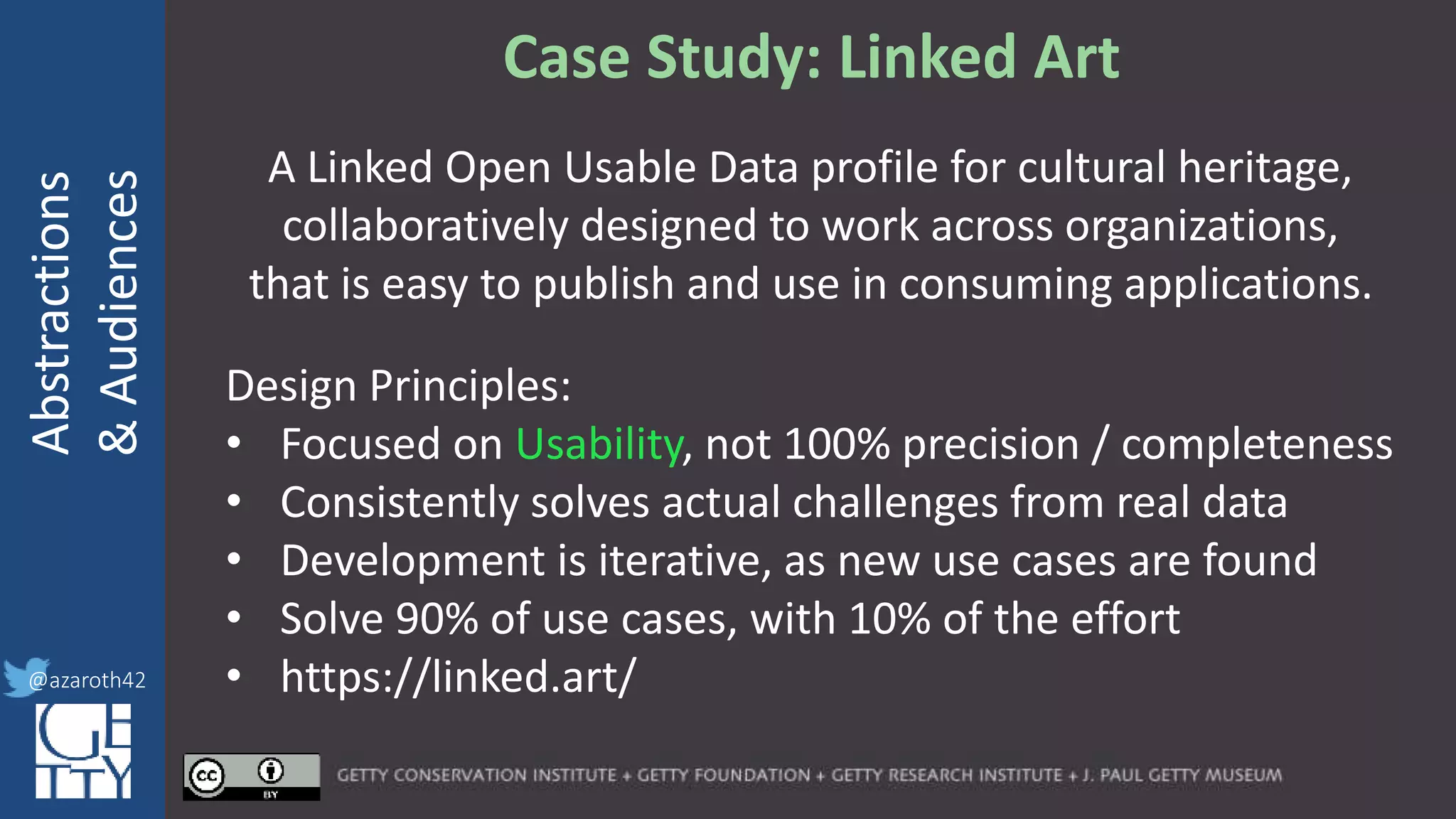
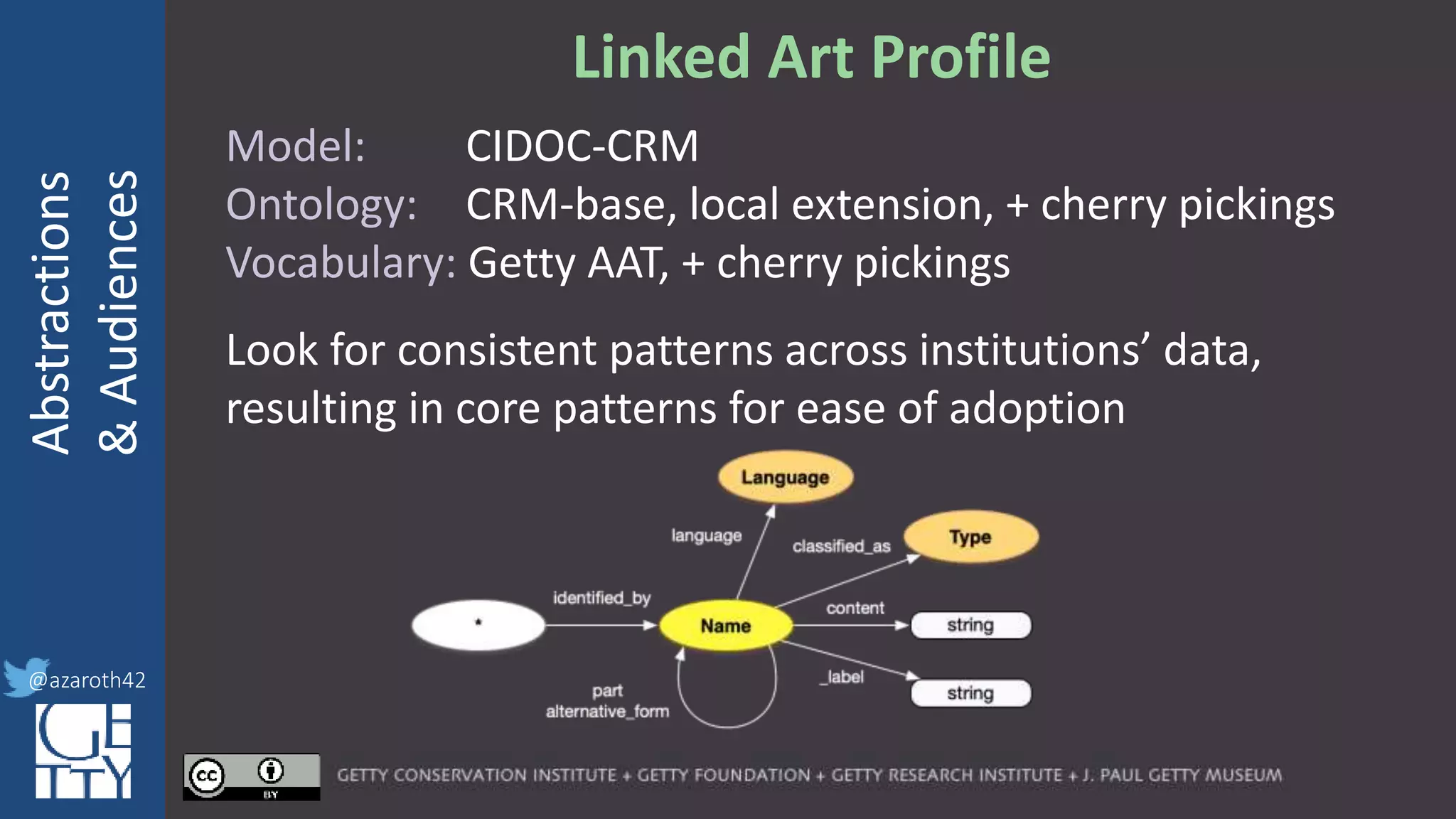
