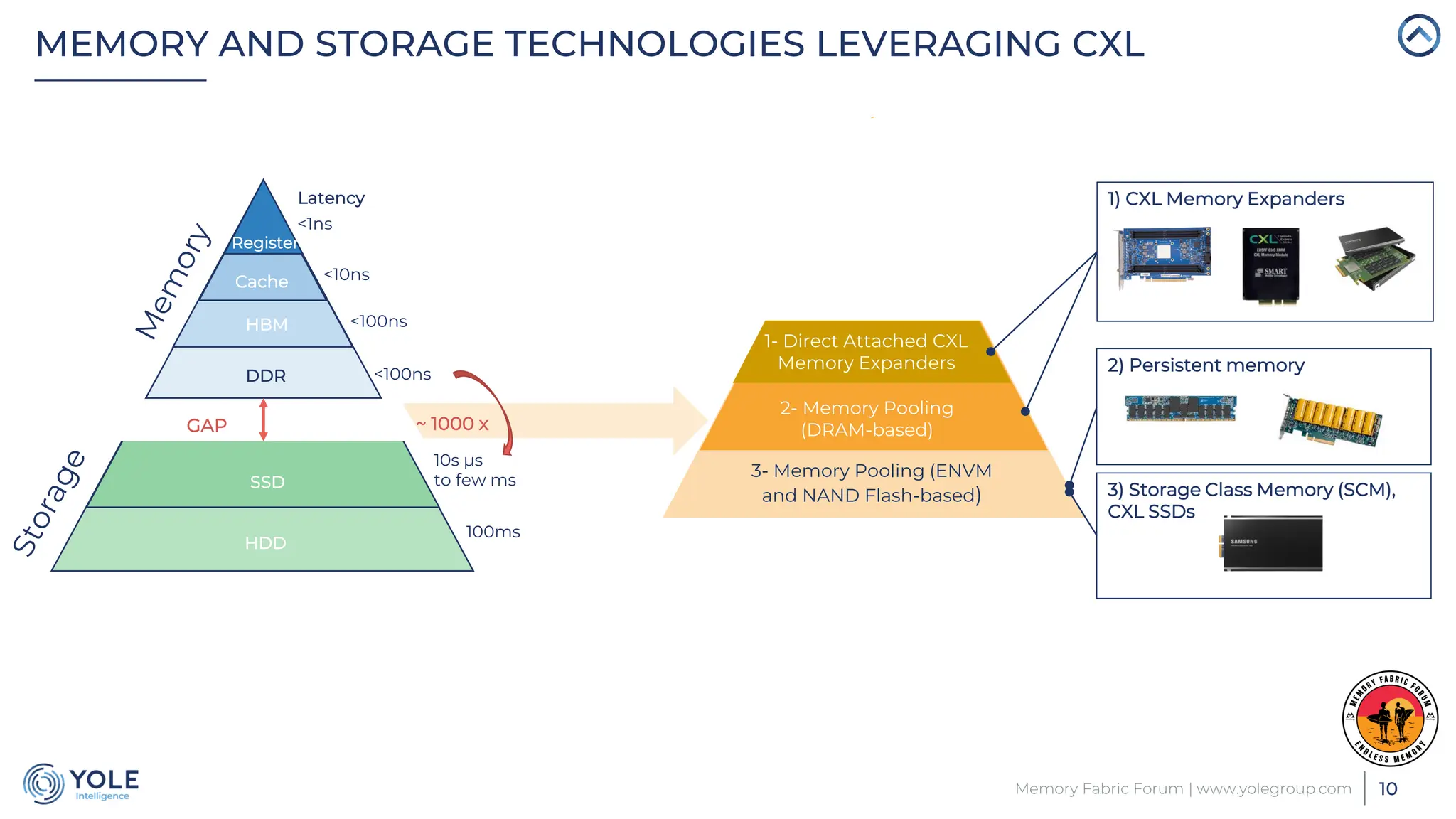
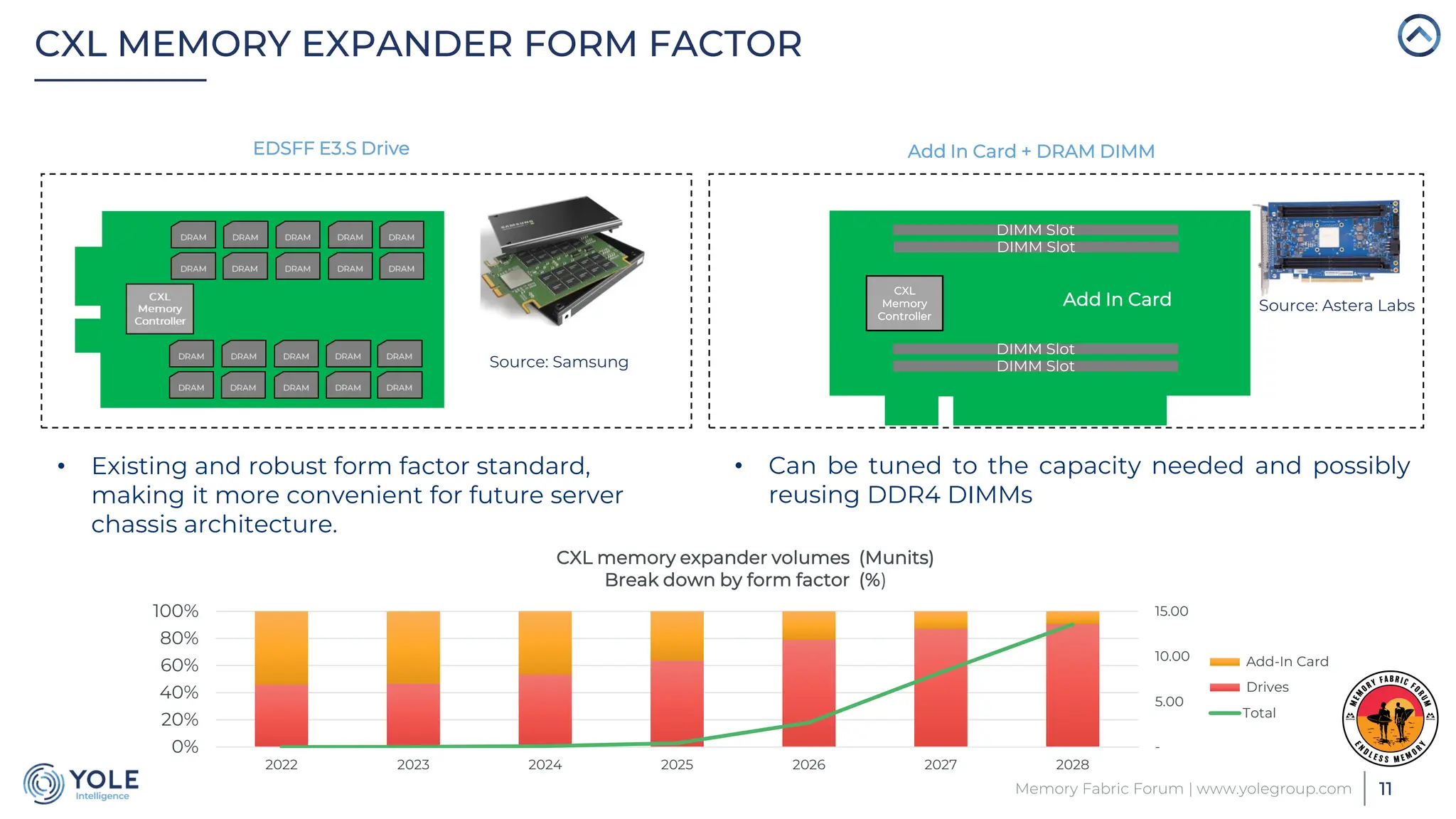
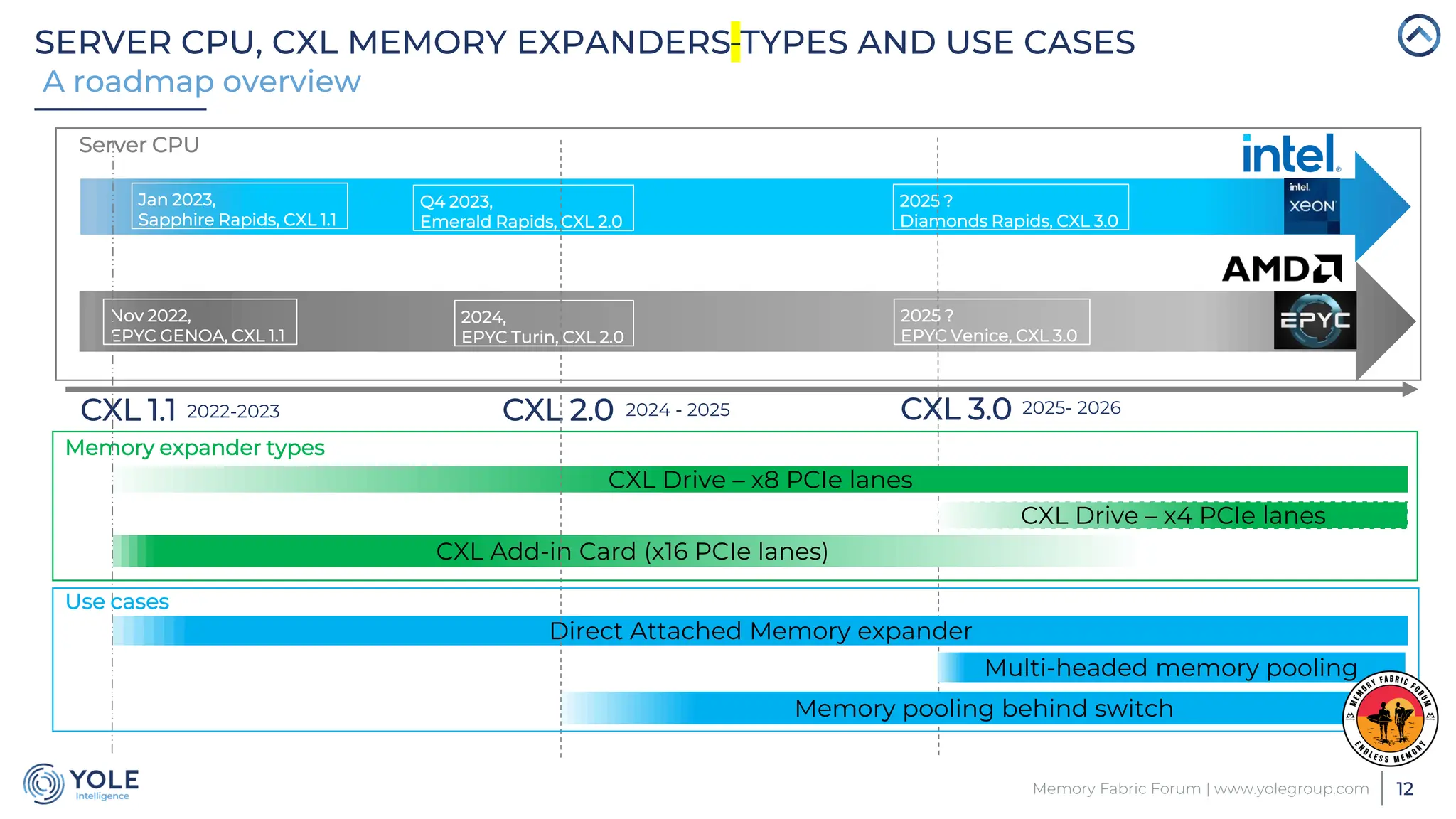
