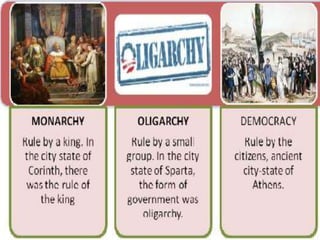
Democracy first emerged in ancient Greek city-states like Athens in 508 BC, where male citizens voted directly on laws. Modern democracy began taking shape in the 17th-18th centuries through events like the English Glorious Revolution, which established the rule of law, and the French Revolution, which overthrew the monarchy and declared liberty and equality for all. Today, a country is considered democratic if it holds free and fair elections, protects civil liberties, and enforces the rule of law.