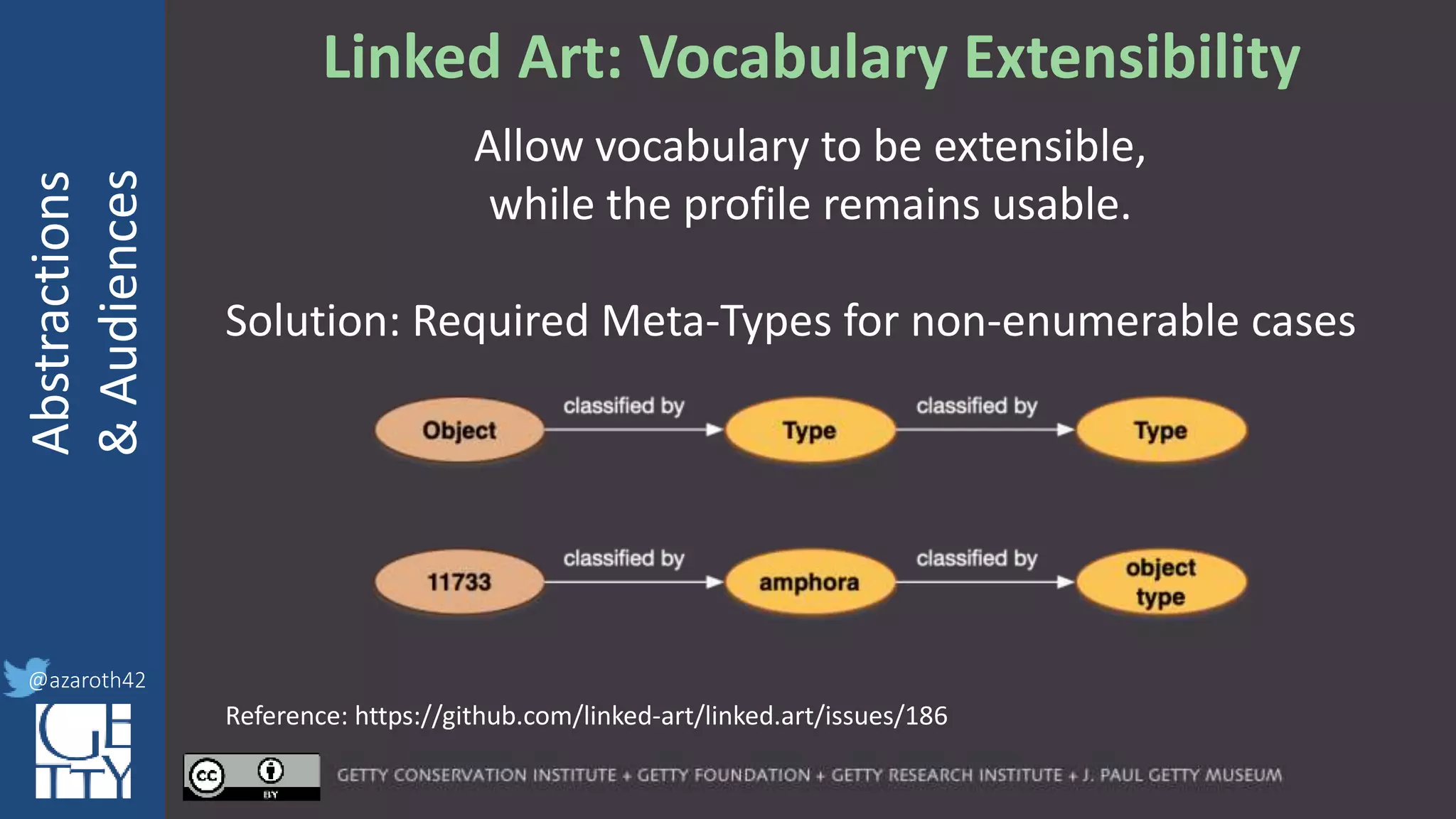
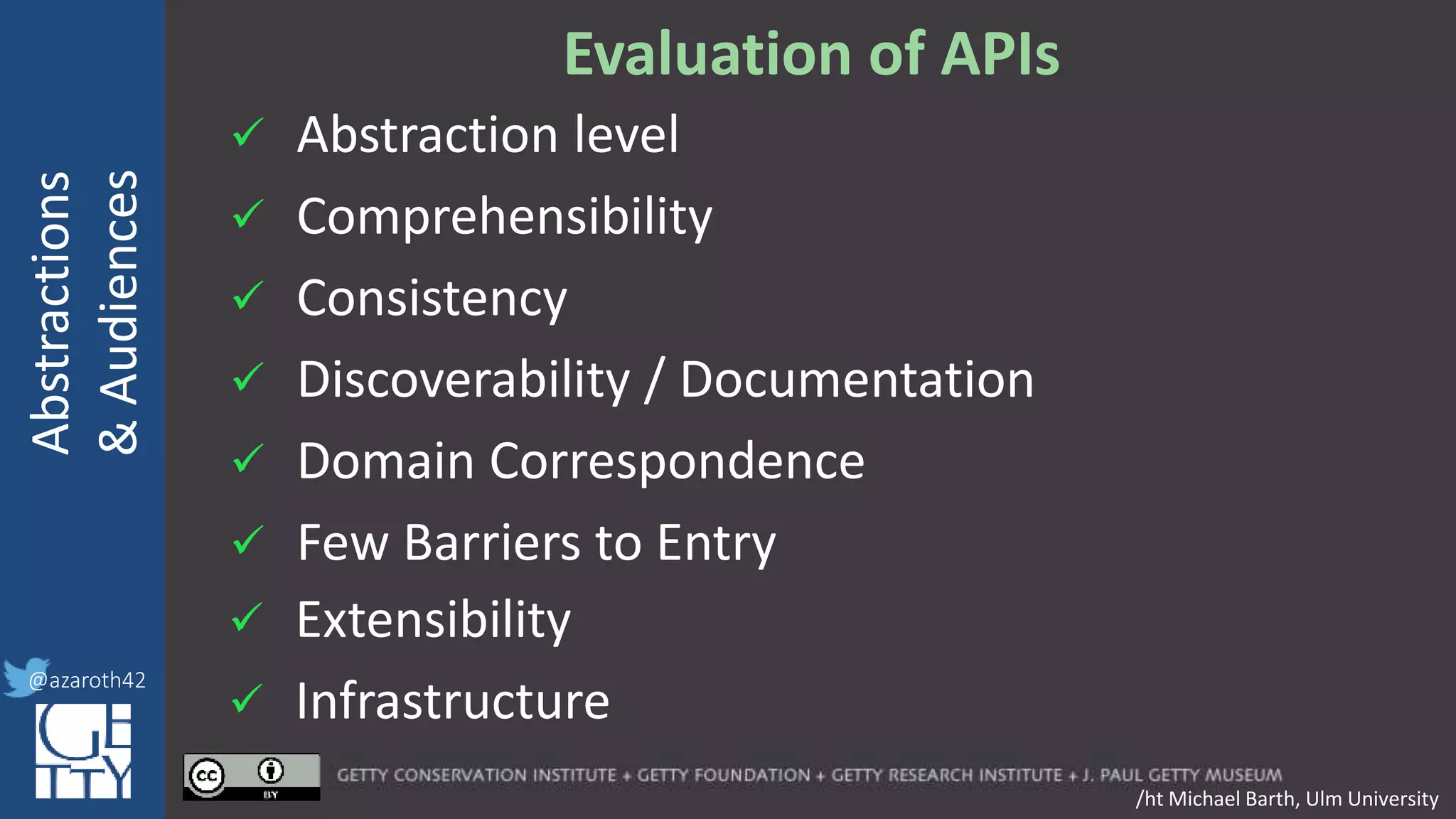