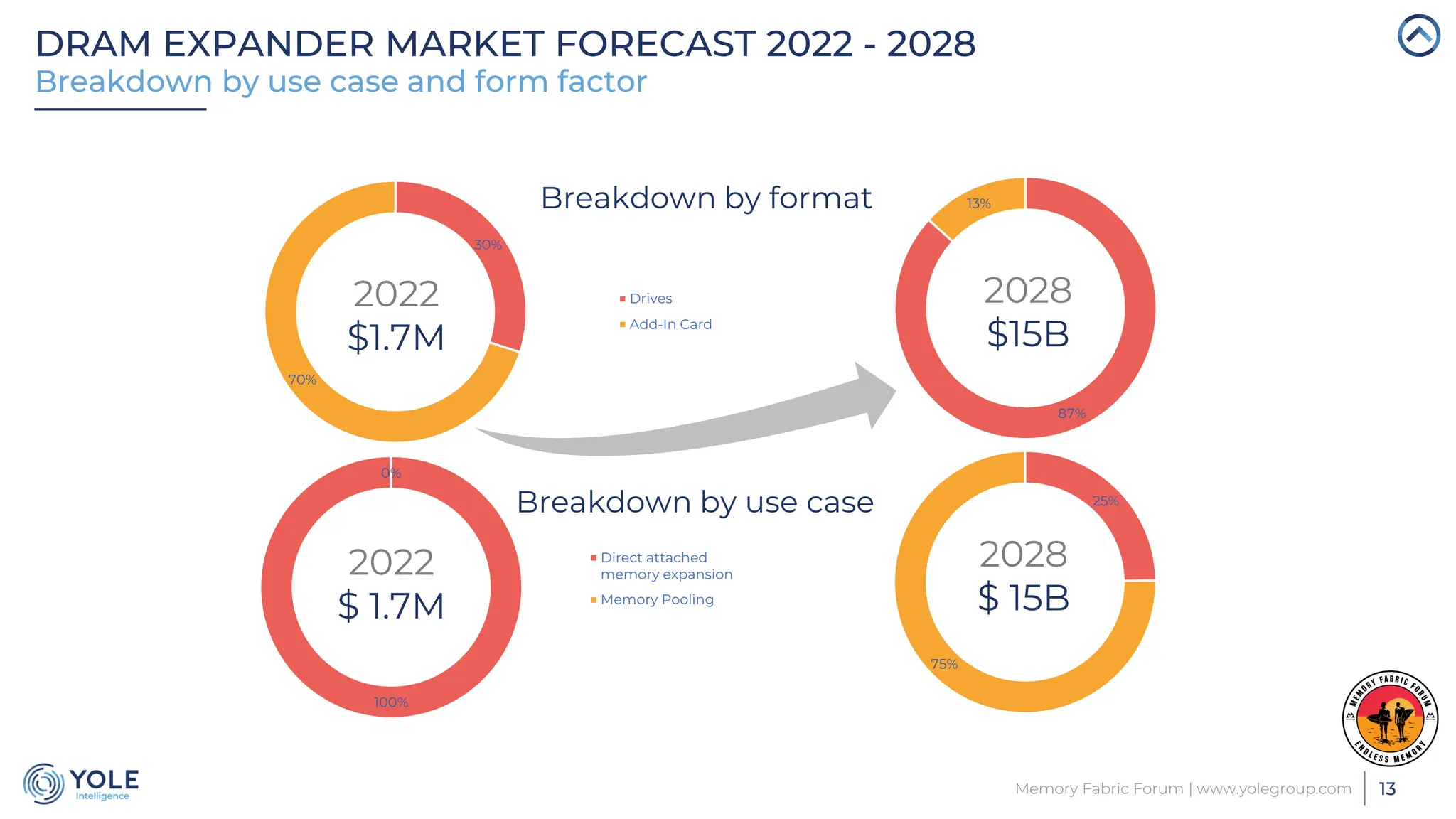
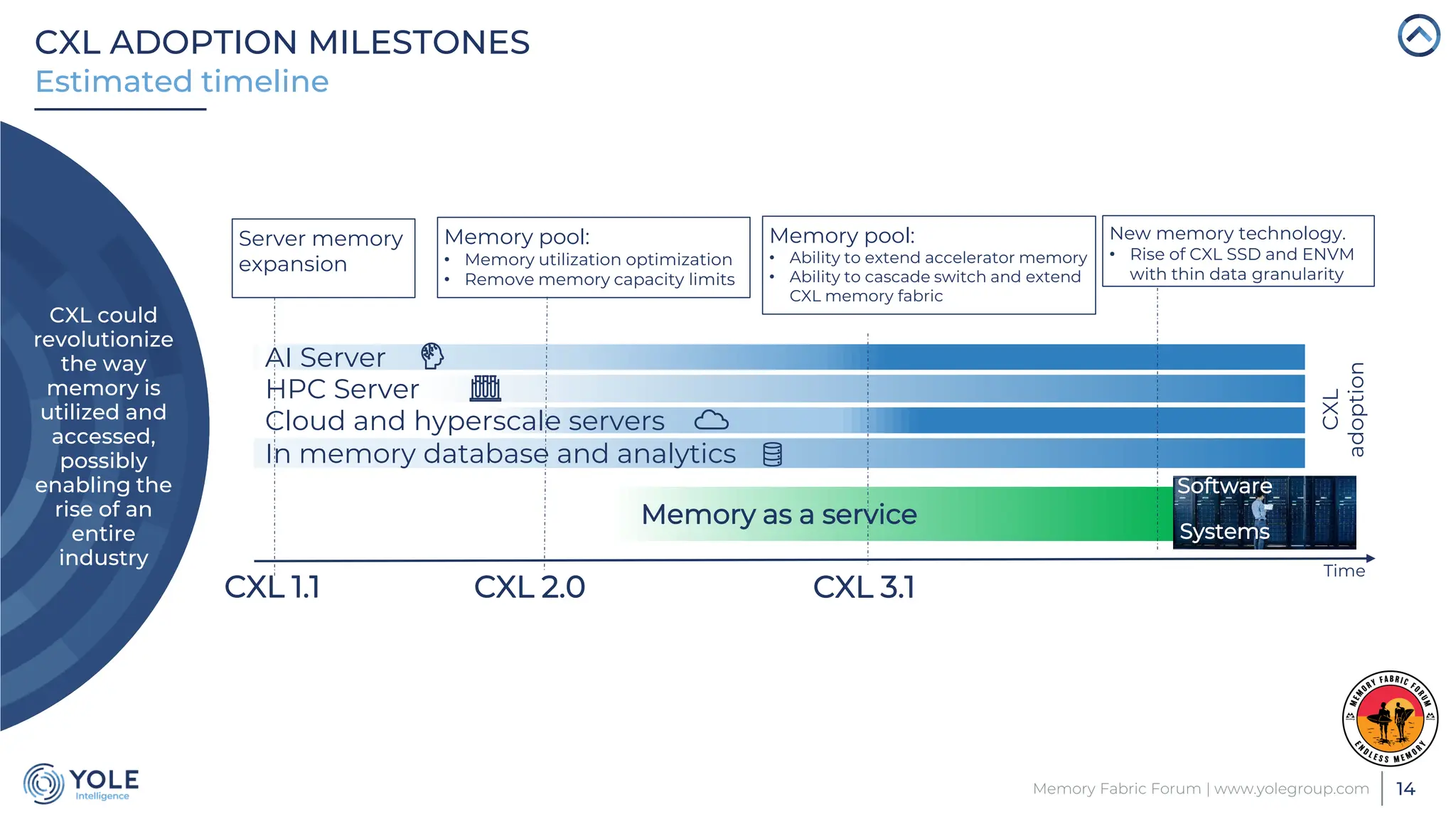
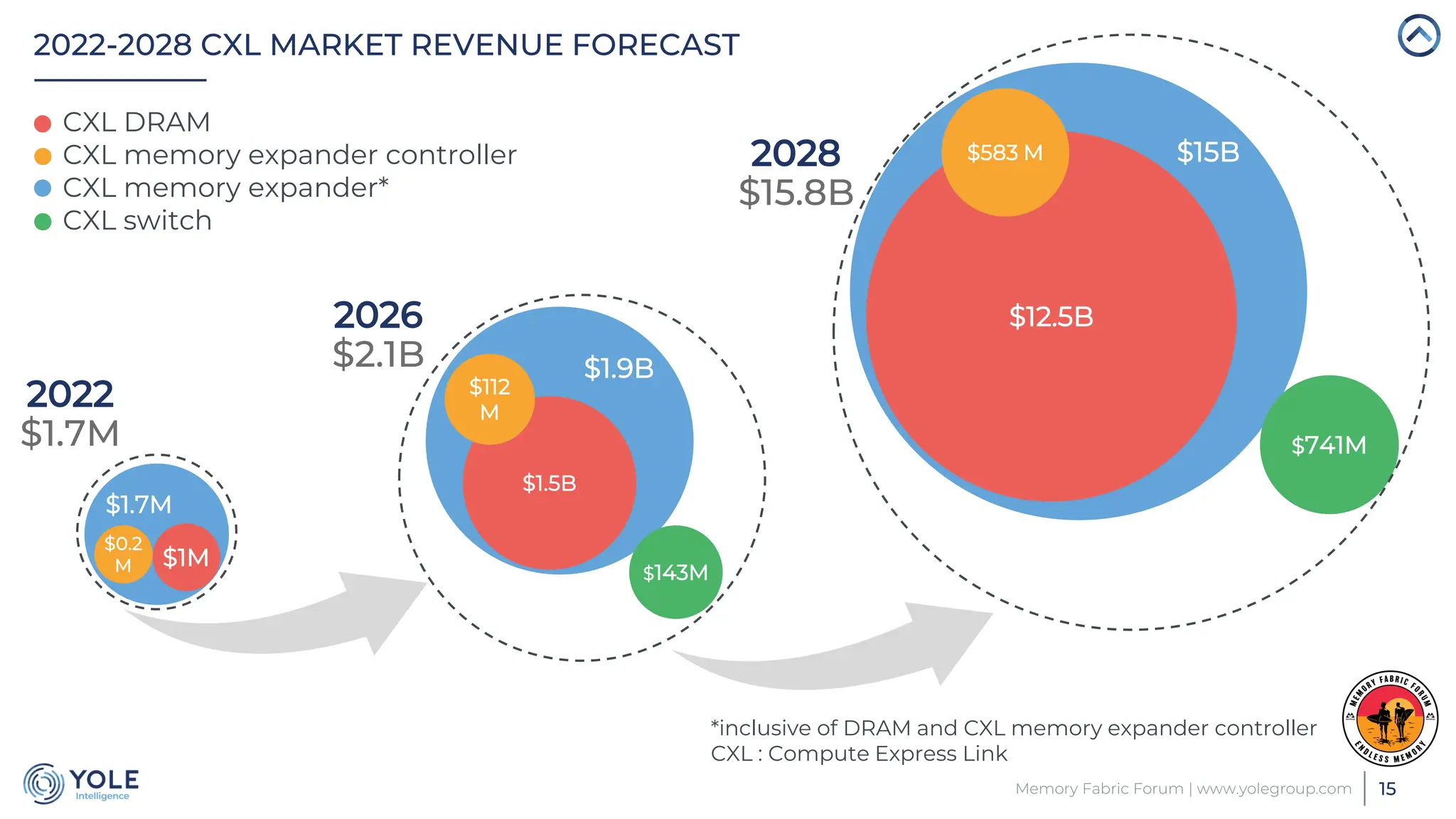
