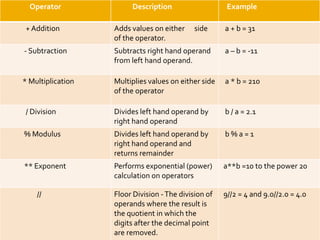
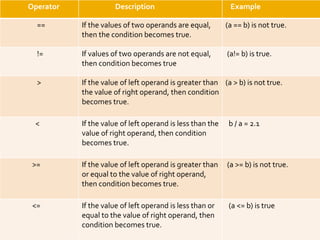
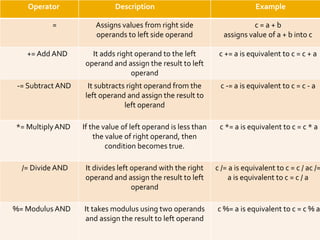
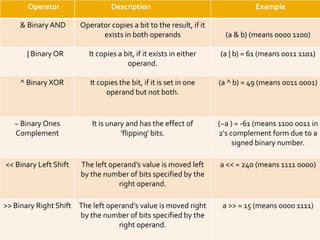
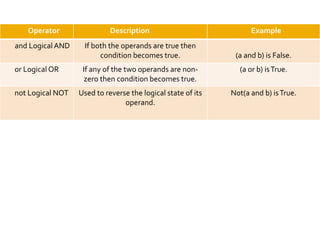
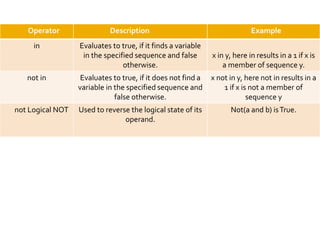
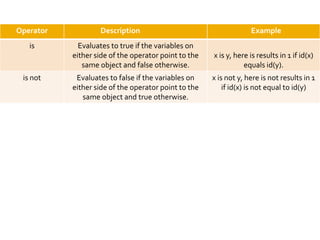
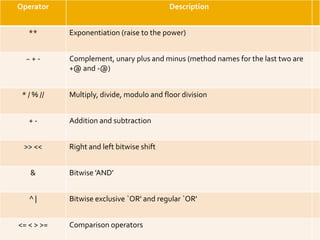
The document provides an overview of Python programming, including its operator types (arithmetic, comparison, assignment, bitwise, and logical operators) and the language's evolution since its inception in 1991. Additionally, it highlights training courses offered by IQ Training, emphasizing Python's relevance in data science careers and the job market. The document also mentions the potential earnings for Python professionals, underscoring the increasing demand for skilled workers in this field.