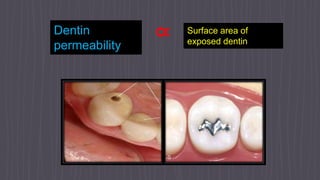
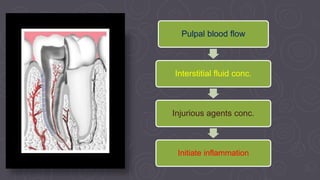
The document provides an overview of the dental pulp, including its embryology, structures, functions, nerves, and conclusion. It discusses how the pulp develops from the fifth week of embryology and continues developing through childhood. It describes the principal cells of the pulp, including odontoblasts, fibroblasts, and immunocompetent cells. The document outlines the layers of the pulp and discusses the microvasculature, interstitial fluid, fibers, ground substance, and nerves found within the pulp. It concludes by emphasizing the importance of thorough knowledge and understanding of the pulp for its preservation and successful management in disease cases.