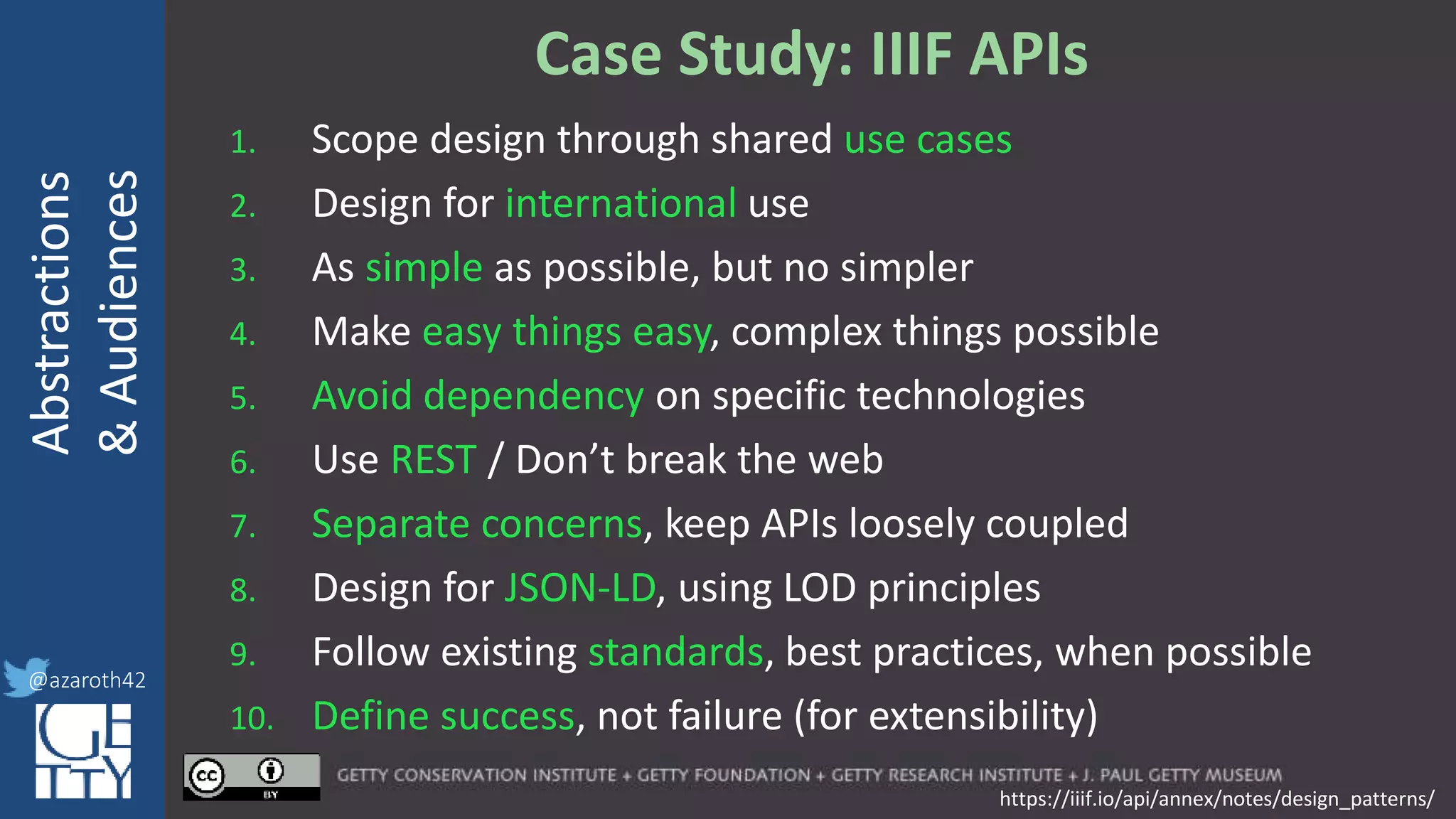
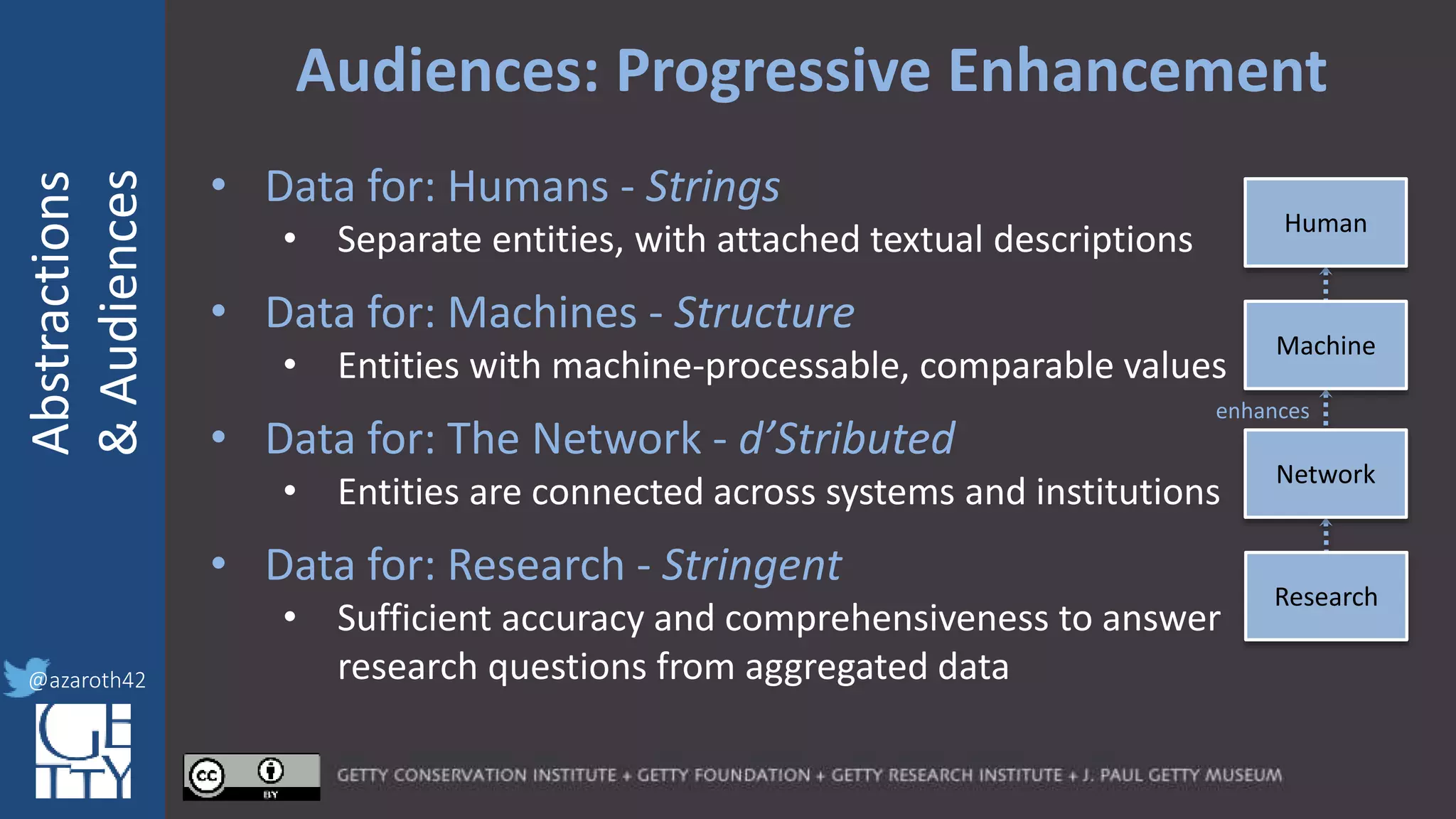
