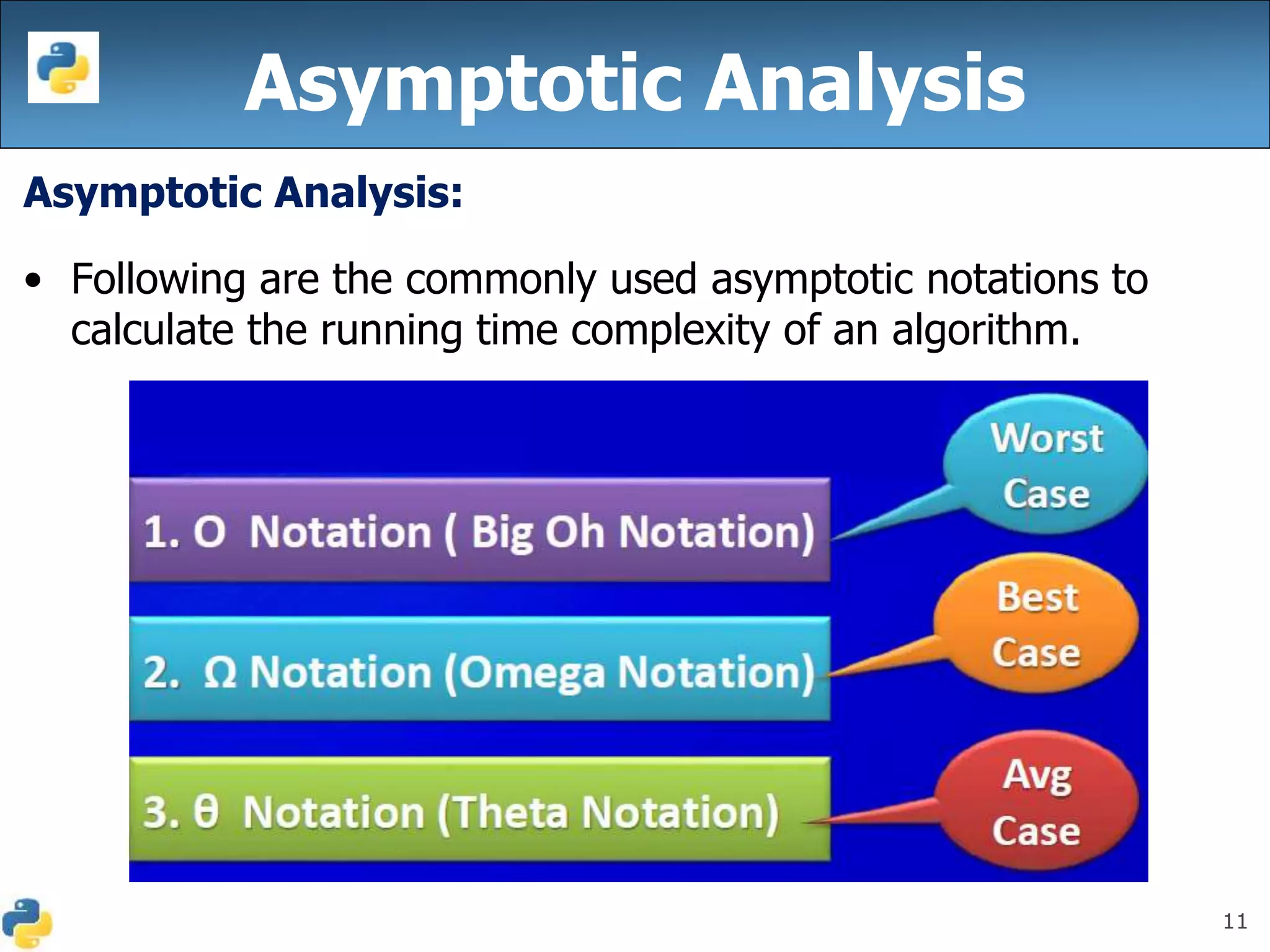
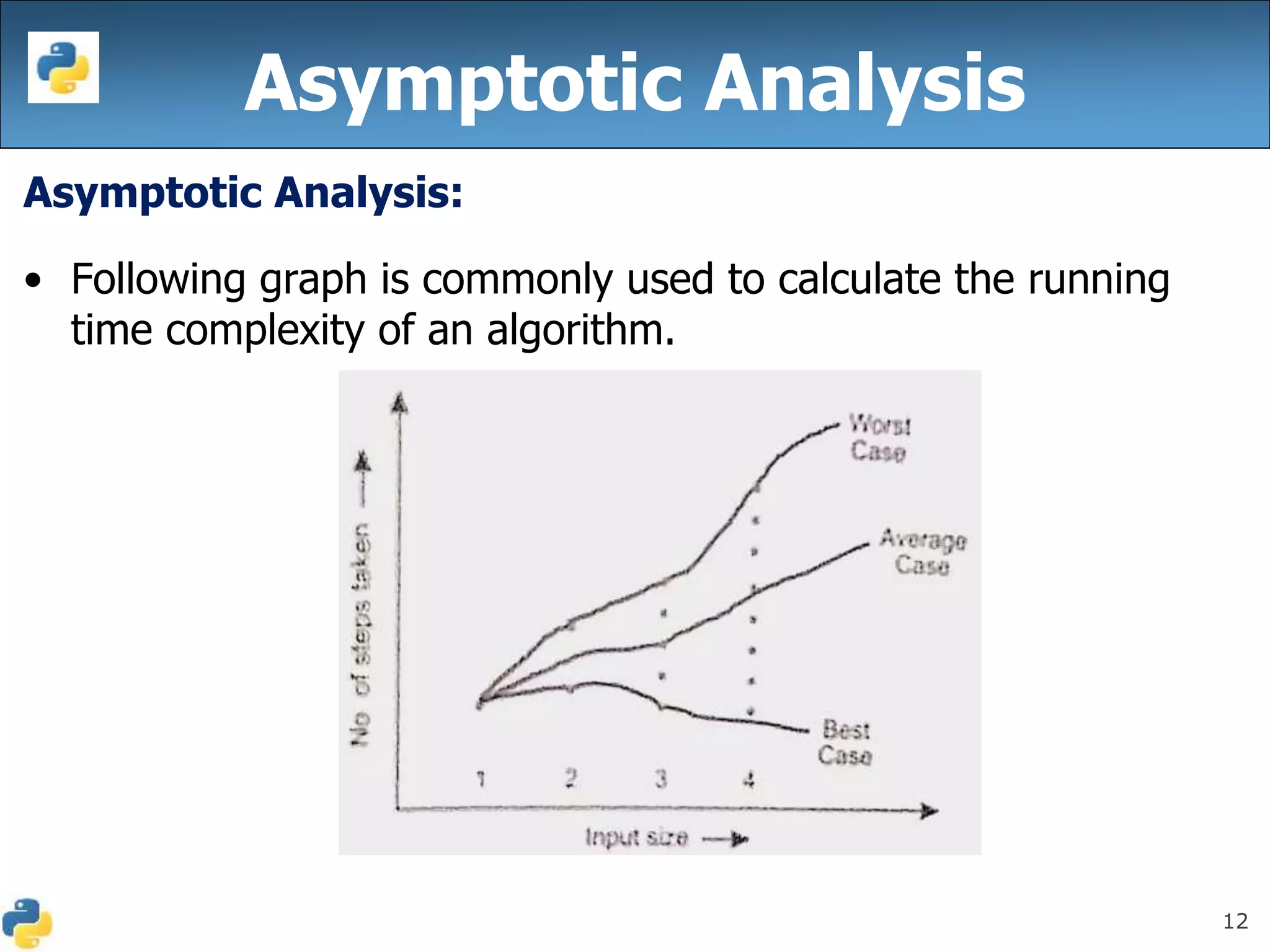
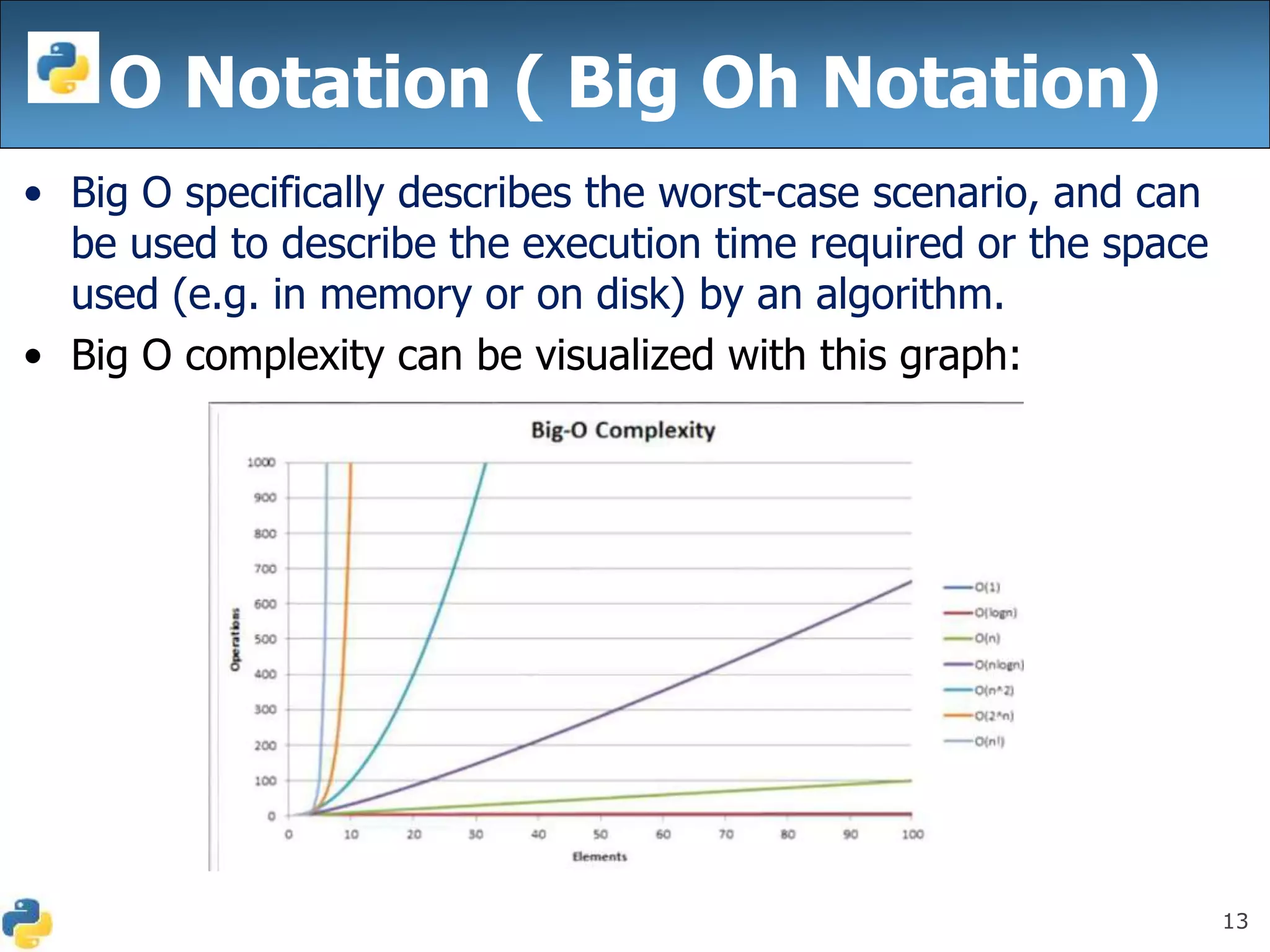
