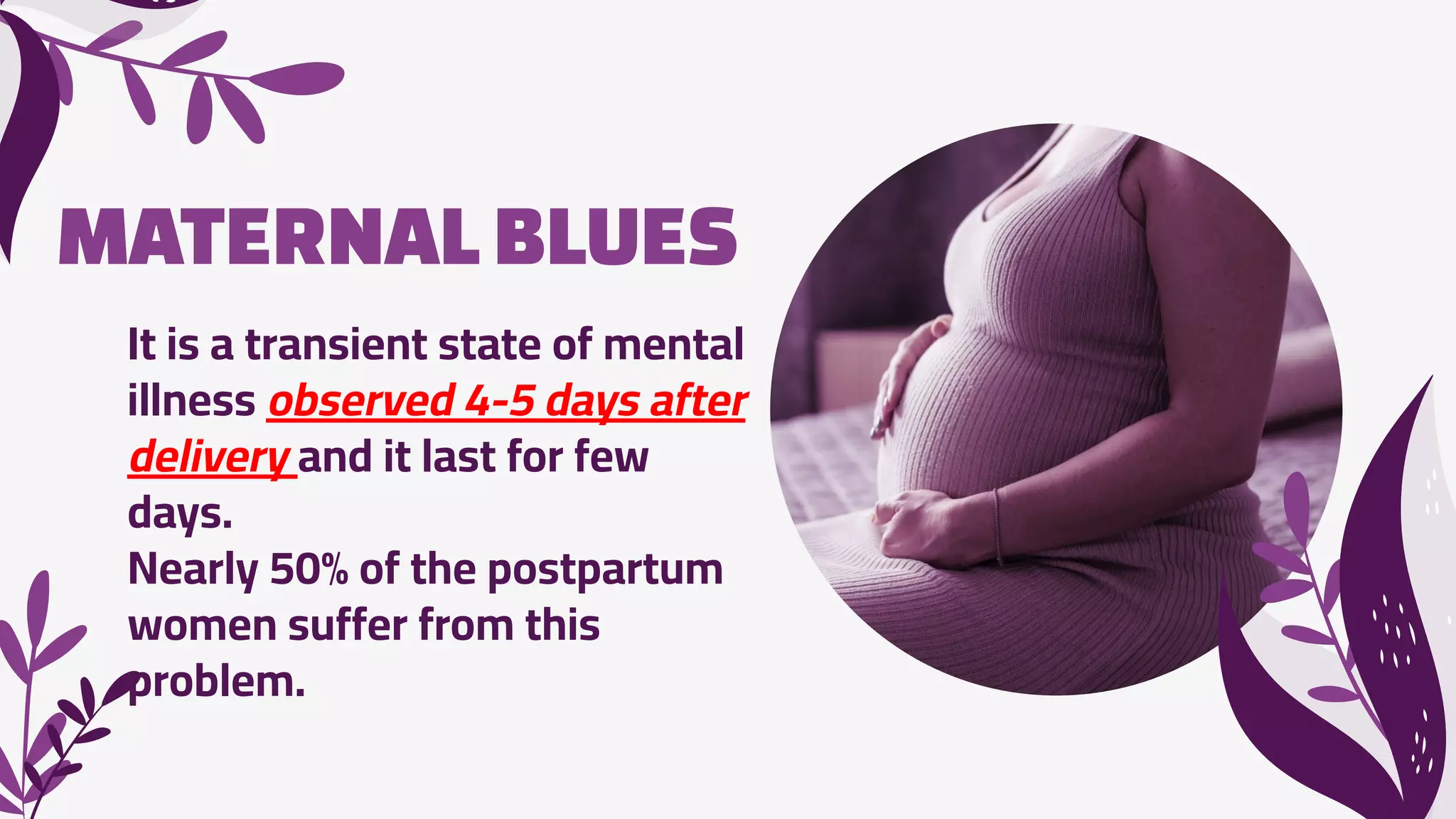
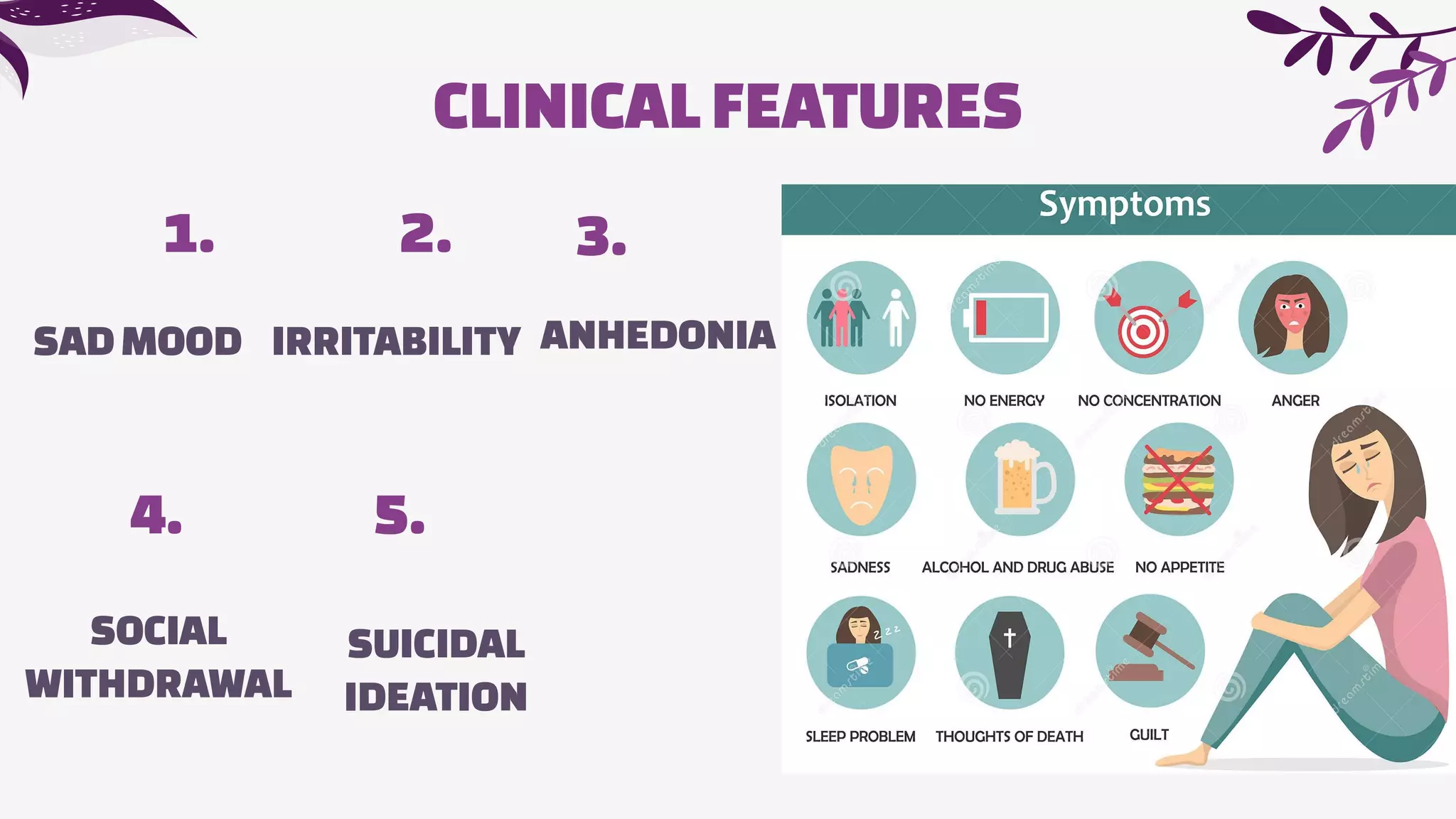
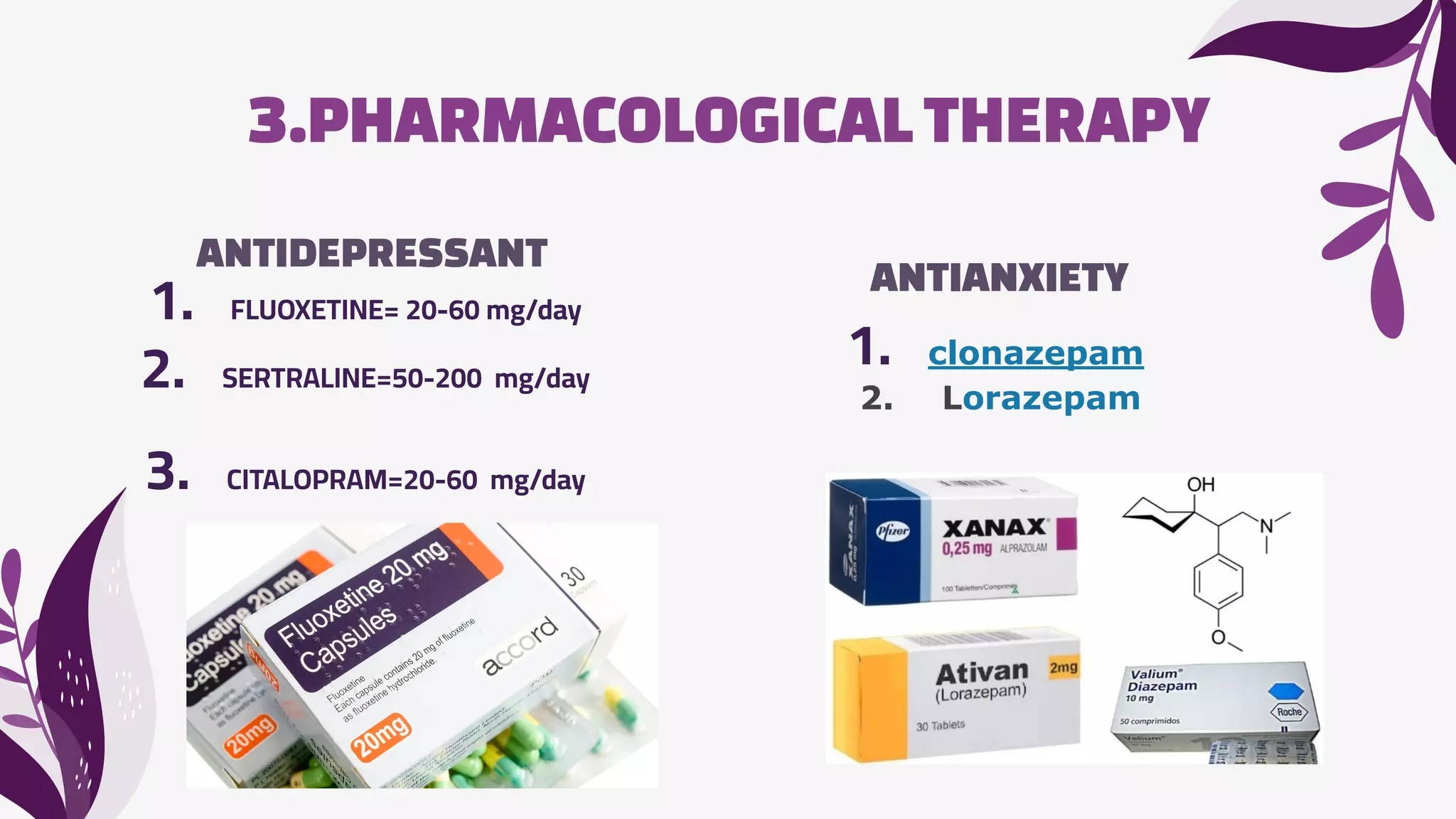
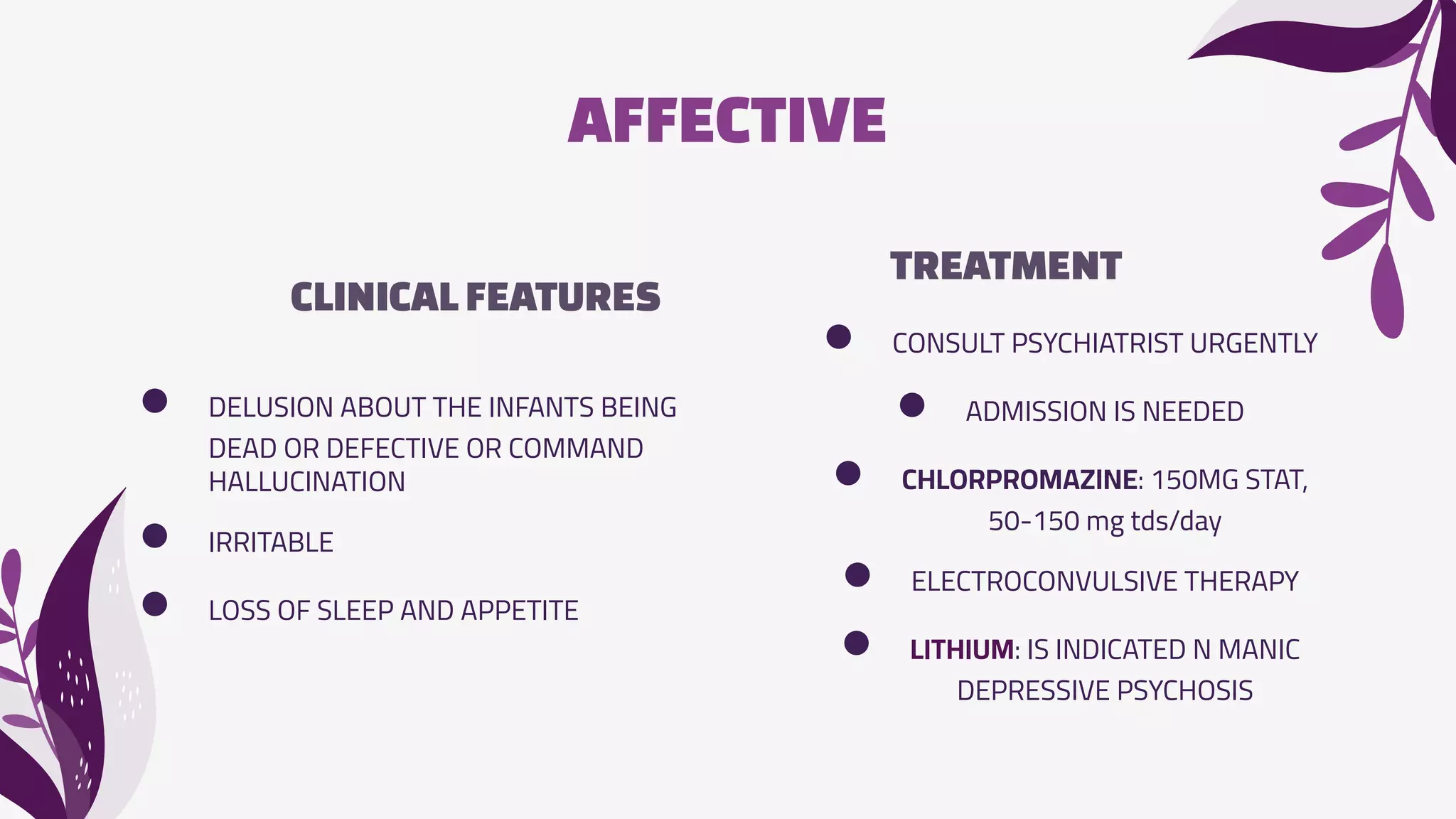
The document discusses psychological complications that can occur during pregnancy, including maternity blues, postpartum depression, and postpartum psychosis. Maternity blues occurs in about 50% of women 4-5 days after delivery and involves mood lability, tearfulness, anxiety, and sleep/appetite disturbances. Postpartum depression occurs in 10-20% of mothers within the first 4-6 months after delivery and is associated with psychiatric, obstetric, and psychosocial risk factors. Postpartum psychosis is a psychiatric emergency that occurs in 1-2% of women and requires hospitalization due to symptoms like delusions, hallucinations, and disorientation. Prevention focuses on identifying at-risk women through