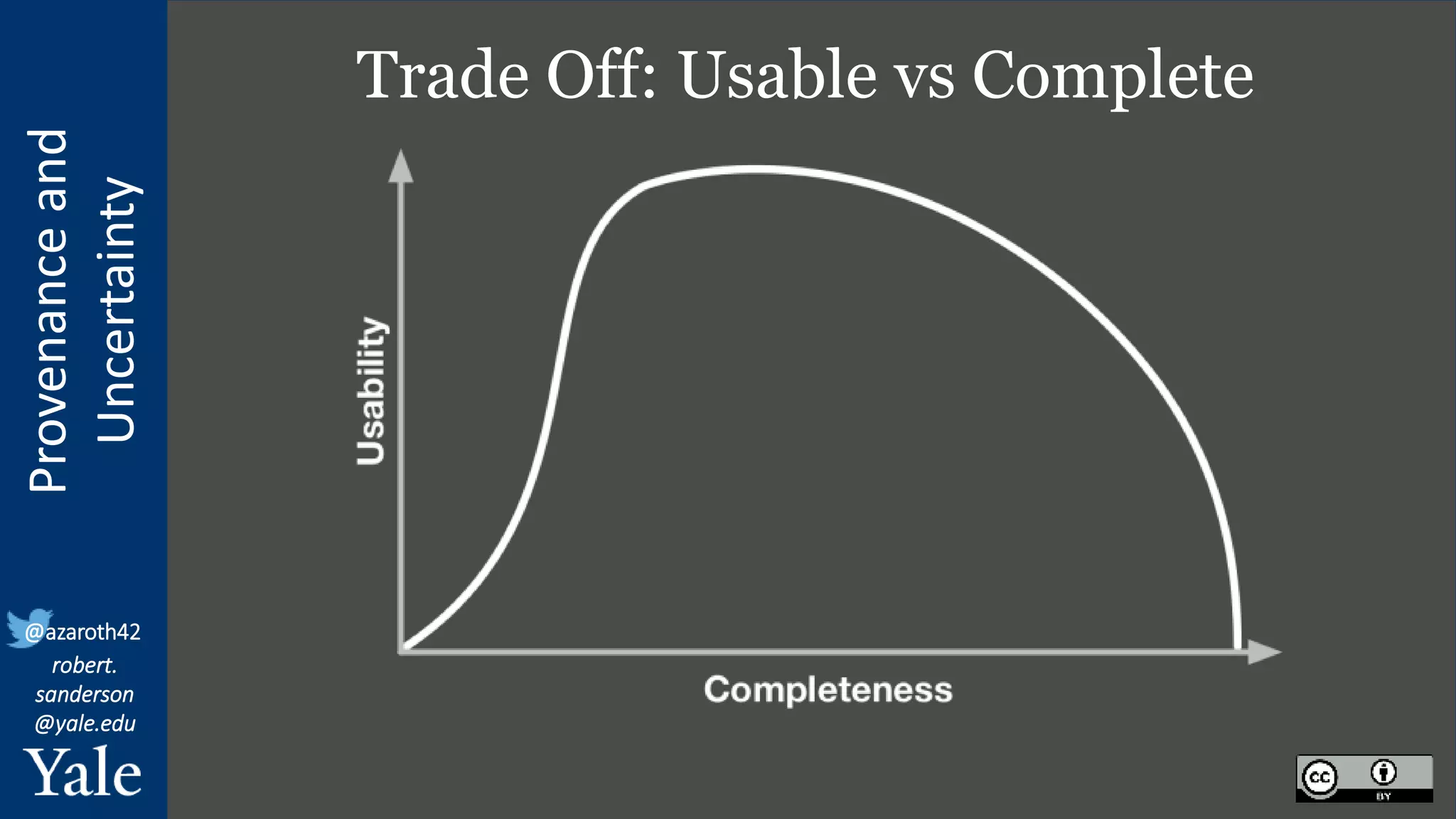
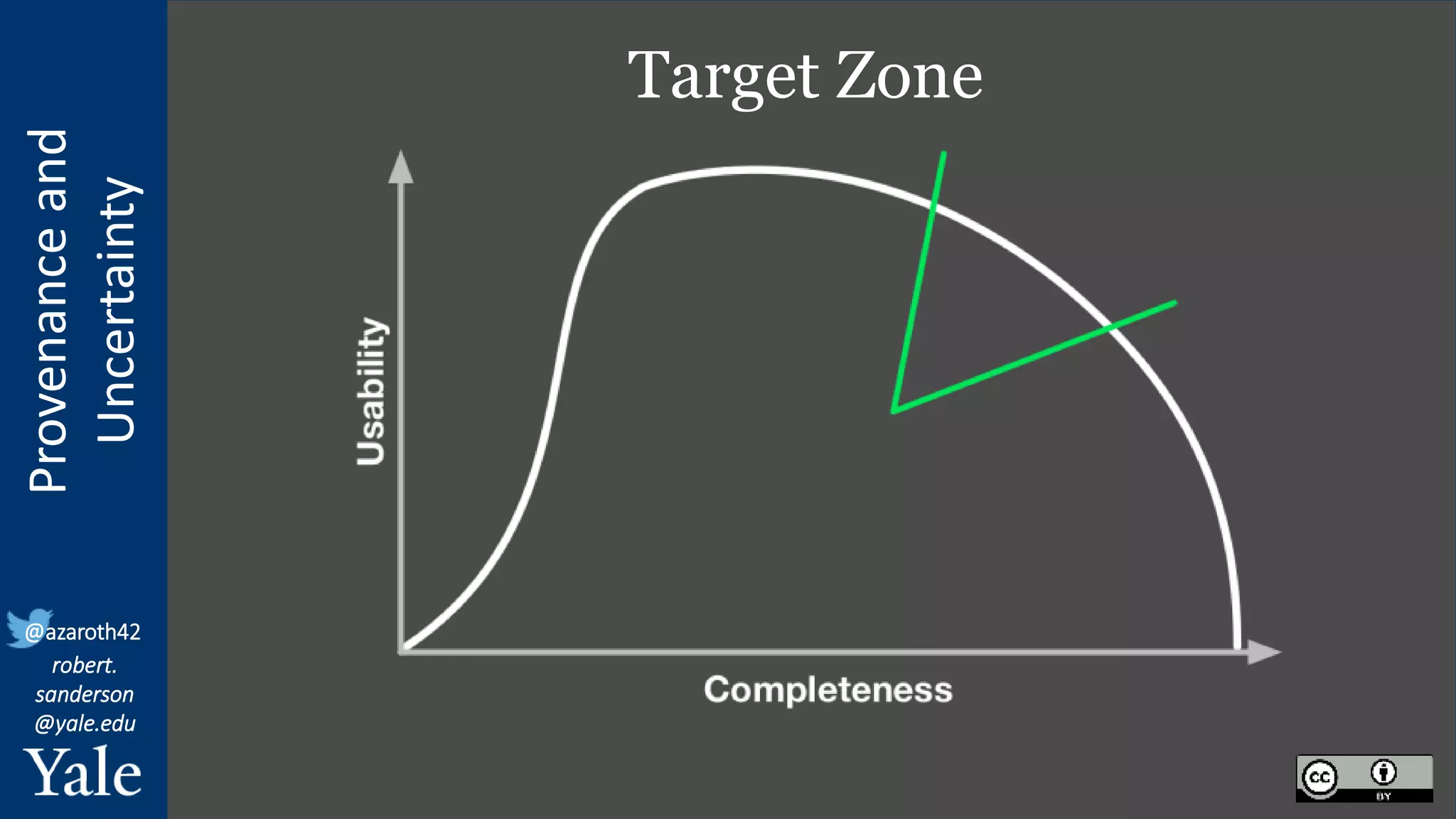
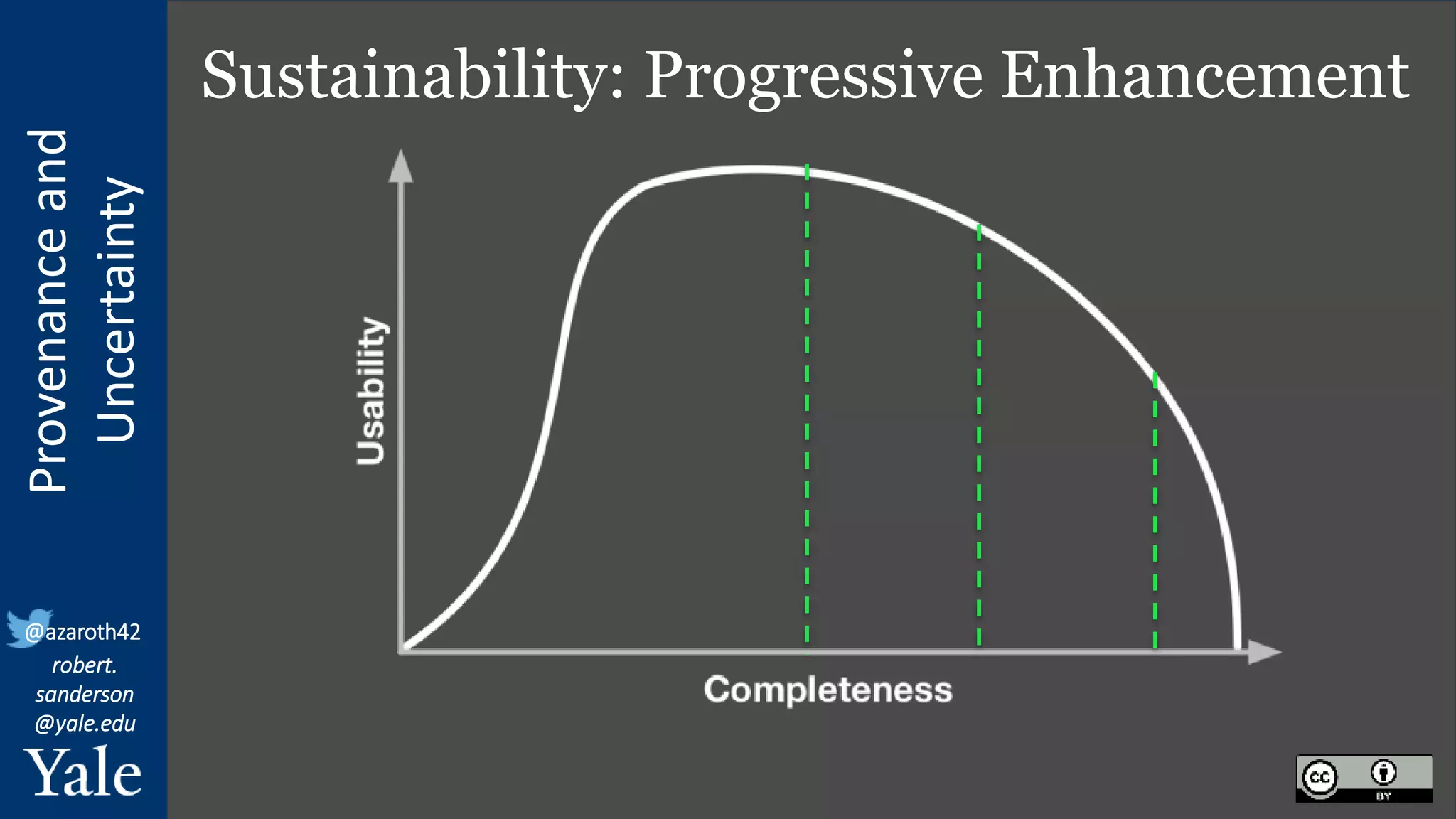
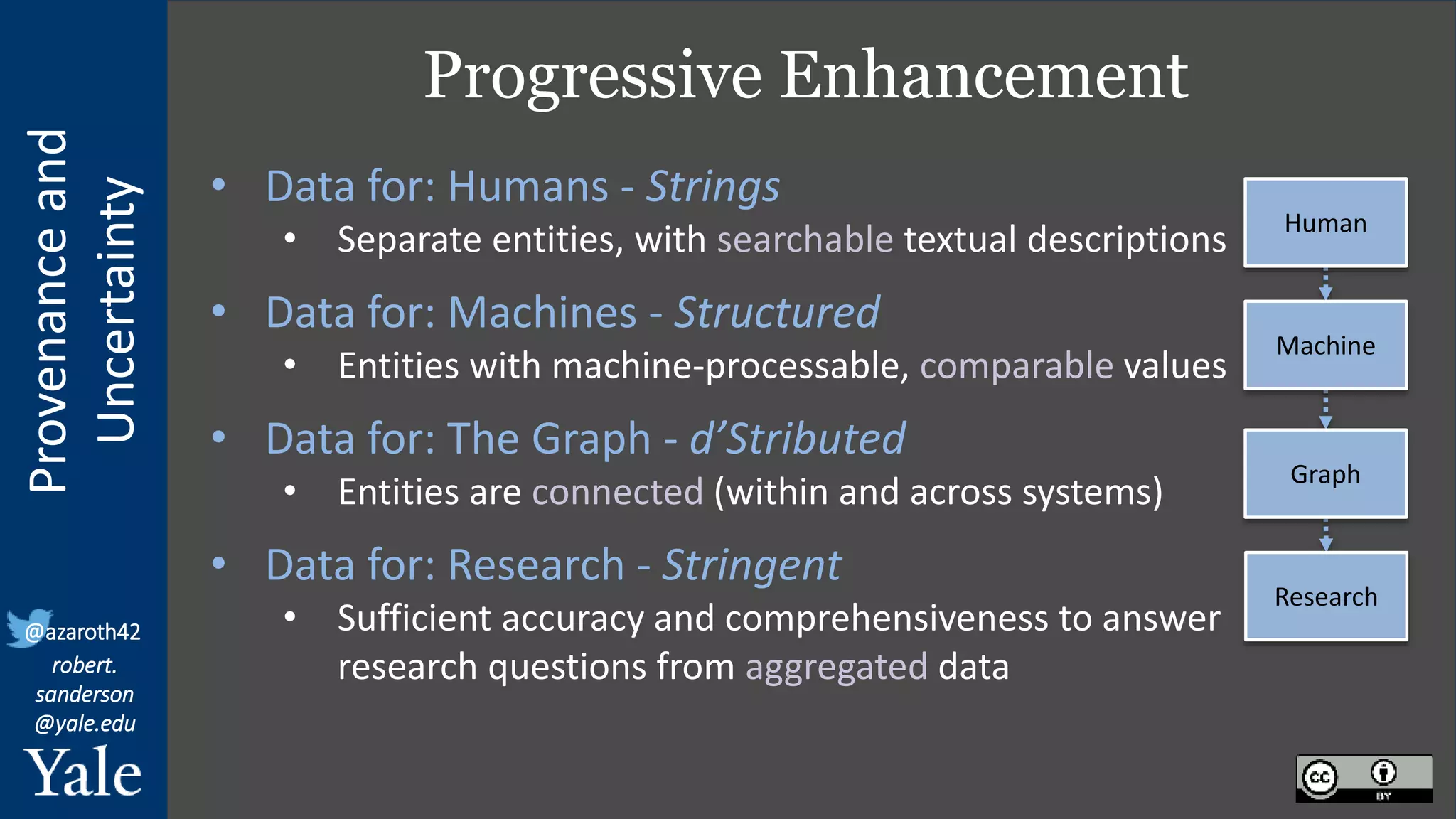
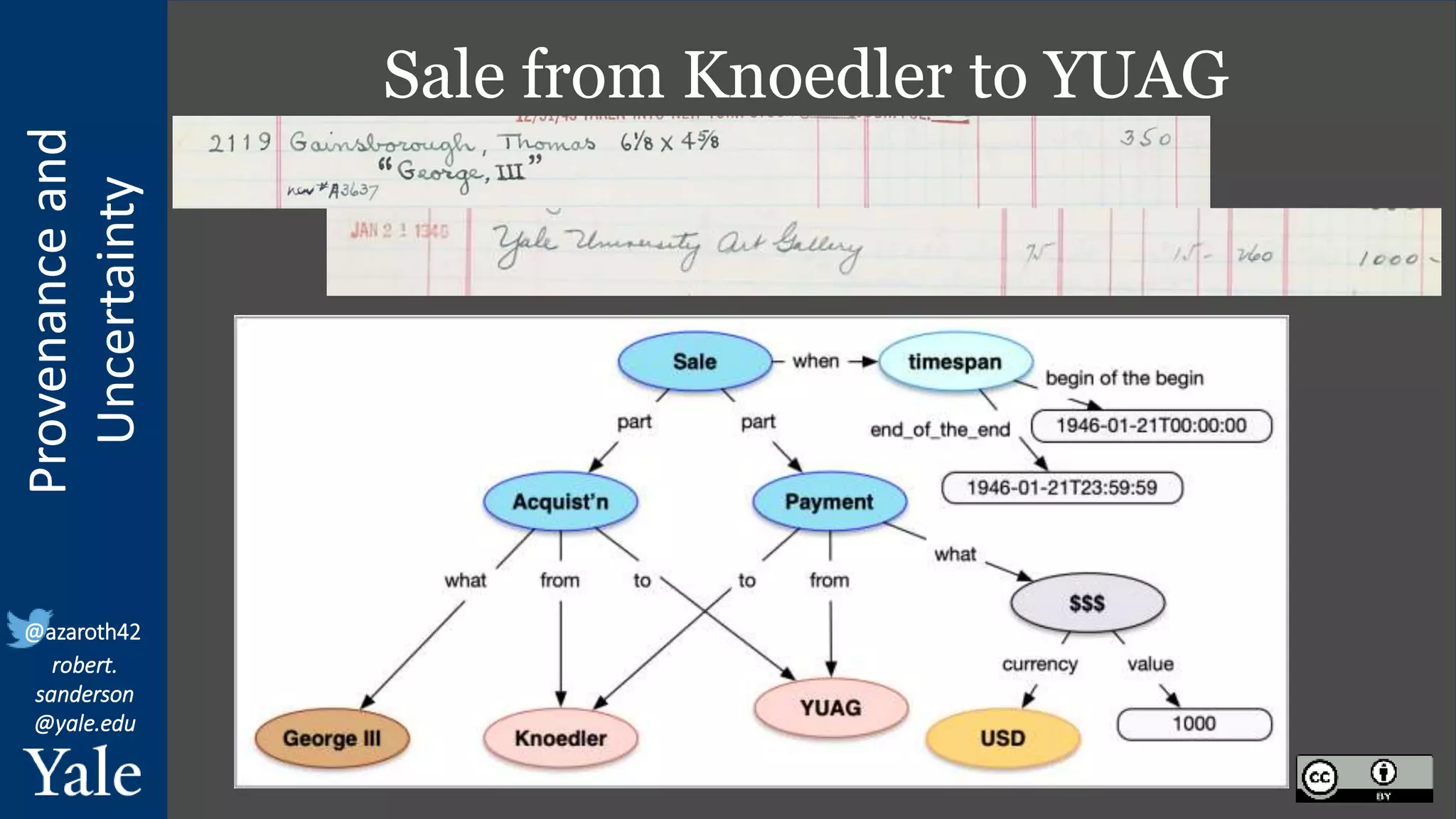
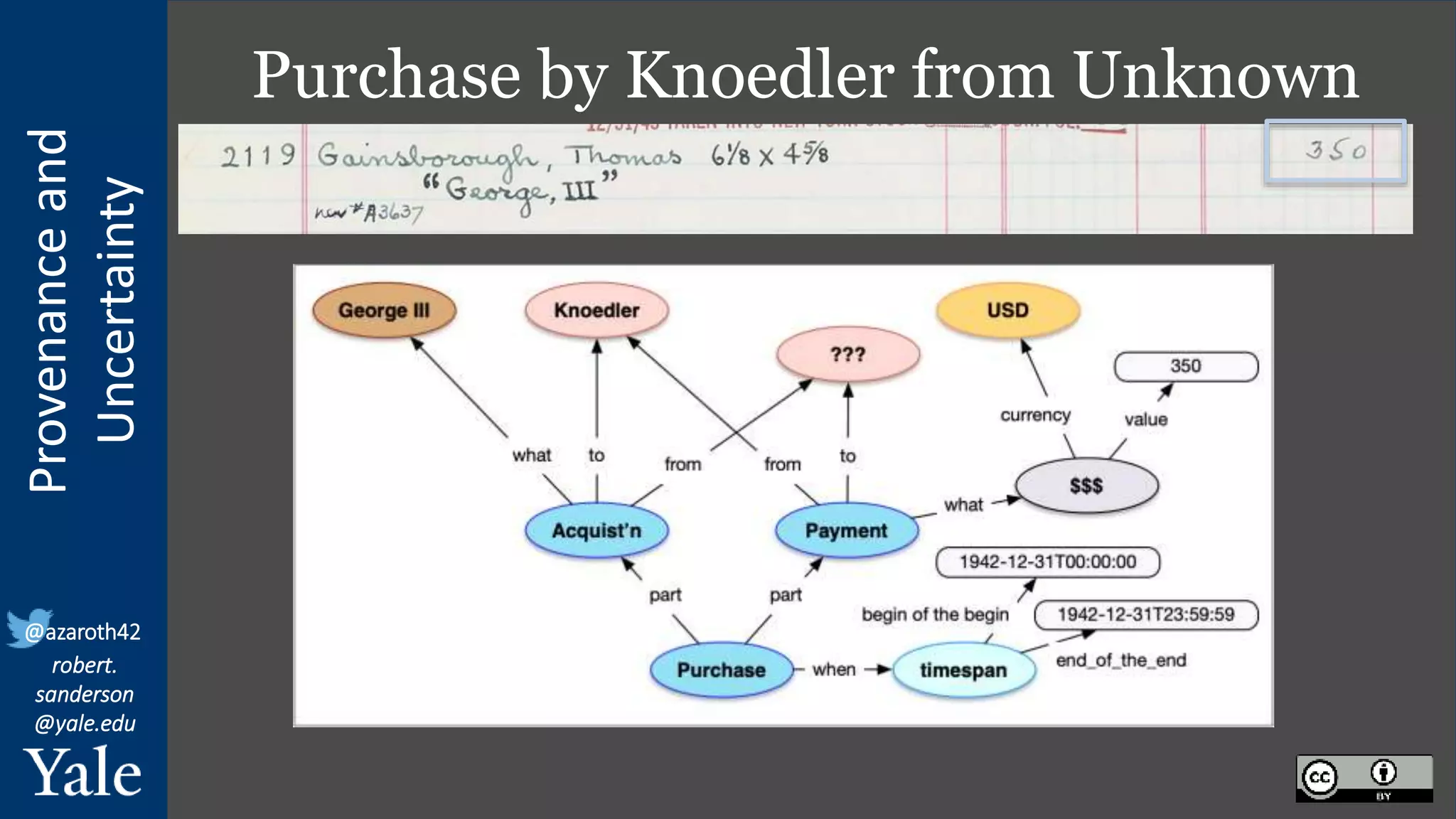
