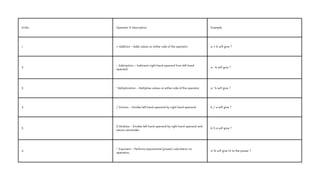
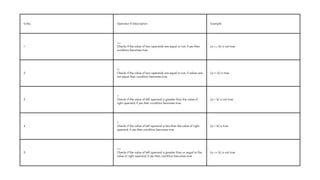
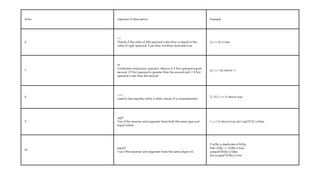
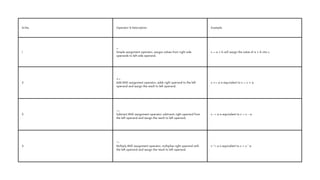
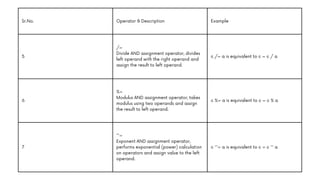
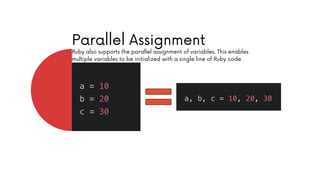
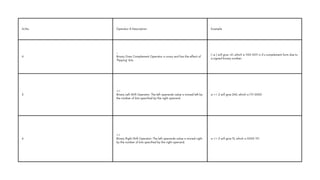
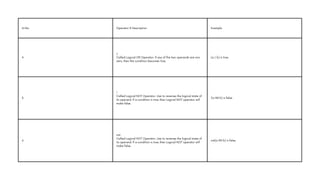
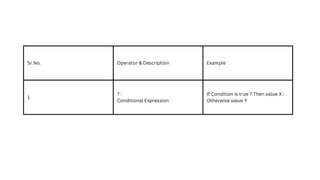
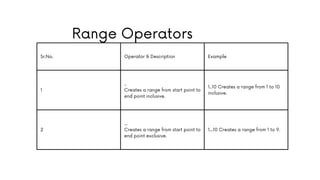
The document comprehensively covers various Ruby operators, including arithmetic, comparison, assignment, bitwise, logical, ternary, range, and defined? operators. It provides detailed descriptions and examples for each operator type, demonstrating their functionality in Ruby programming. Additionally, it highlights operator precedence and parallel assignment features in Ruby.