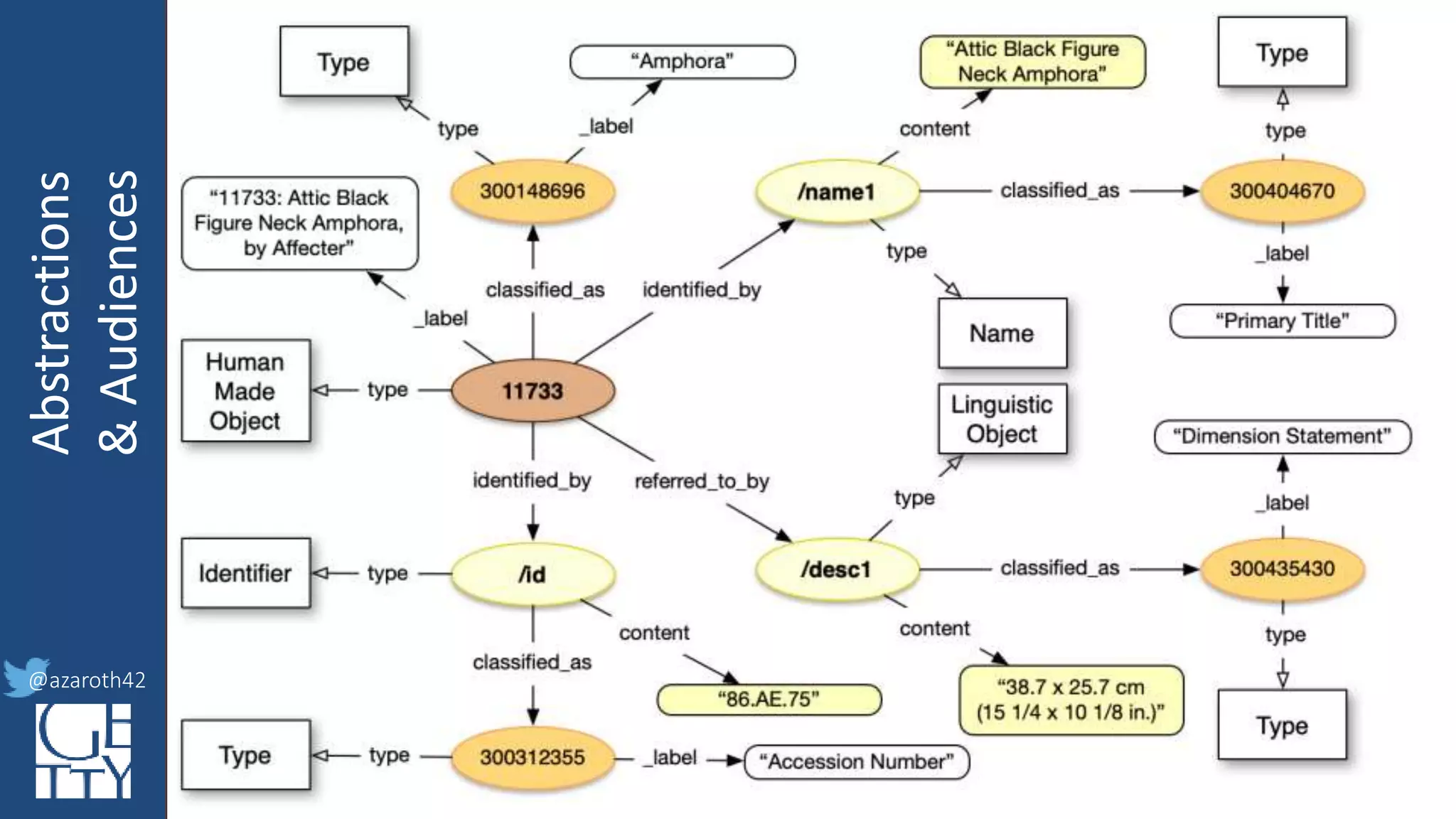
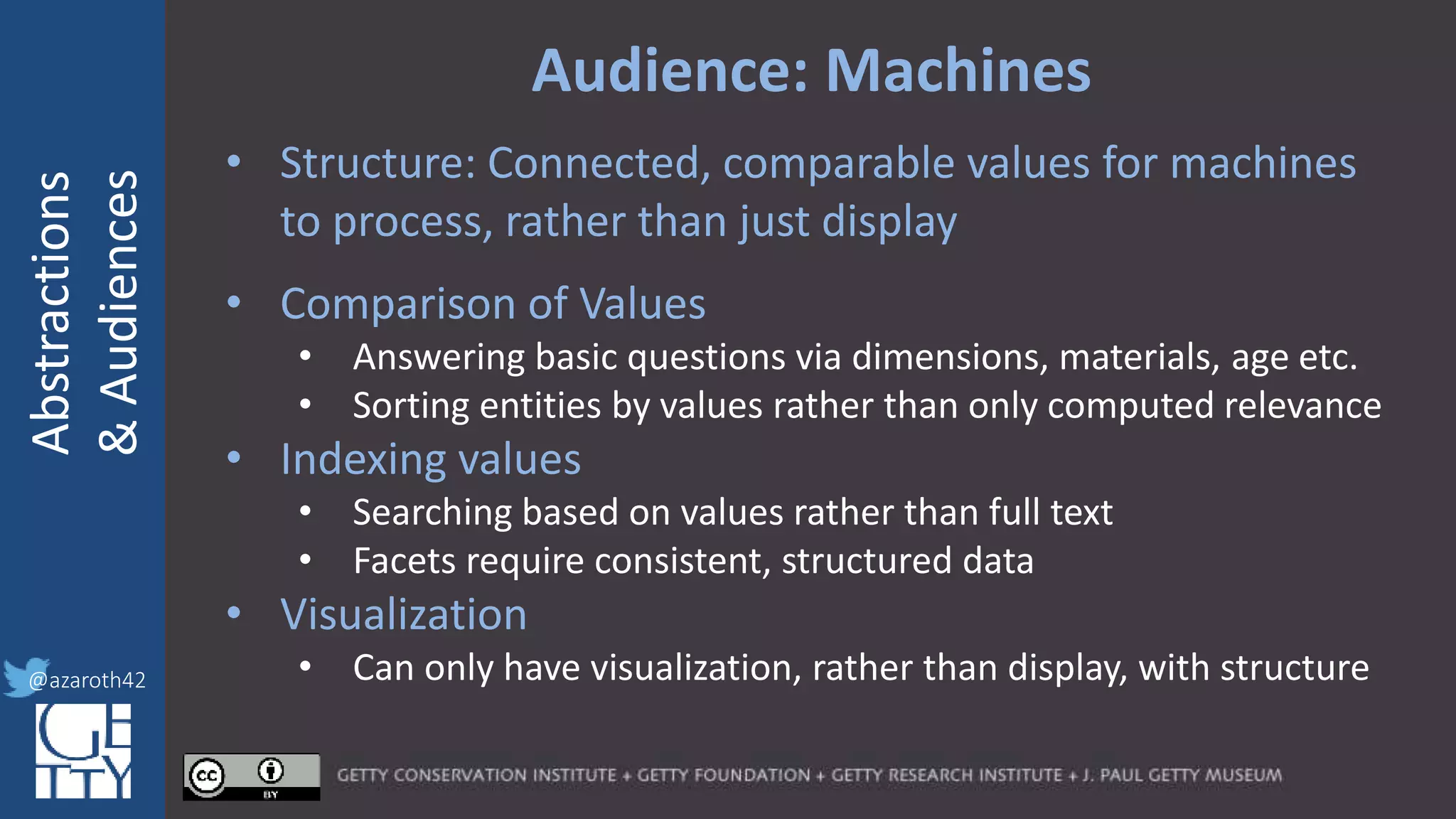
