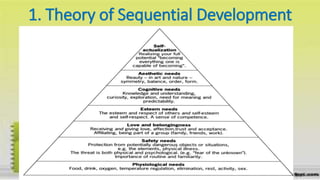
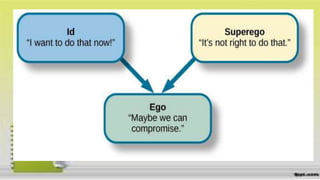
This document discusses motivation and theories of motivation. It defines motivation, motive, need, drive, and goal. It describes physiological motives like hunger, thirst, sleep, temperature regulation, elimination, and pain avoidance. It also discusses social motives like affiliation, security, and social approval. Ego-integrative motives aim for recognition, power, achievement, autonomy, and defensiveness. Theories of motivation mentioned include Freud's psychoanalytic theory of id, ego, and superego; Adler's superiority and inferiority theories; Murray's need theory; and Allport's theory of functional autonomy of motives.