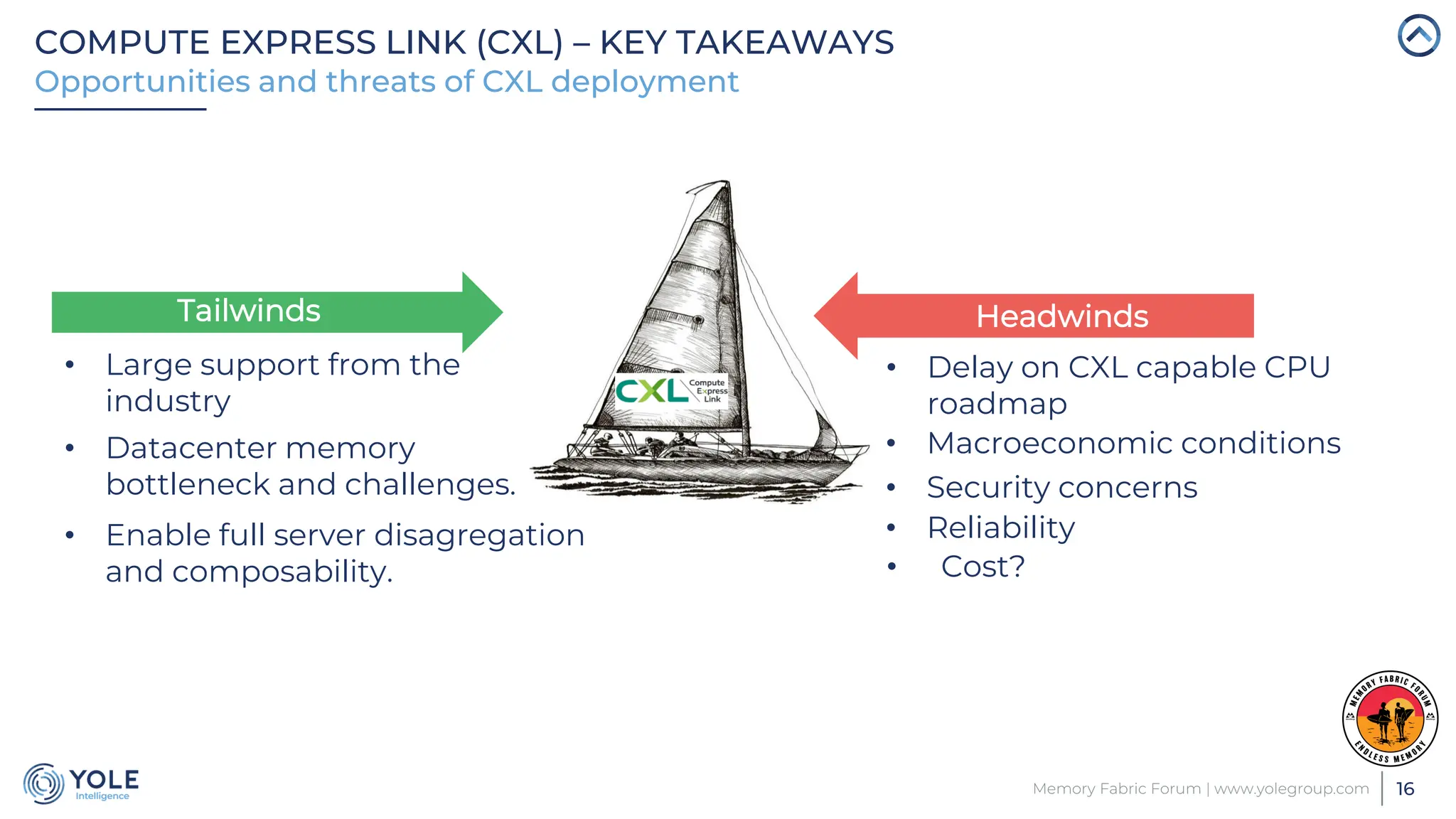
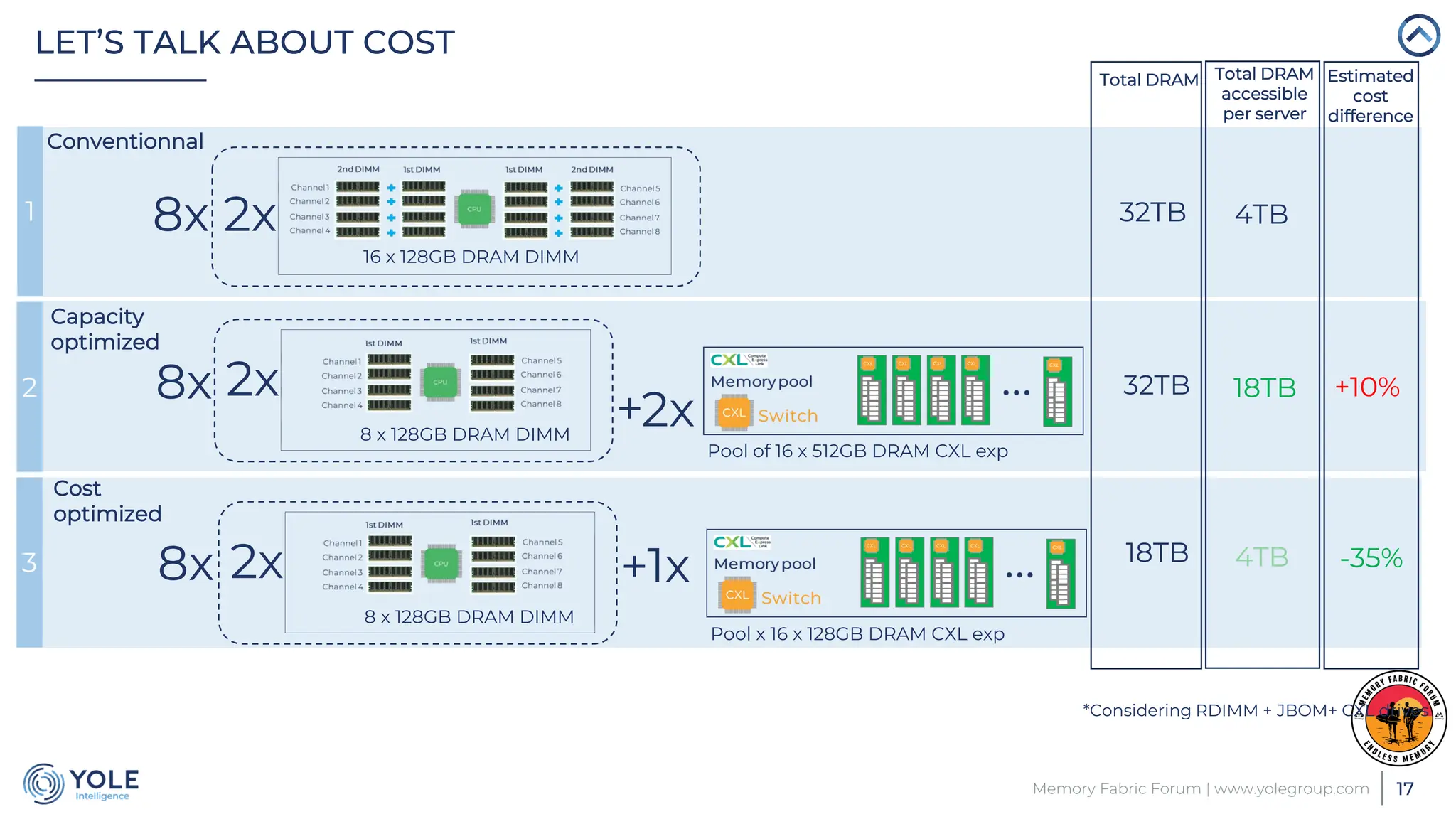
The document discusses the Compute Express Link (CXL) technology and its potential to address key challenges in data center memory management, including latency and capacity gaps between memory and storage. The CXL market is projected to grow significantly from $1.7 million in 2022 to $15.8 billion by 2028, driven by the increasing complexity of workloads and demand for optimization in memory hierarchy. It also highlights various use cases for CXL, including memory pooling and disaggregation, and emphasizes the importance of high reliability and low power consumption in data center operations.