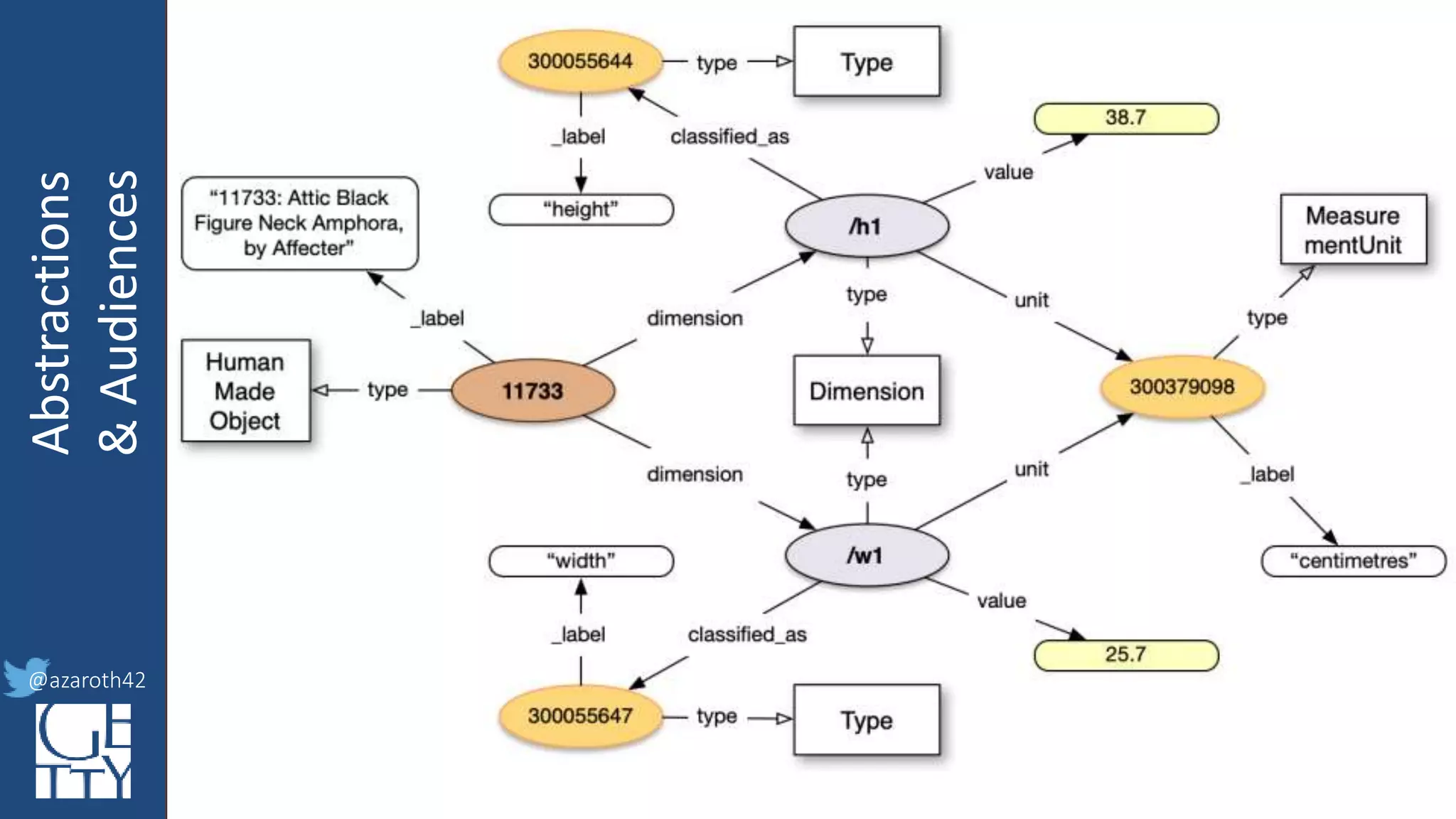
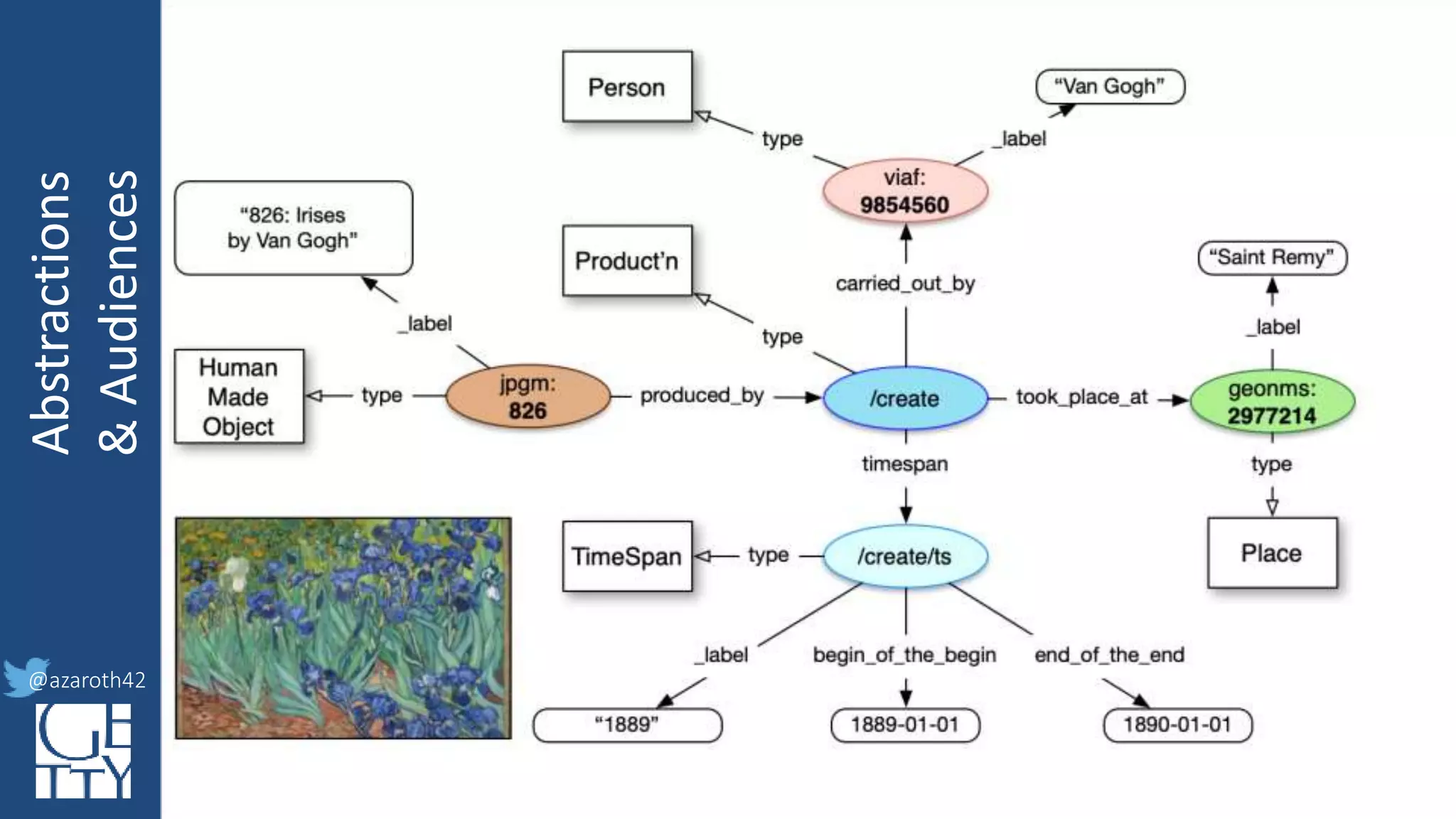