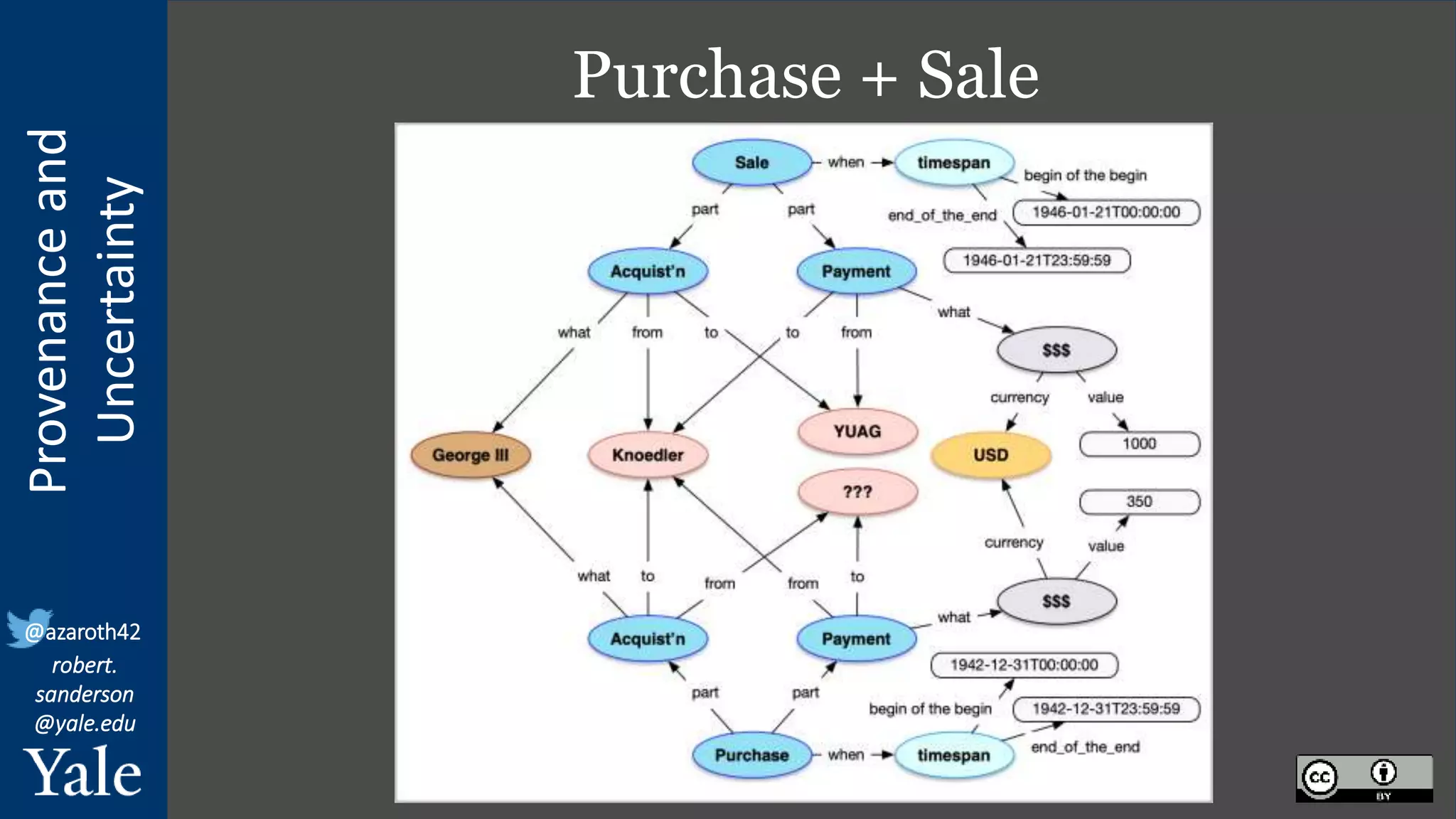
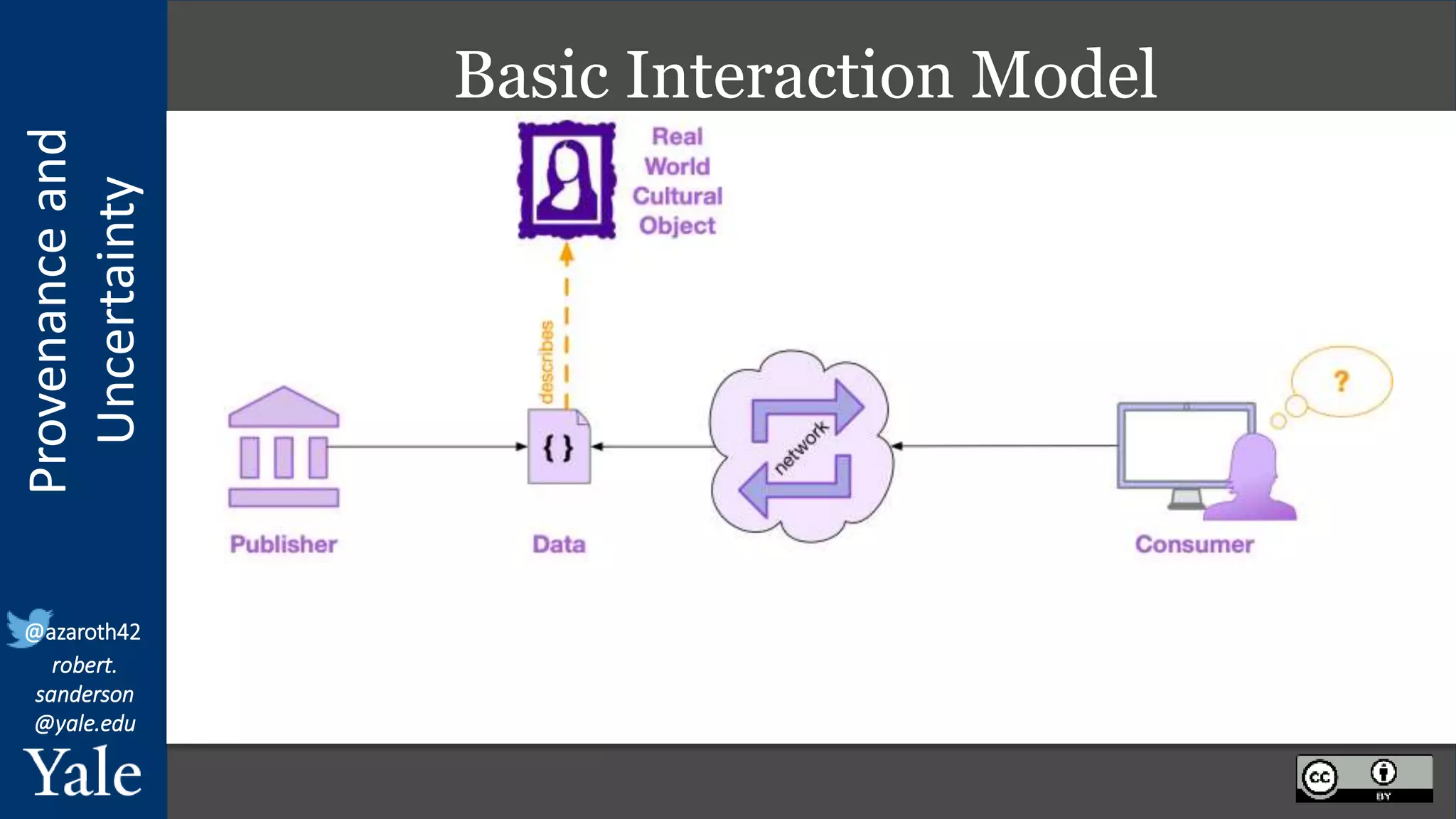
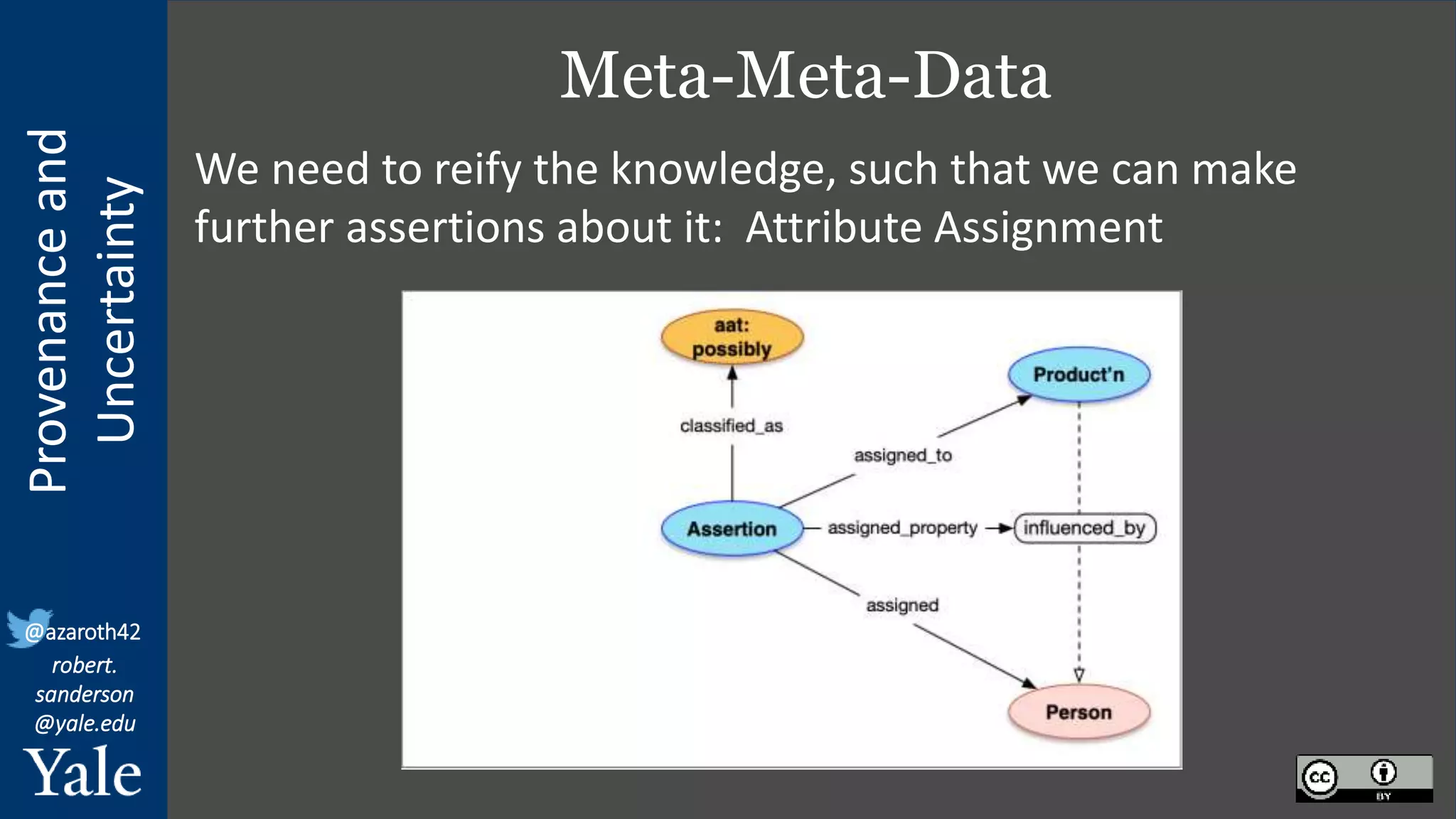
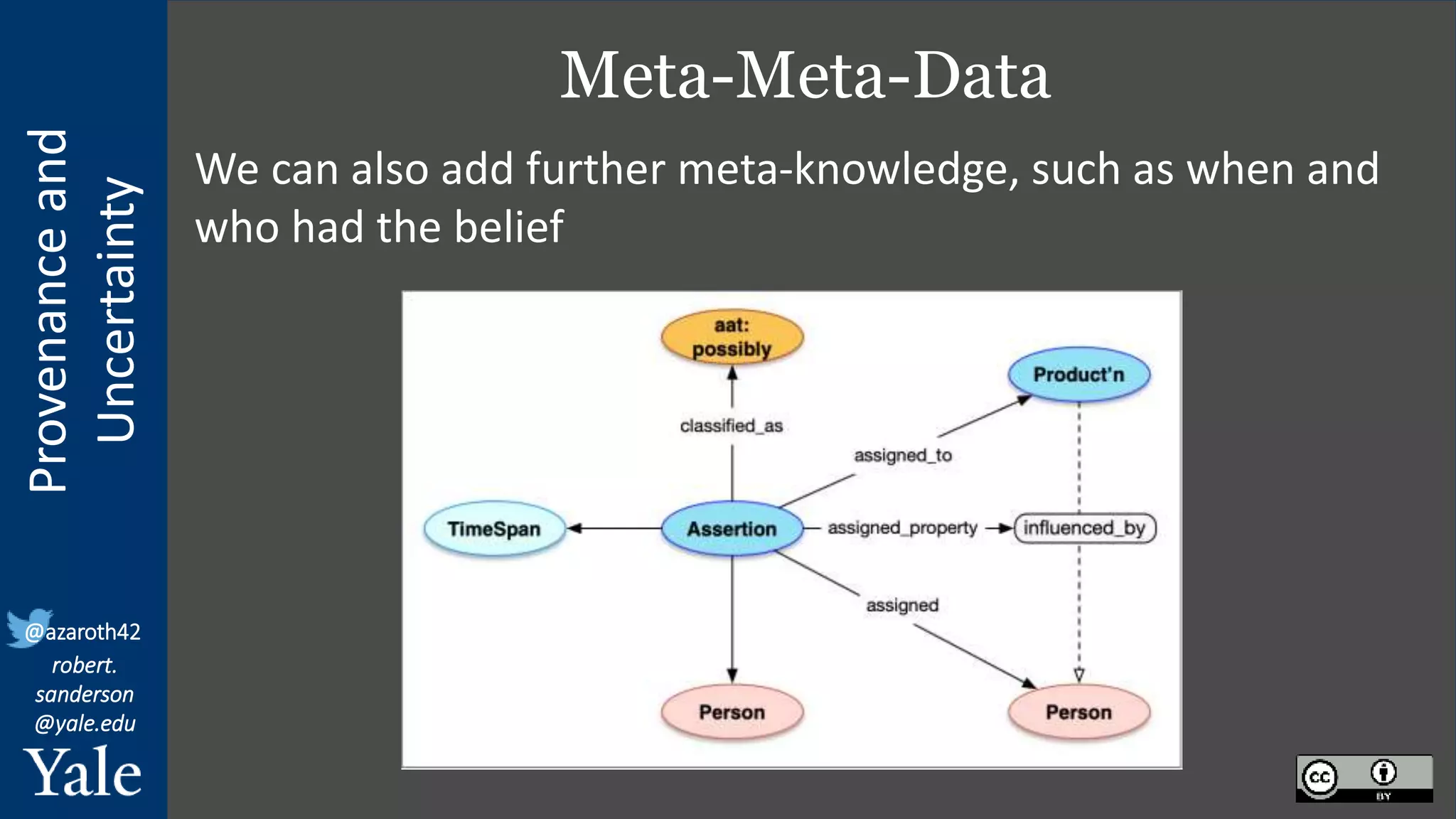
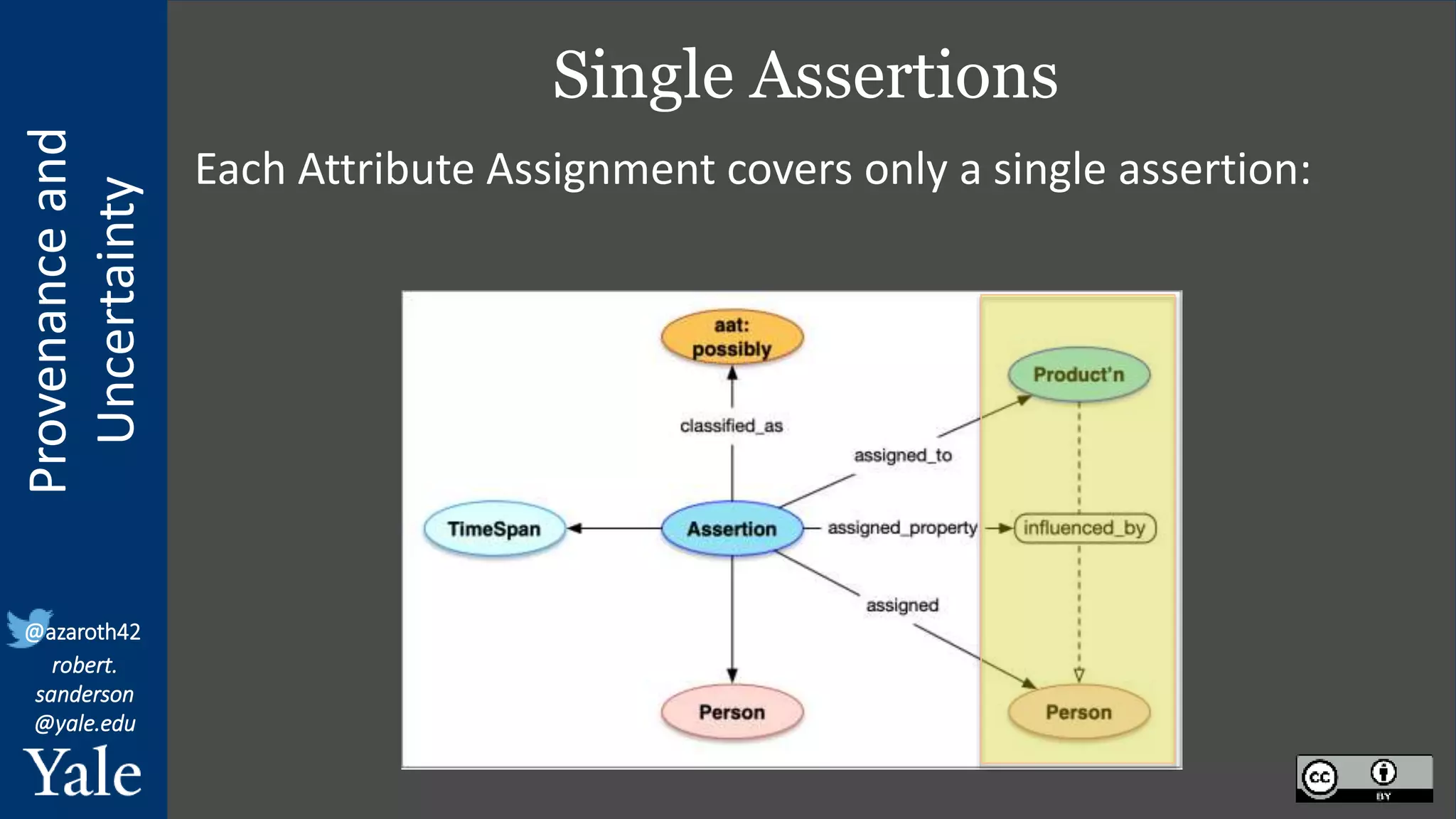
