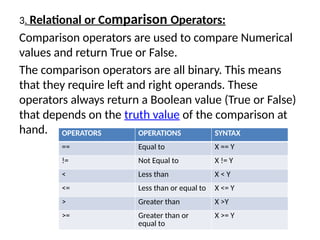
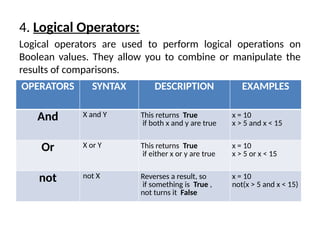
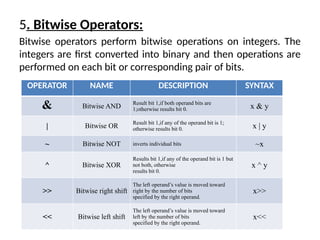
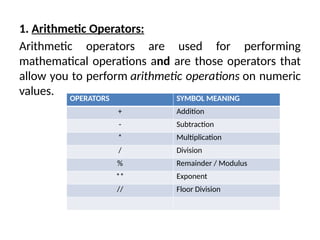
The document provides an overview of operators in Python, categorizing them into various types such as arithmetic, assignment, comparison, logical, bitwise, membership, and identity operators. Each type is explained with its function, syntax, and examples illustrating their use in performing computations and comparisons. The text emphasizes how operators can be combined with operands to execute specific operations within Python programming.





![2. Assignment Operators :
The assignment operator is one of the most
frequently used operators in Python. The
operator consists of a single equal sign (=).
it operates on two operands.
The left-hand operand is typically a Variable,
while the right-hand operand is an expression.
number = 42
day = "Friday"
digits = (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9)
letters = ["a", "b", "c"]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pythonlec-6operators-240917051747-35aa71ec/85/Python-Lec-6-Operatorguijjjjuugggggs-pptx-7-320.jpg)