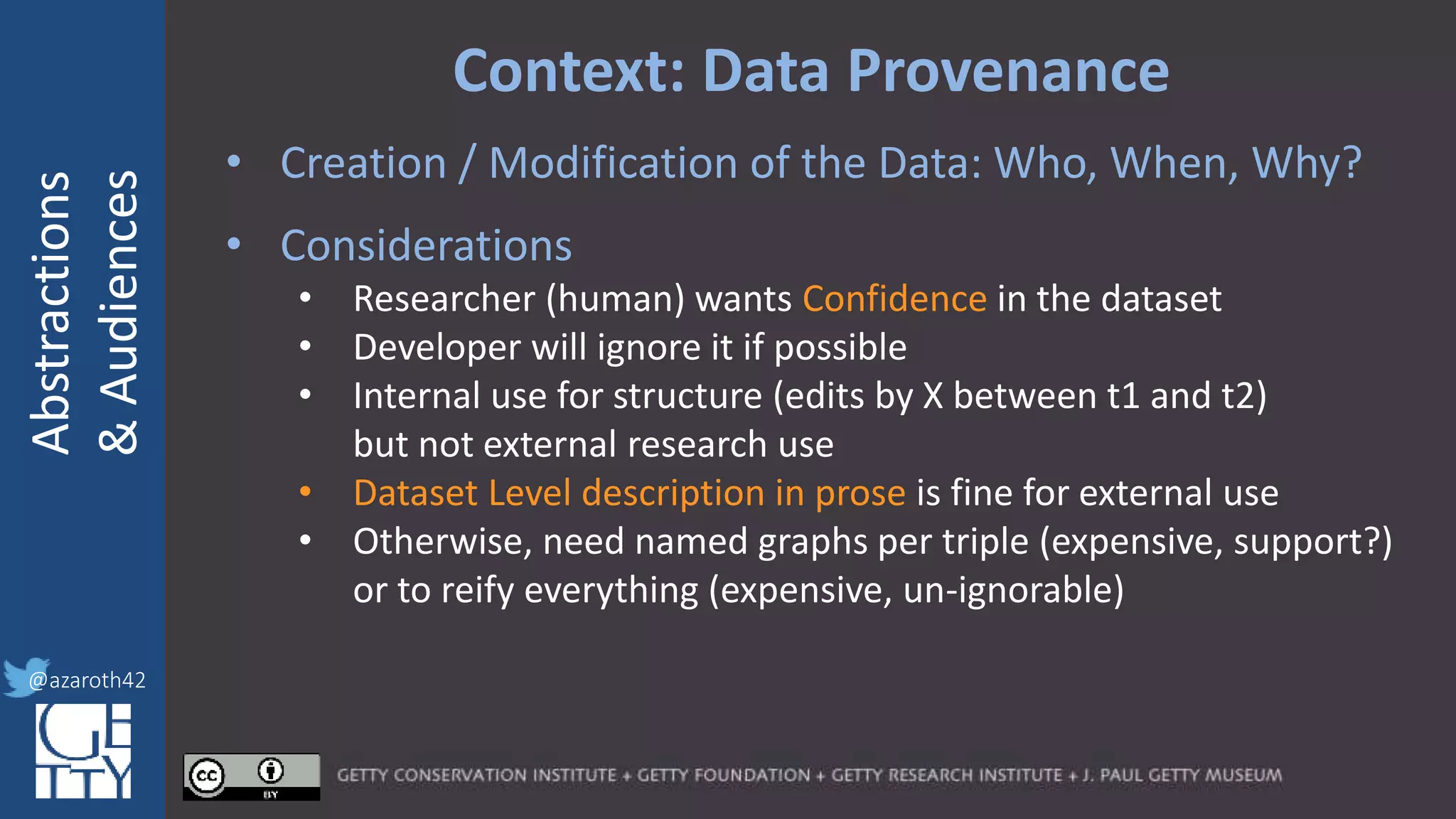
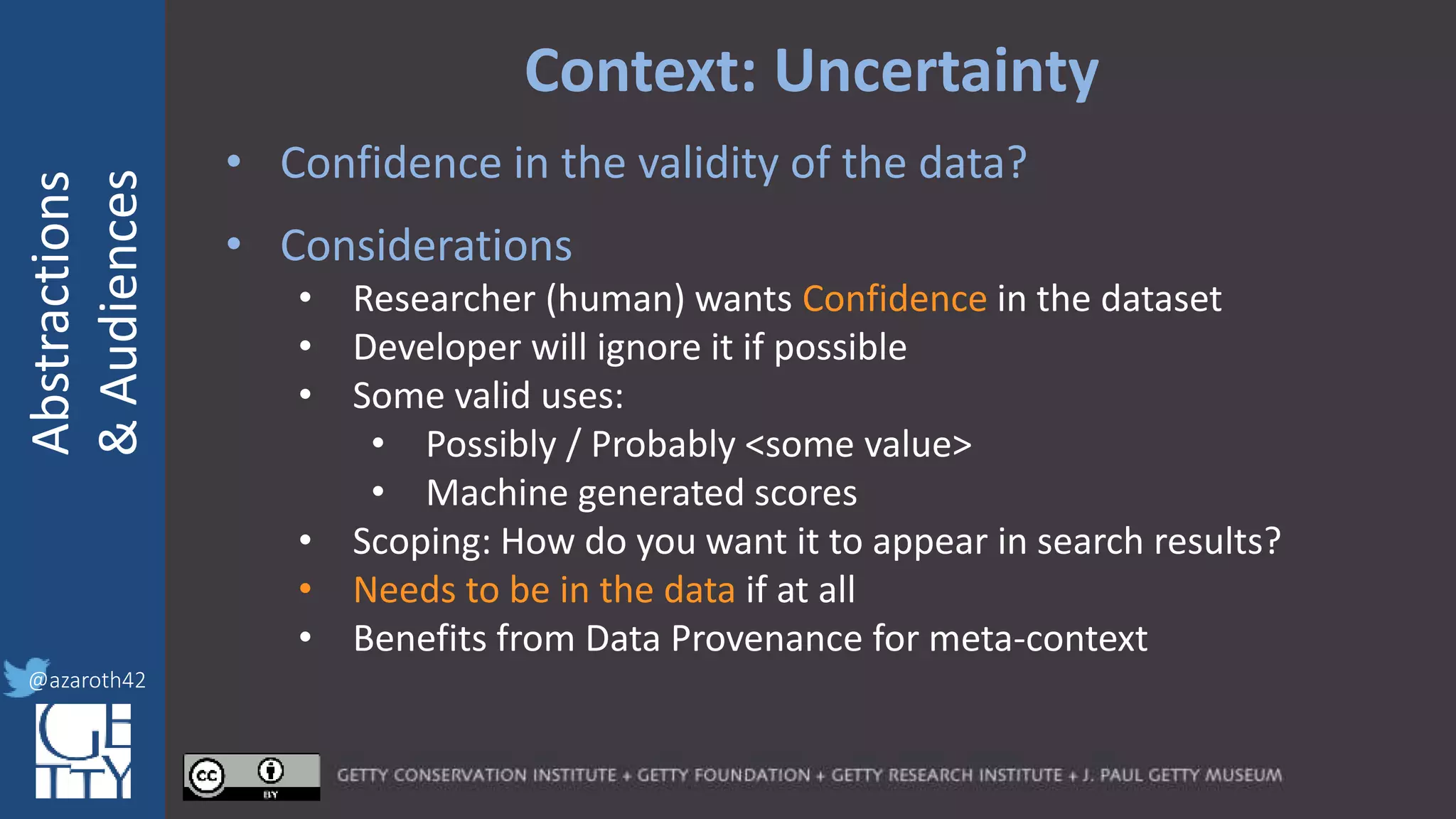
