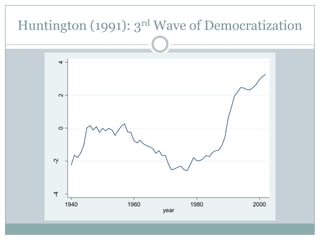
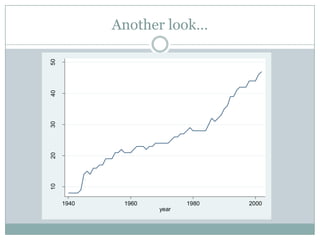
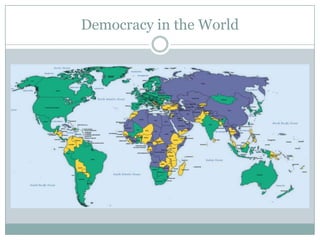
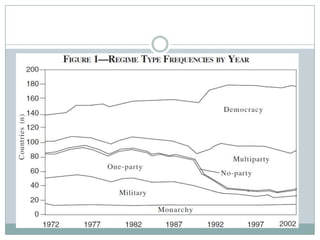
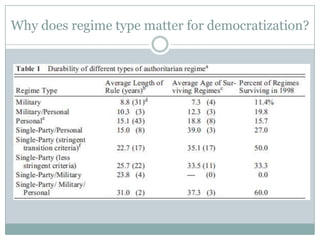
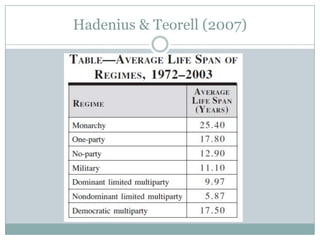
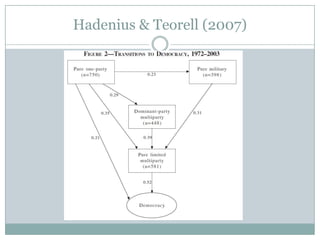
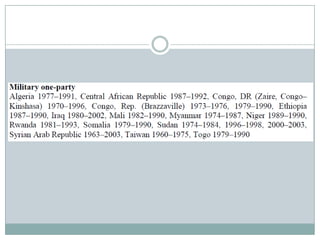
This document discusses democratization and different perspectives on democracy. It examines Geddes' work on democratization after 20 years and definitions of democracy from scholars like Schumpeter focusing on competitive elections and broad participation. Trends are discussed like wealthier countries being more democratic and economic crises increasing breakdowns. The document also explores the variety of authoritarian regimes, limited multi-party systems as stepping stones to democracy, and why the regime type matters for democratization processes according to studies like Hadenius and Teorell from 2007.