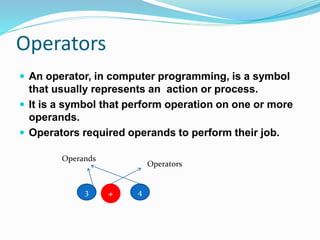
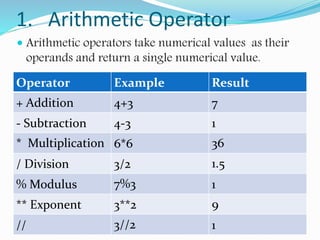
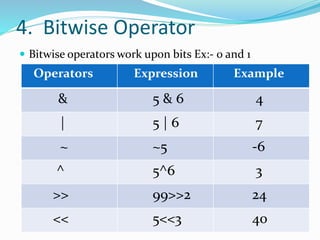
Operators are symbols that represent actions or processes performed on operands. There are several types of operators including arithmetic, relational, logical, bitwise, assignment, identity, and membership operators. Arithmetic operators perform math operations, relational operators compare values, logical operators combine conditional statements, bitwise operators work with bits, assignment operators assign values, identity operators check object equality, and membership operators check if a value is contained within an object. Operators require operands as inputs to perform their defined actions and return results.