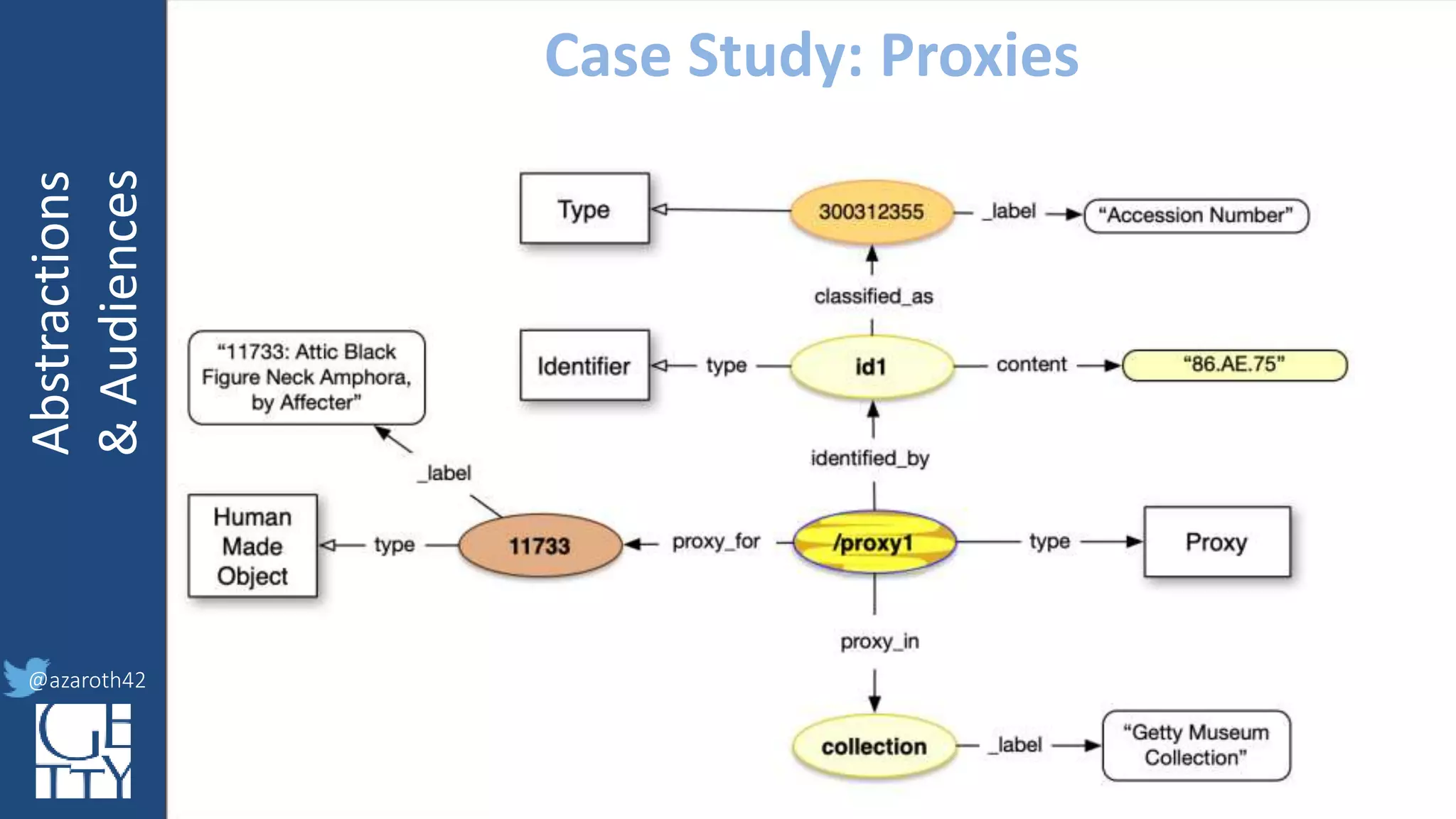
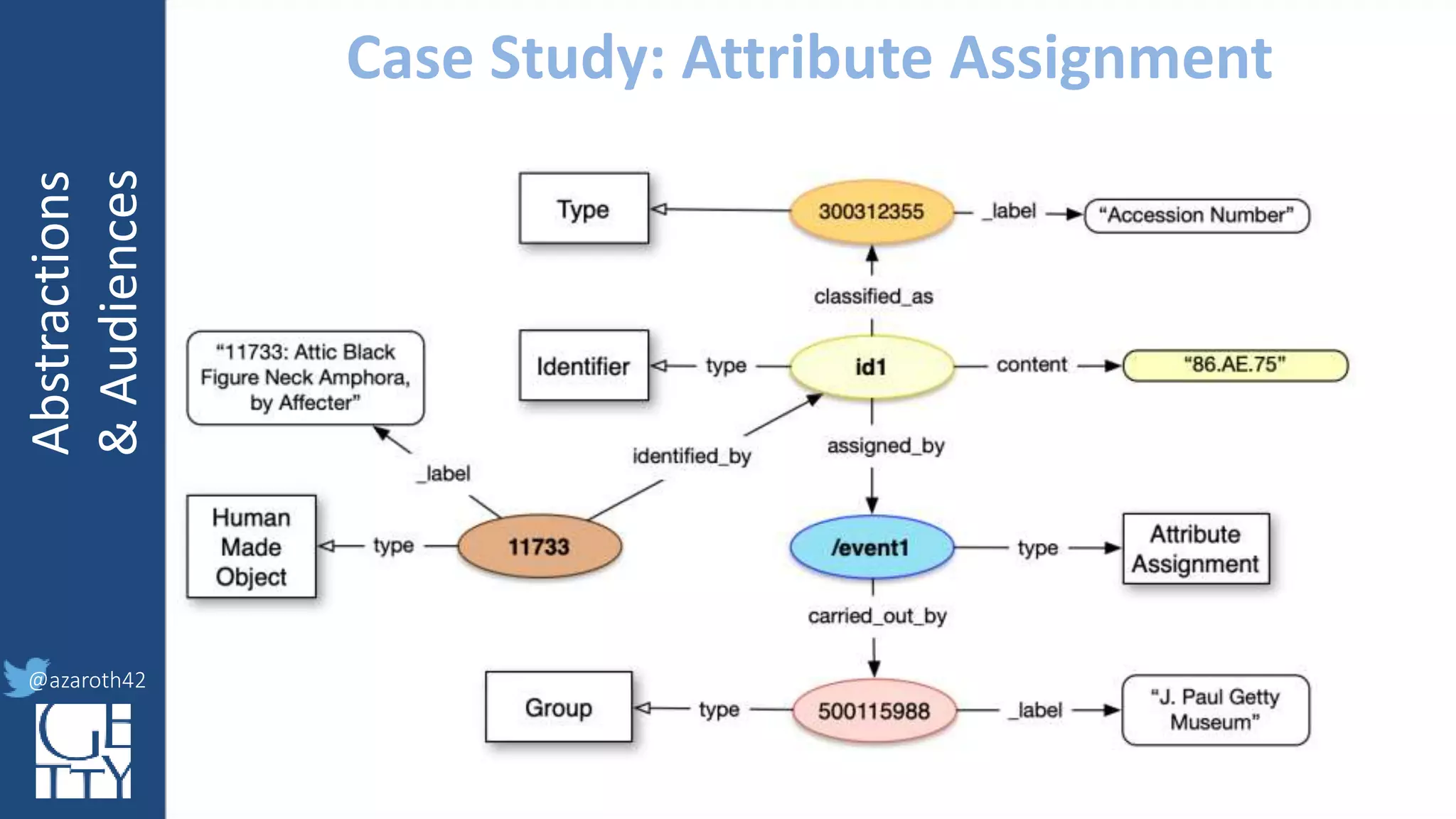