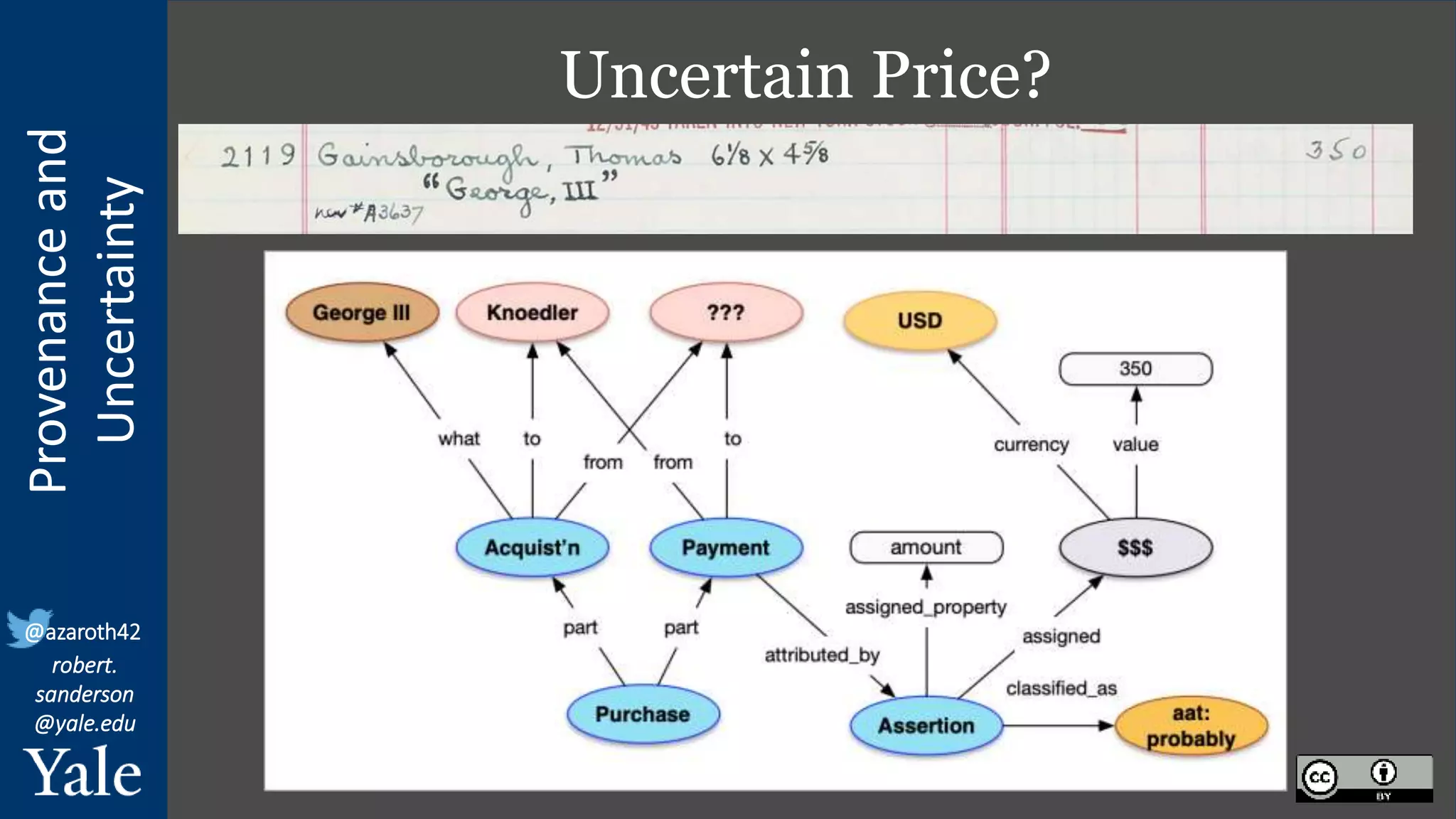
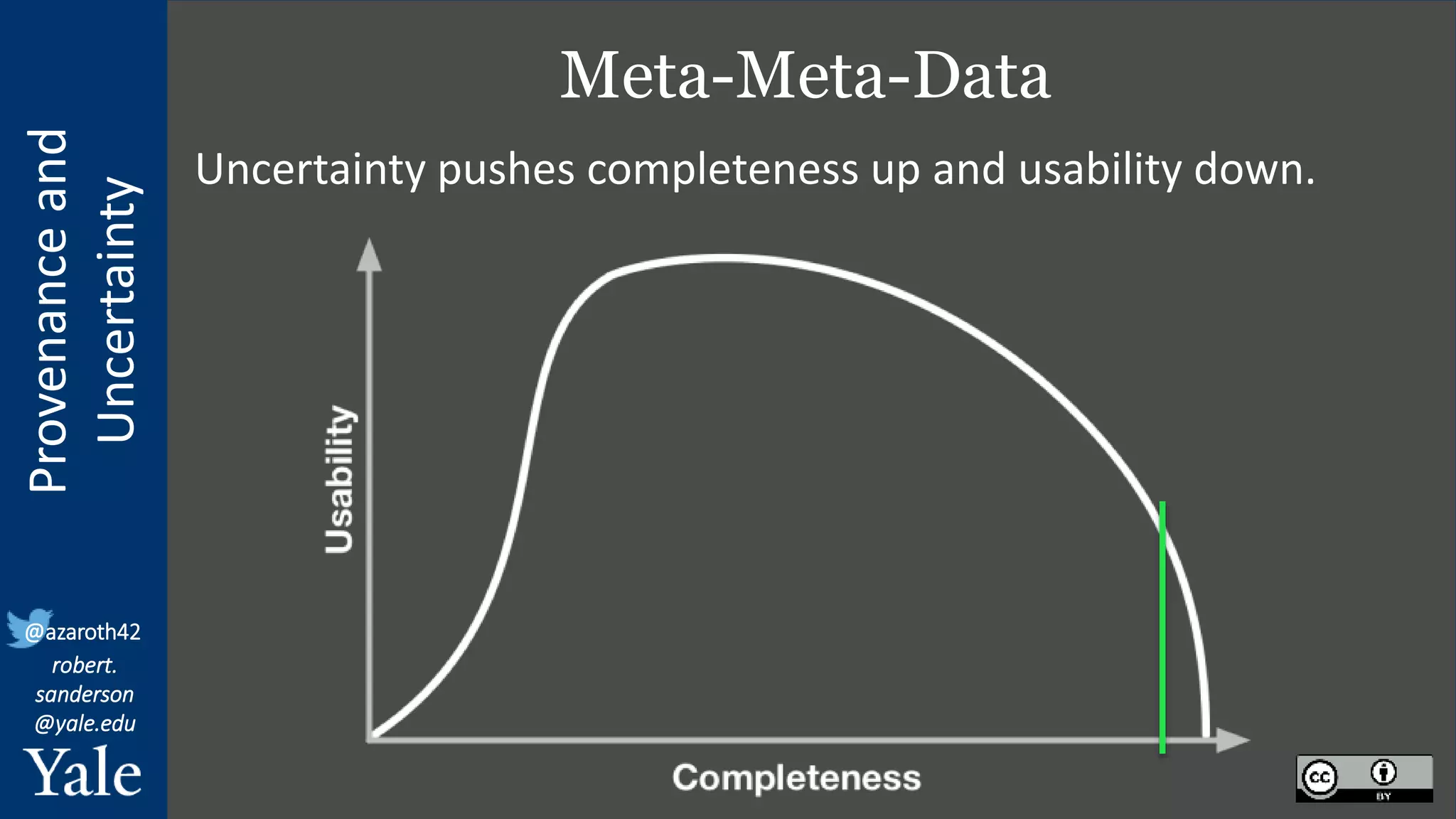
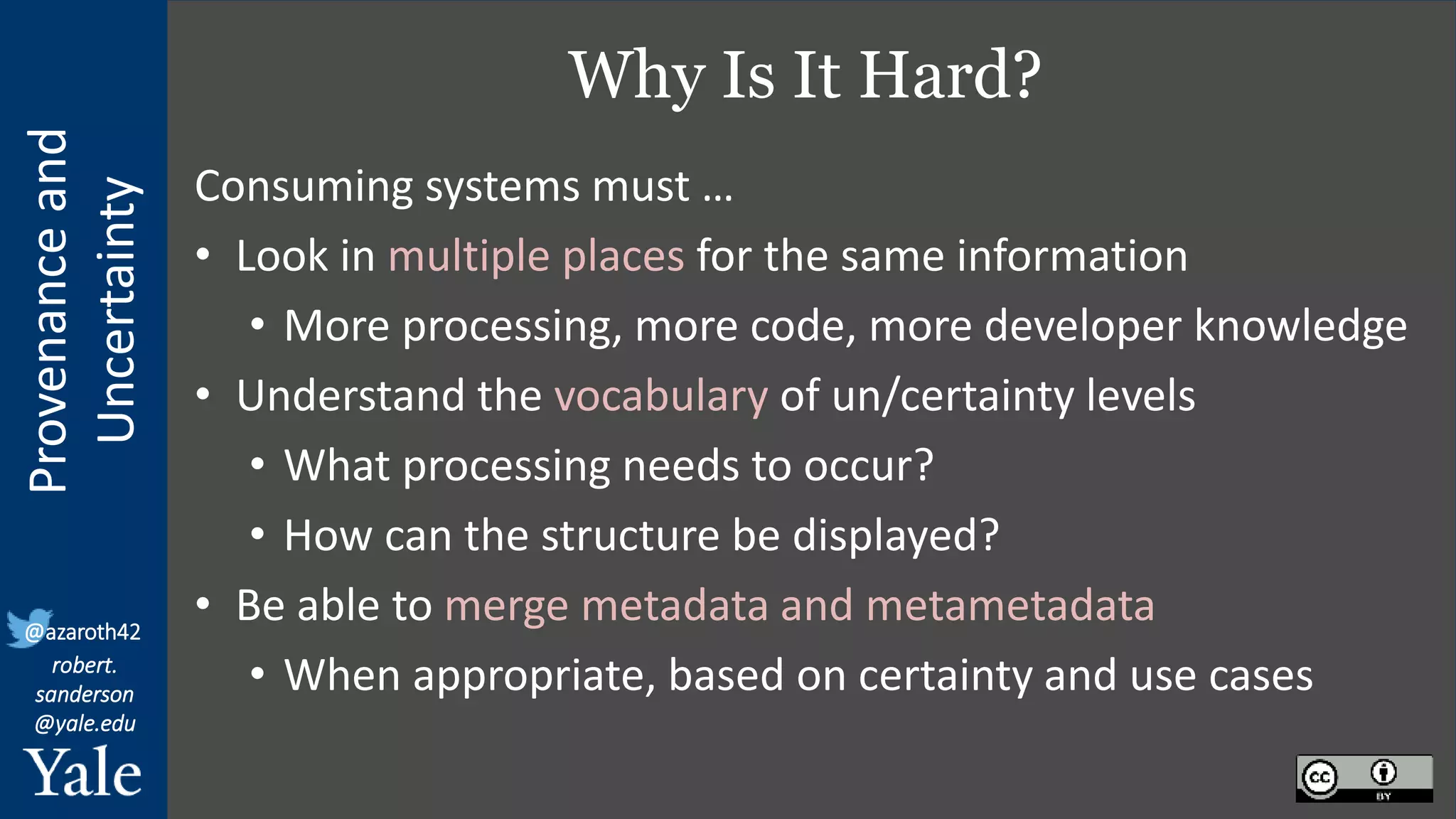
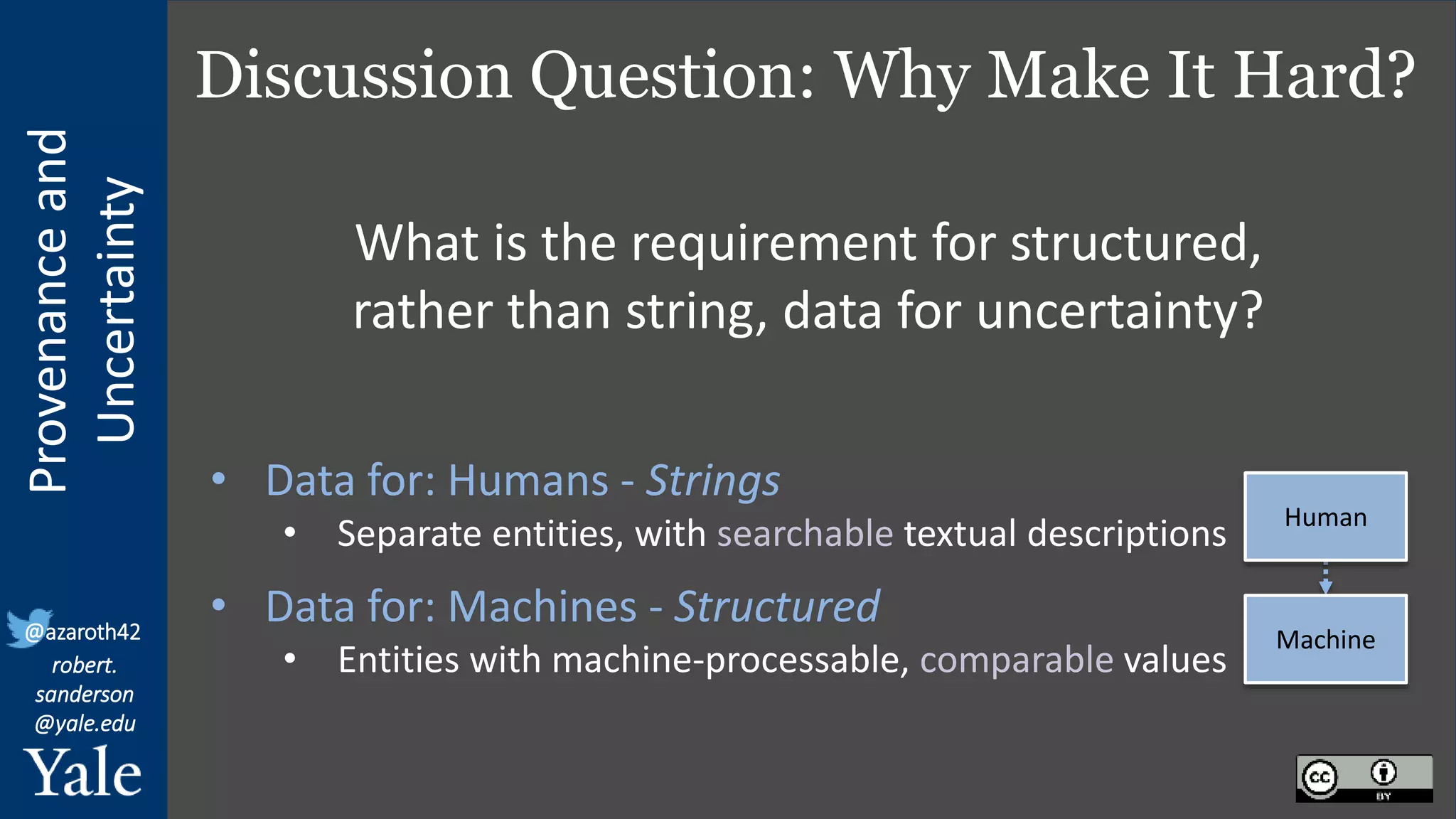
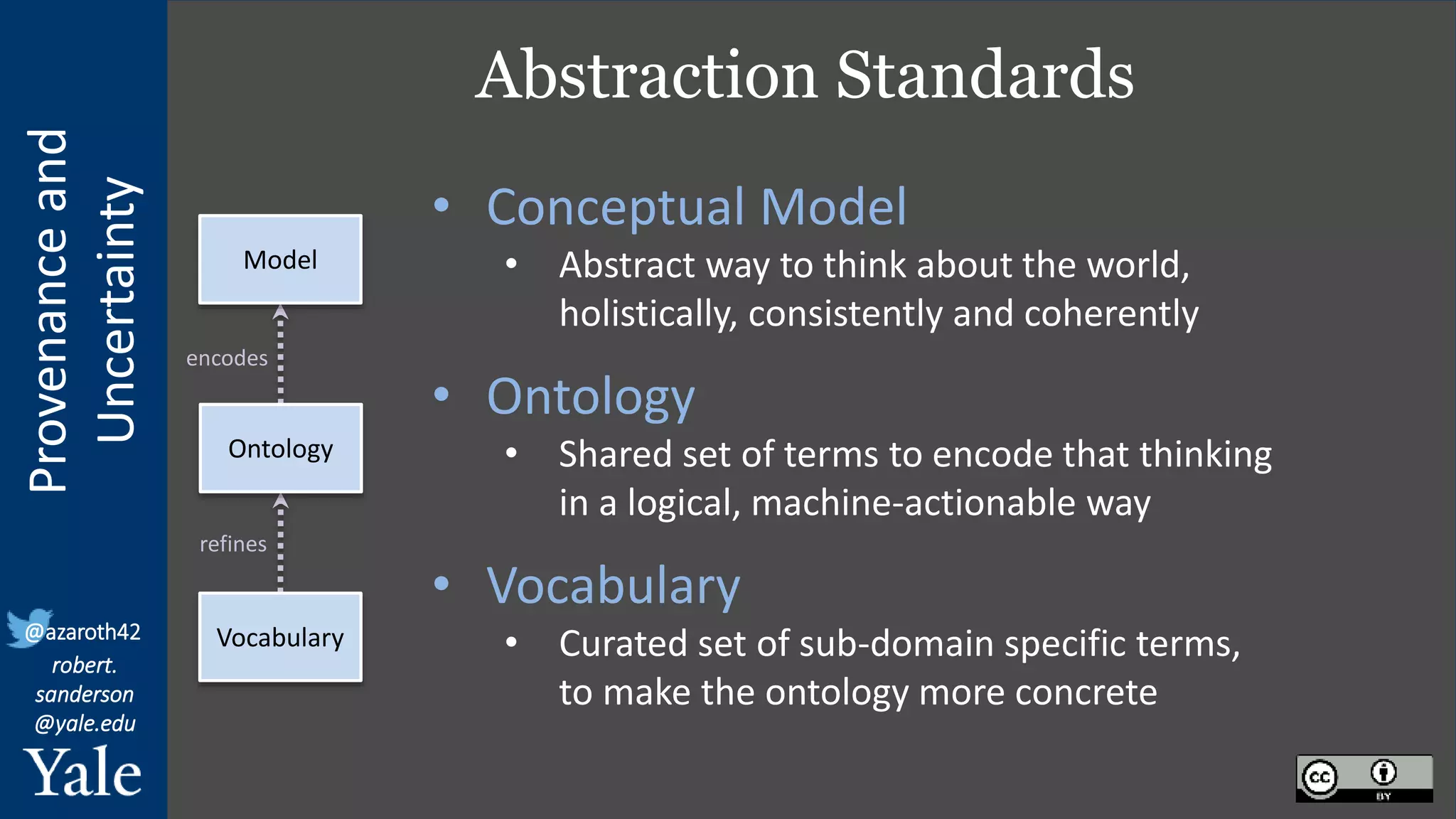
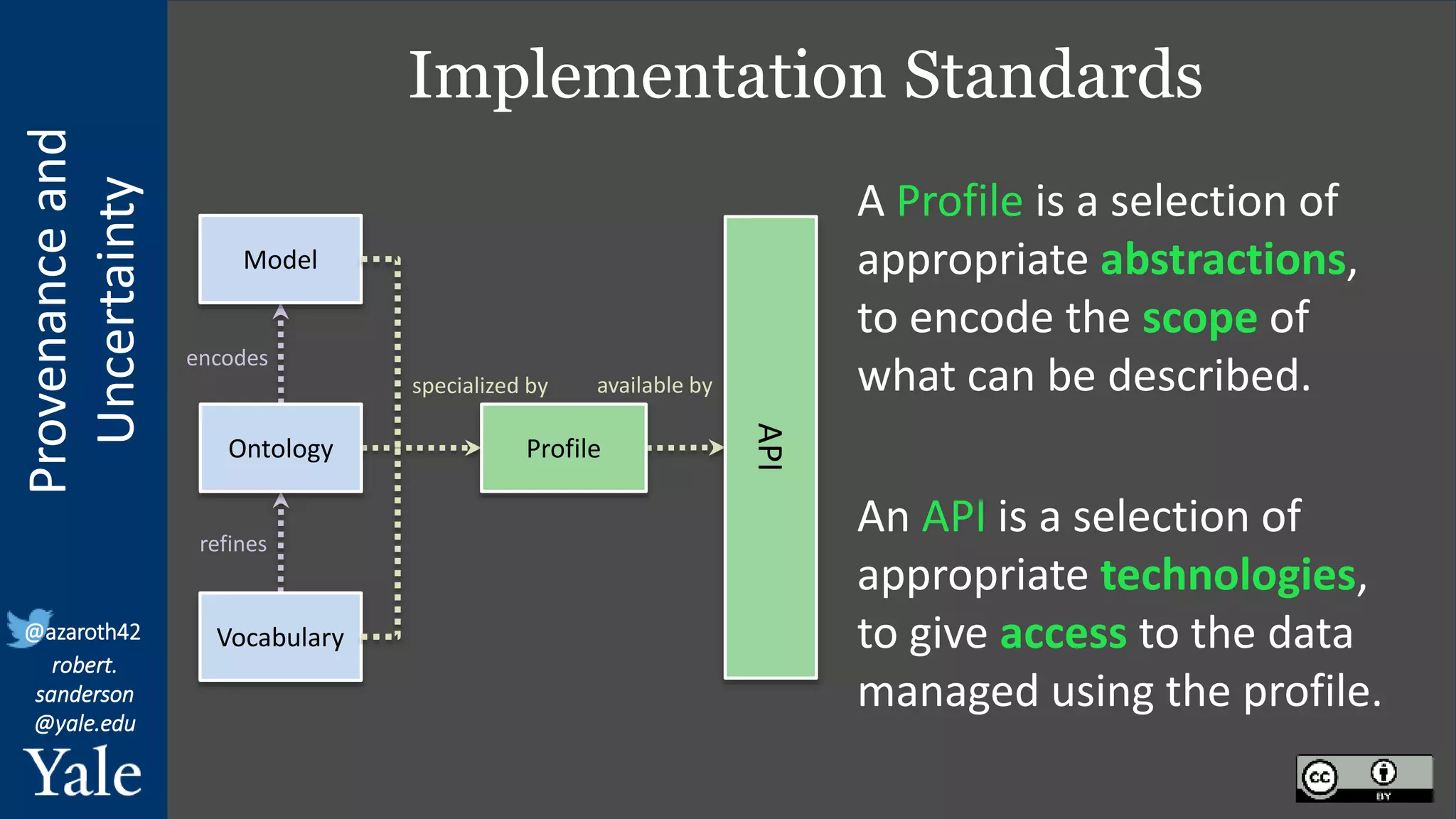