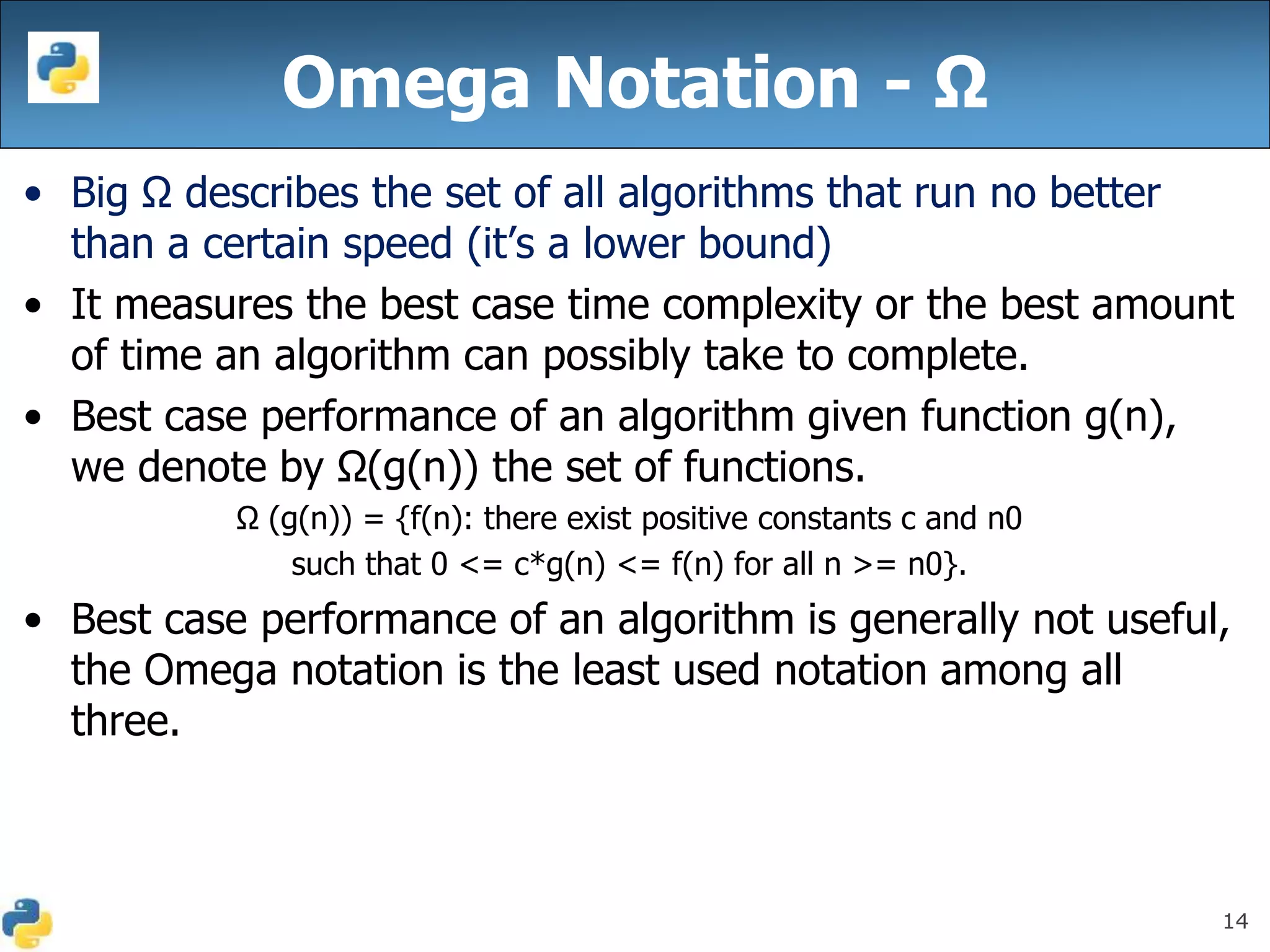
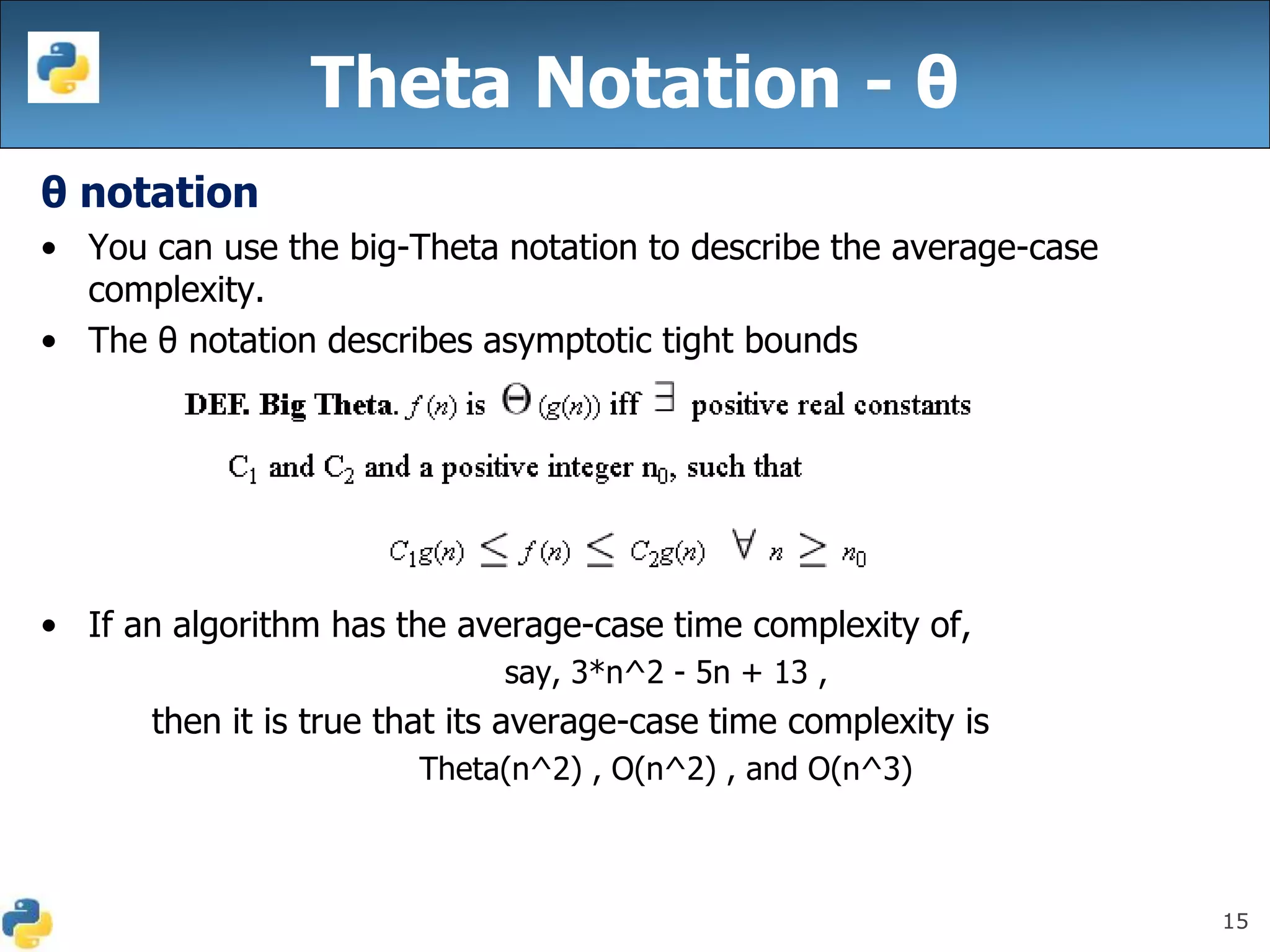
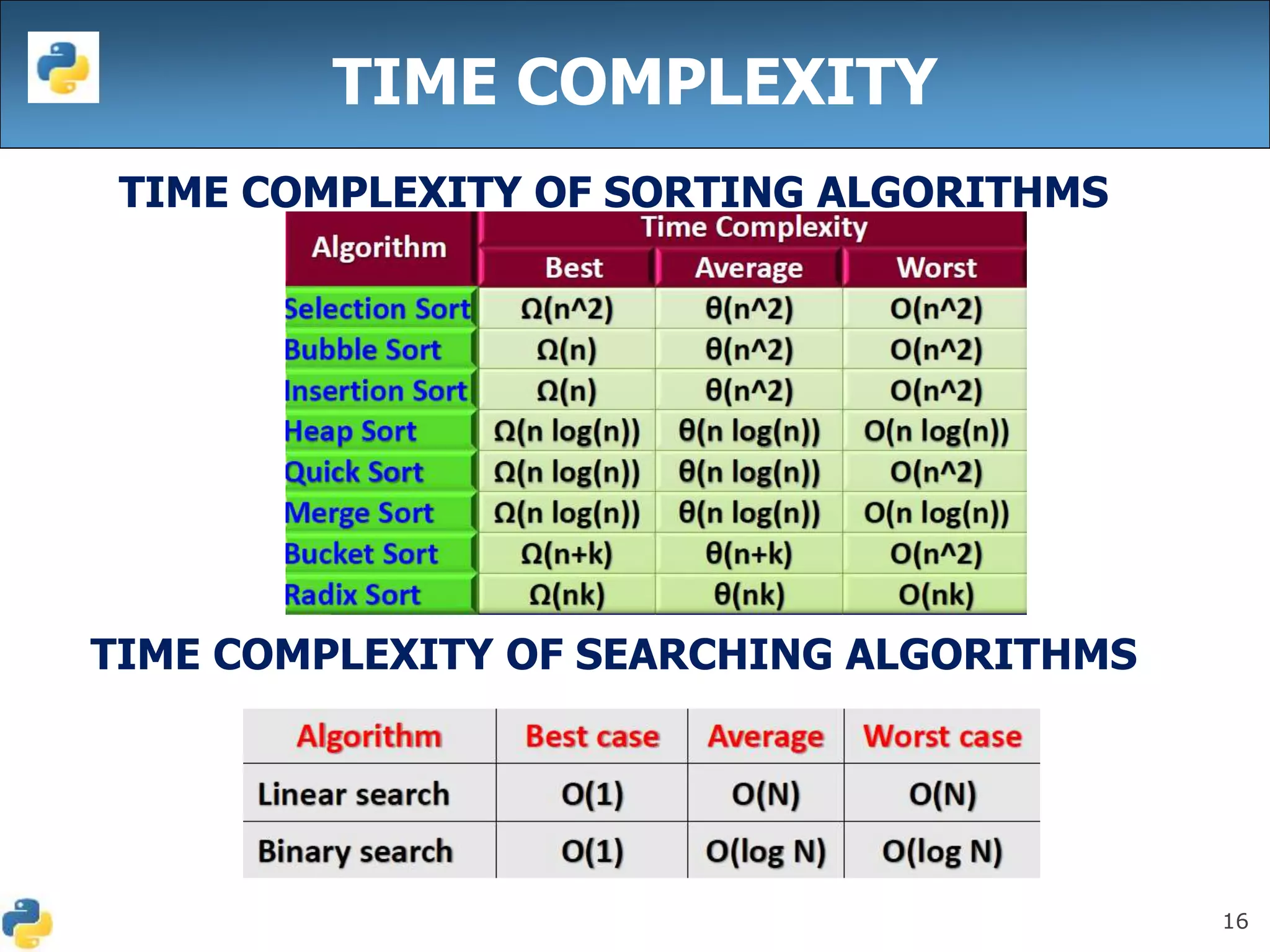
