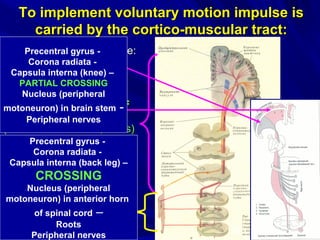
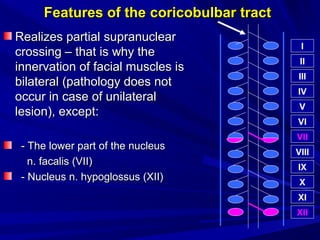
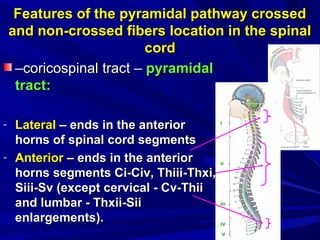
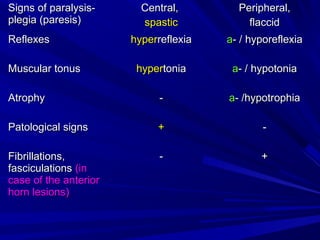
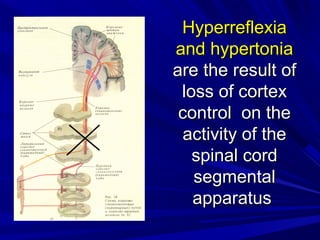
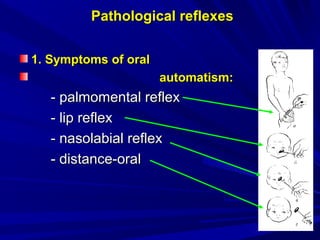
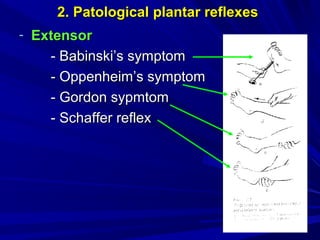
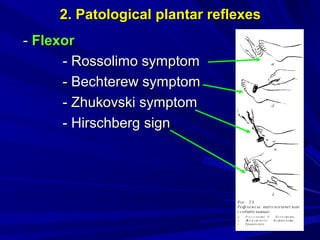
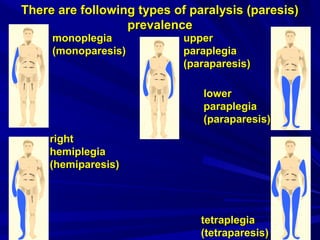
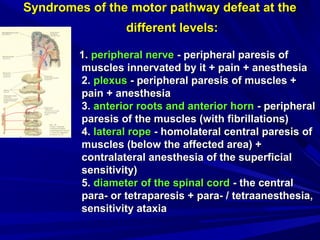
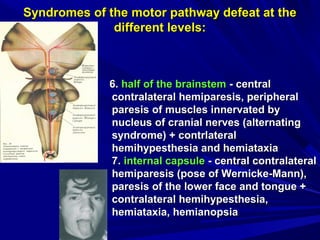
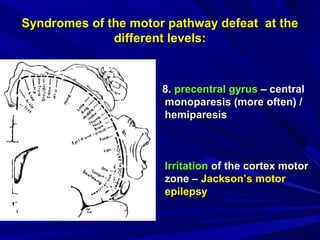
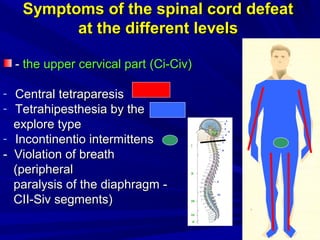
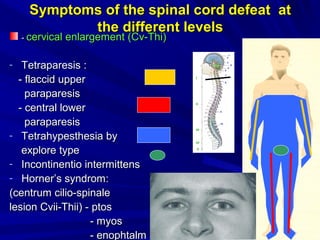
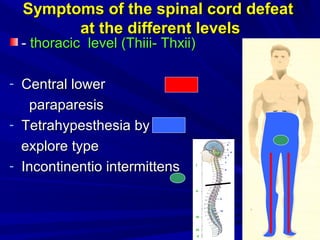
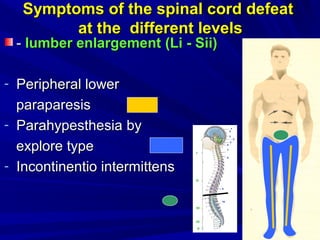
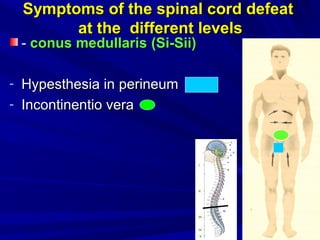
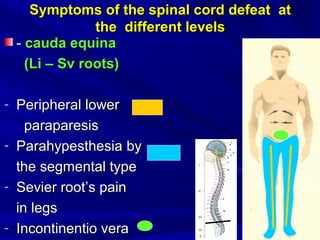
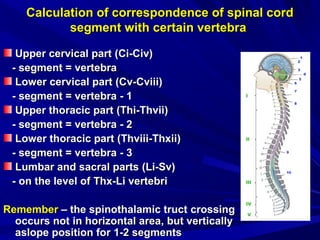
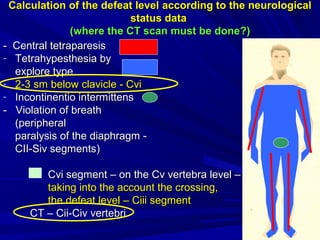
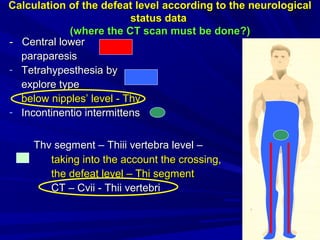
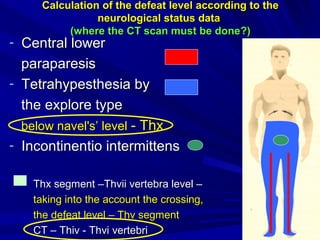
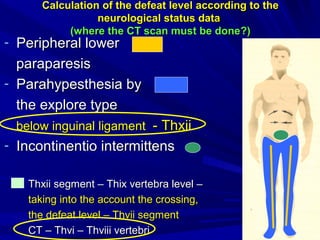
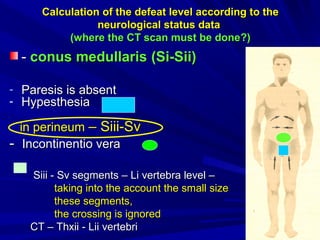
This document discusses voluntary movements and disorders of the pyramidal tract. It describes the pathways involved in voluntary motor control from the motor cortex through the brainstem and spinal cord. It outlines syndromes that can occur with disorders at different levels, including signs of paralysis or paresis. Specific pathways, such as the corticobulbar and corticospinal tracts, and features like crossed and uncrossed fibers are examined. Pathological reflexes and synkinesia that may arise are also detailed.