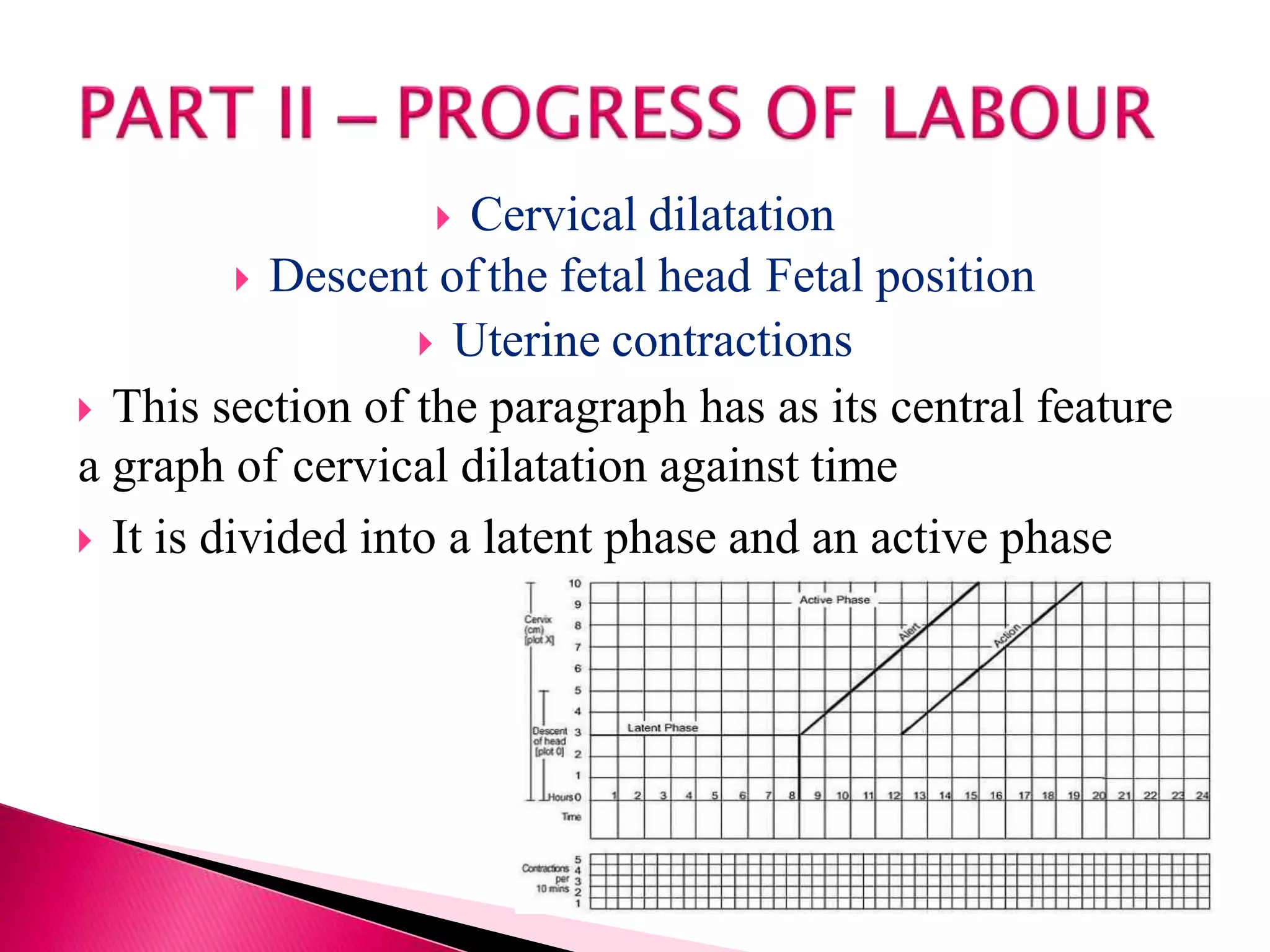
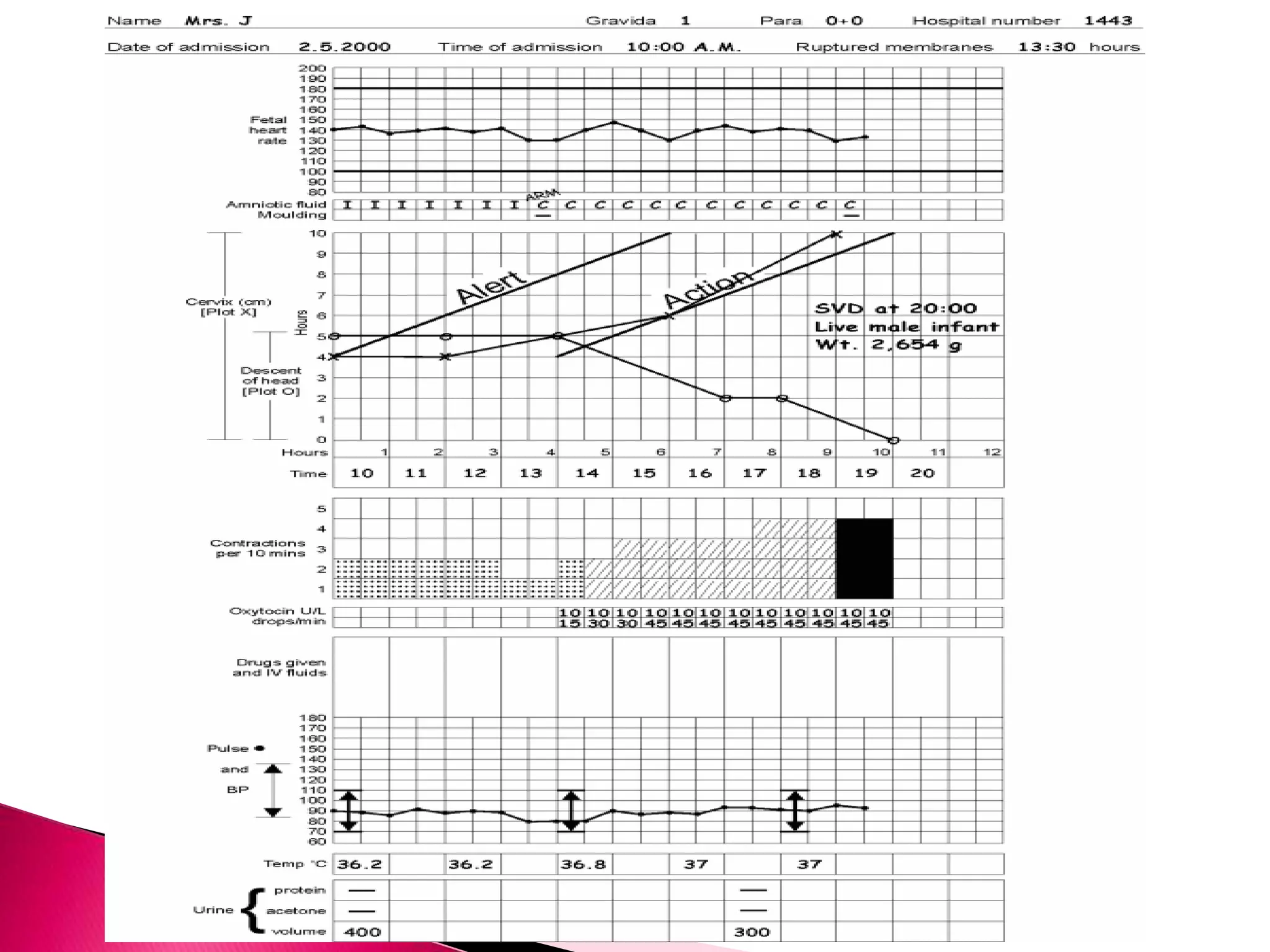
The partograph is a graphical tool used to monitor labor. It records key maternal and fetal data over time on a single sheet. The World Health Organization developed and tested the partograph. It allows early detection of abnormal labor and prevents prolonged labor by recognizing issues like cephalopelvic disproportion before obstructed labor occurs. Using a partograph can reduce complications for both mother and baby by ensuring early intervention when needed.