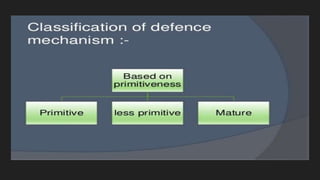
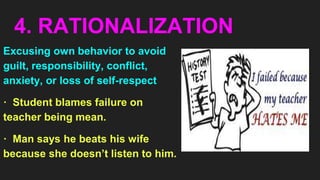
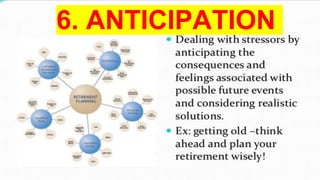
This document provides an overview of defense mechanisms, which are unconscious psychological strategies used to manage anxiety and protect the ego. It categorizes defenses as primitive, less primitive, or mature. Primitive defenses include denial, regression, acting out, dissociation, compartmentalization, projection, and reaction formation. Less primitive defenses involve repression, displacement, intellectualization, rationalization, and undoing. Mature defenses include sublimation, compensation, affiliation, self-assertion, altruism, and anticipation. Examples are given for each defense mechanism.