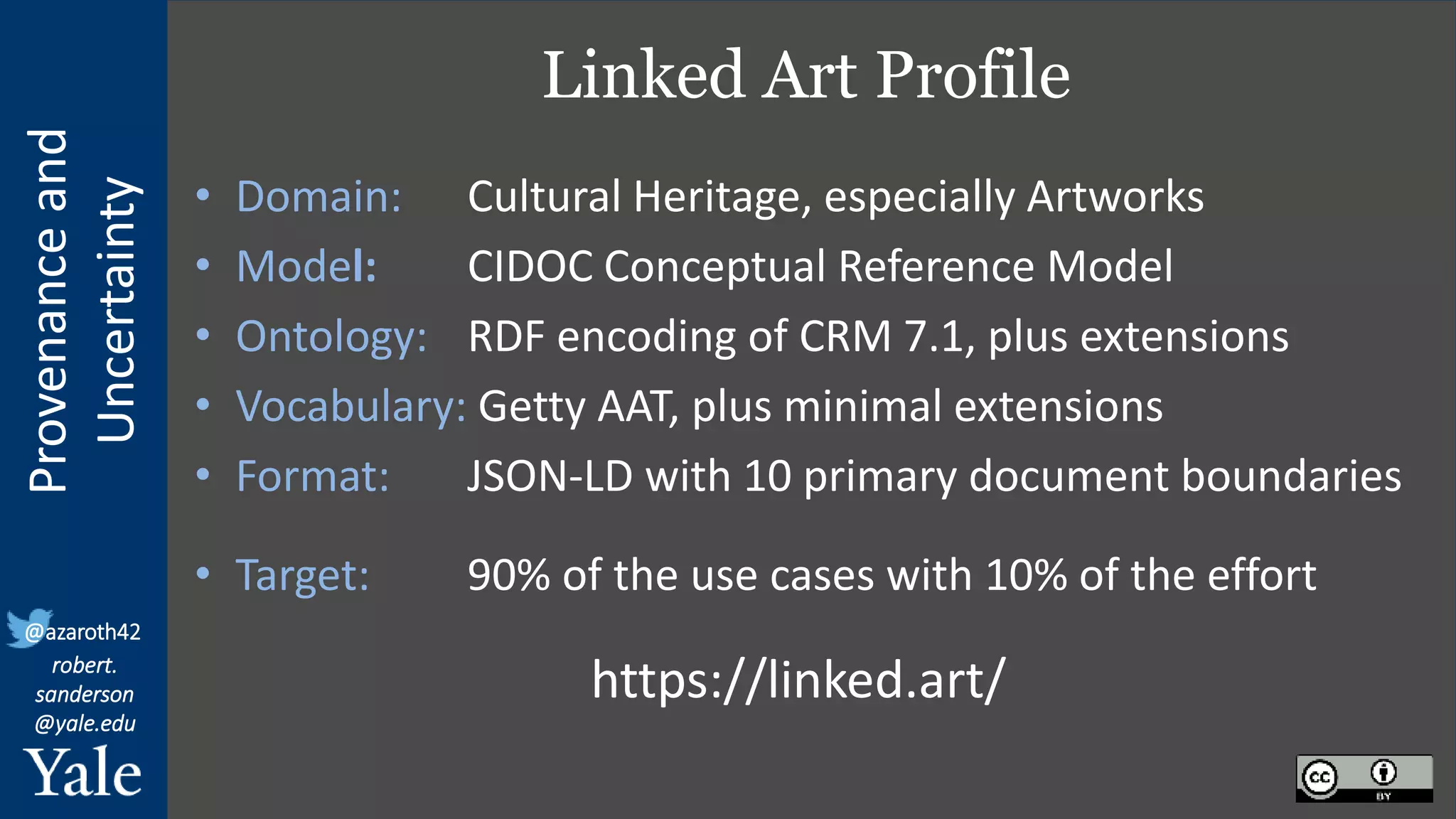
The document discusses the importance of provenance and uncertainty in cultural heritage metadata, emphasizing the need for standards to ensure data is findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable. It outlines a linked art profile that focuses on usability and describes various use cases related to ownership, custody, and the complexities of data accuracy and certainty. The text highlights the challenges in providing clear data due to varying levels of certainty and the need for structured data for both human and machine usability.


![Provenance
and
Uncertainty
@azaroth42
robert.
sanderson
@yale.edu
What is Data Usability?
… usability is the degree to which [a thing]
can be used by specified consumers to
achieve [their] quantified objectives with
effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction
in a quantified context of use.
who
what
how
where
Usability is dependent on the Audience
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/usability
“ ”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/linked-art-uncertainty-220630130501-7910ffca/75/Provenance-and-Uncertainty-in-Linked-Art-6-2048.jpg)