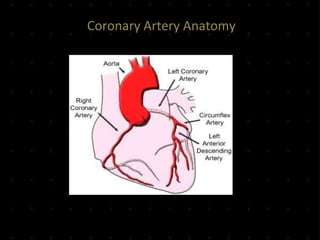
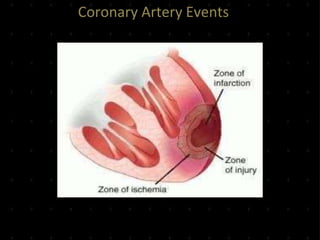
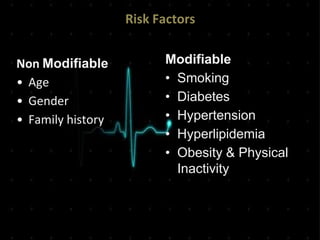
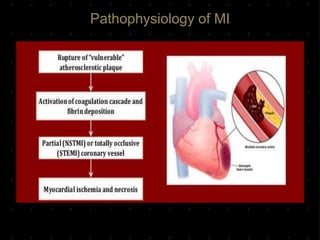
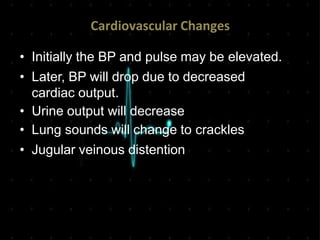
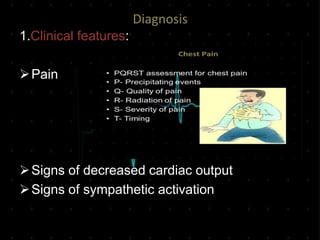
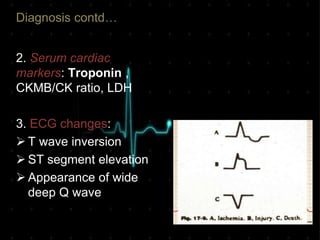
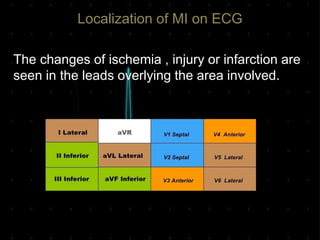
Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow to part of the heart is reduced or blocked, depriving heart muscle cells of oxygen and nutrients and leading to cell damage or death. This is usually due to a blood clot forming on a fatty buildup in the coronary arteries. Immediate treatment goals for an AMI focus on restoring blood flow through the blocked vessel to limit heart muscle damage. Management includes oxygen, aspirin, morphine, nitroglycerin, blood tests, an ECG, and reperfusion through percutaneous coronary intervention or a clot-busting drug within 12 hours when possible. Long term care focuses on lifestyle changes and controlling risk factors