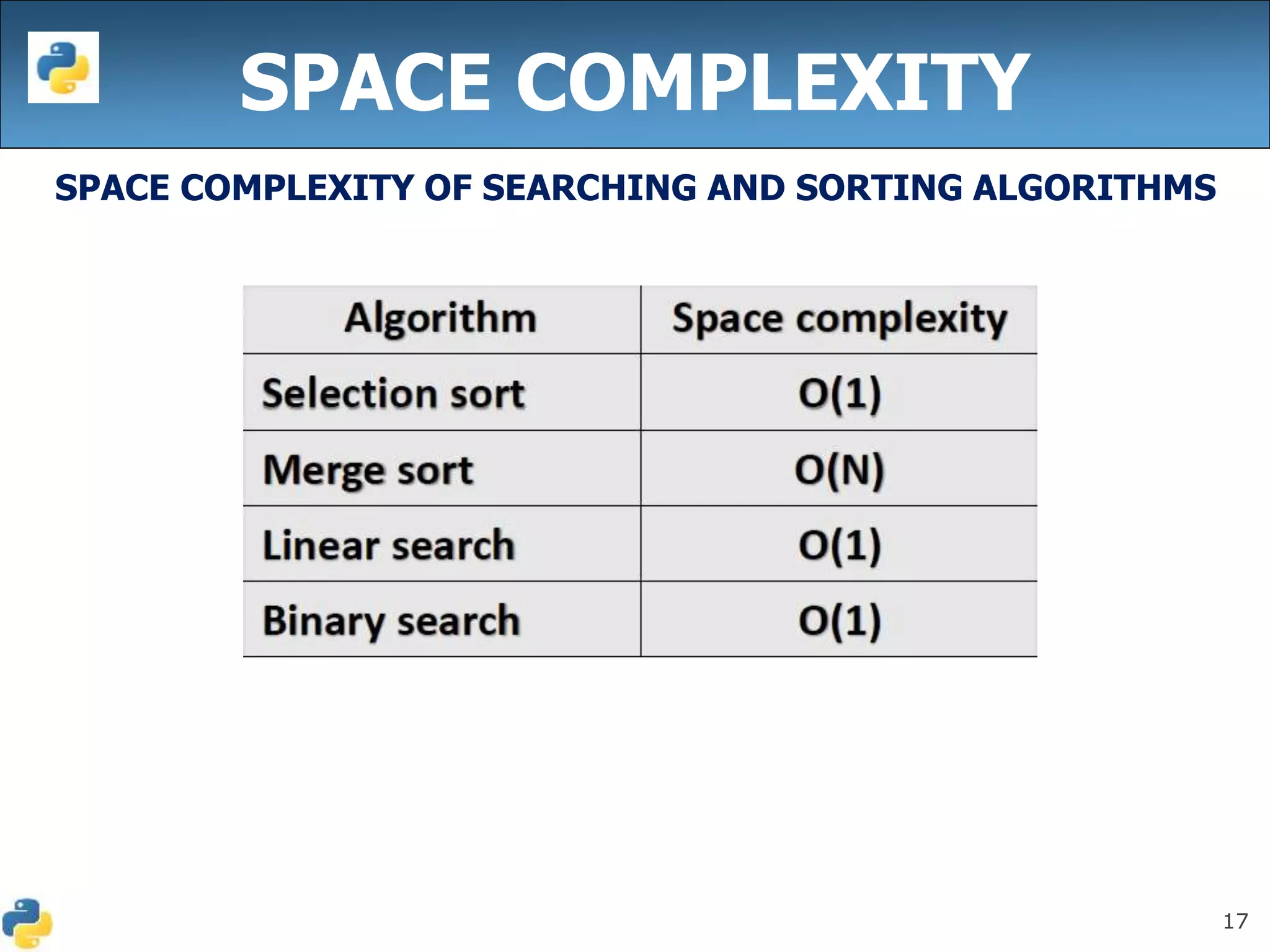
This document discusses algorithmic efficiency and complexity. It begins by defining an algorithm as a step-by-step procedure for solving a problem in a finite amount of time. It then discusses estimating the complexity of algorithms, including asymptotic notations like Big O, Big Omega, and Theta that are used to describe an algorithm's time and space complexity. The document provides examples of time and space complexity for common algorithms like searching and sorting. It concludes by emphasizing the importance of analyzing algorithms to minimize their cost and maximize efficiency.