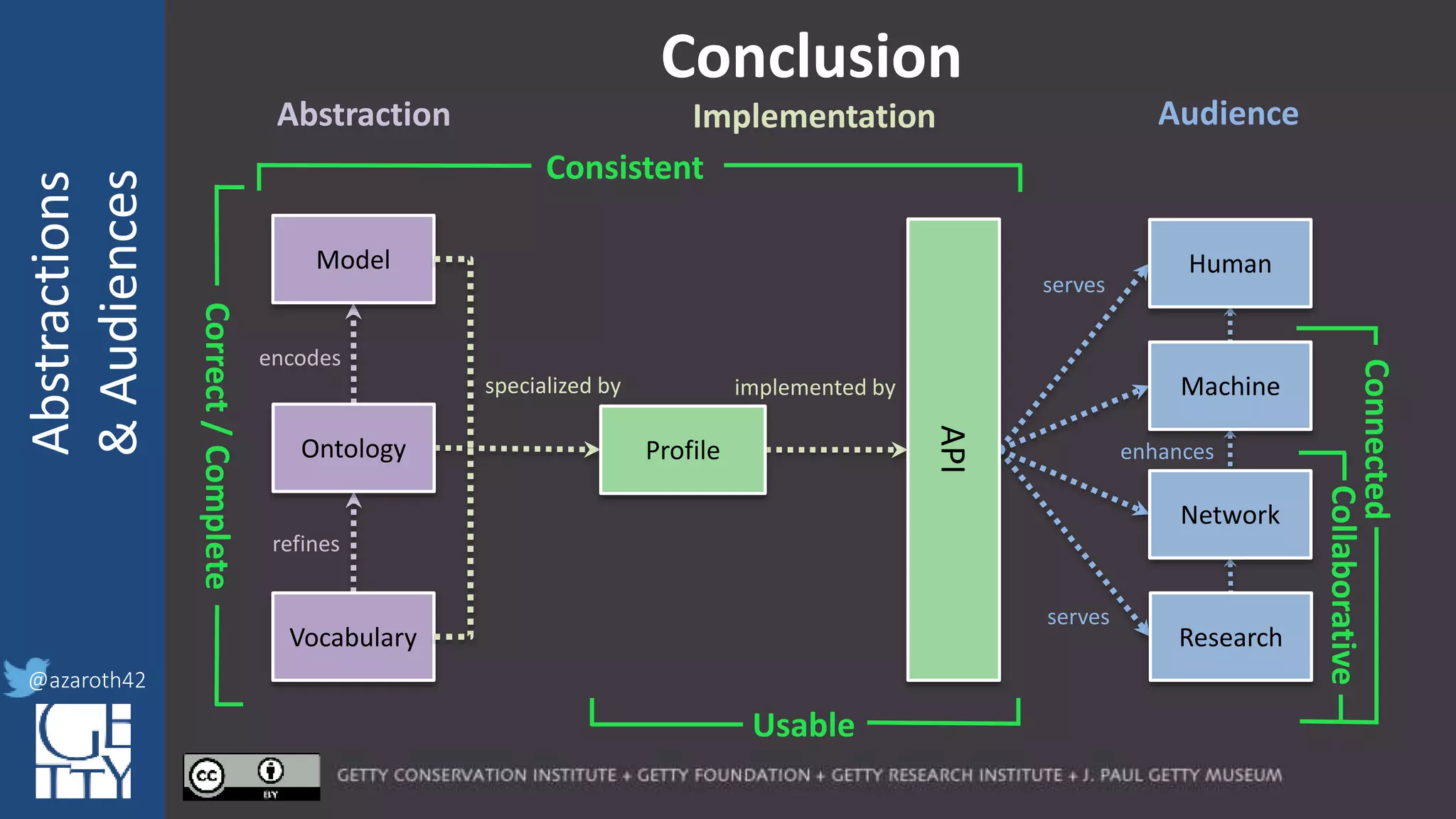
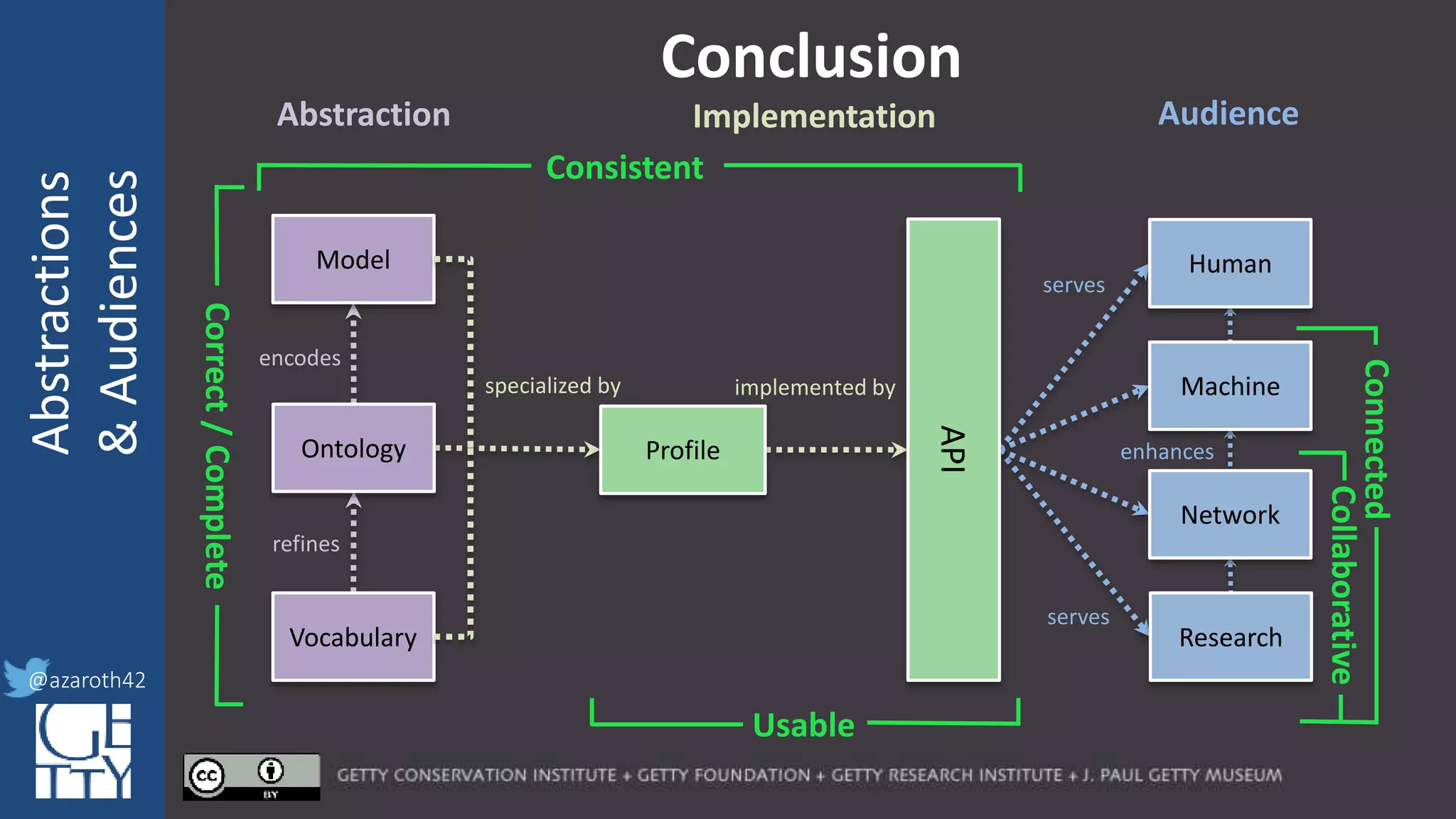
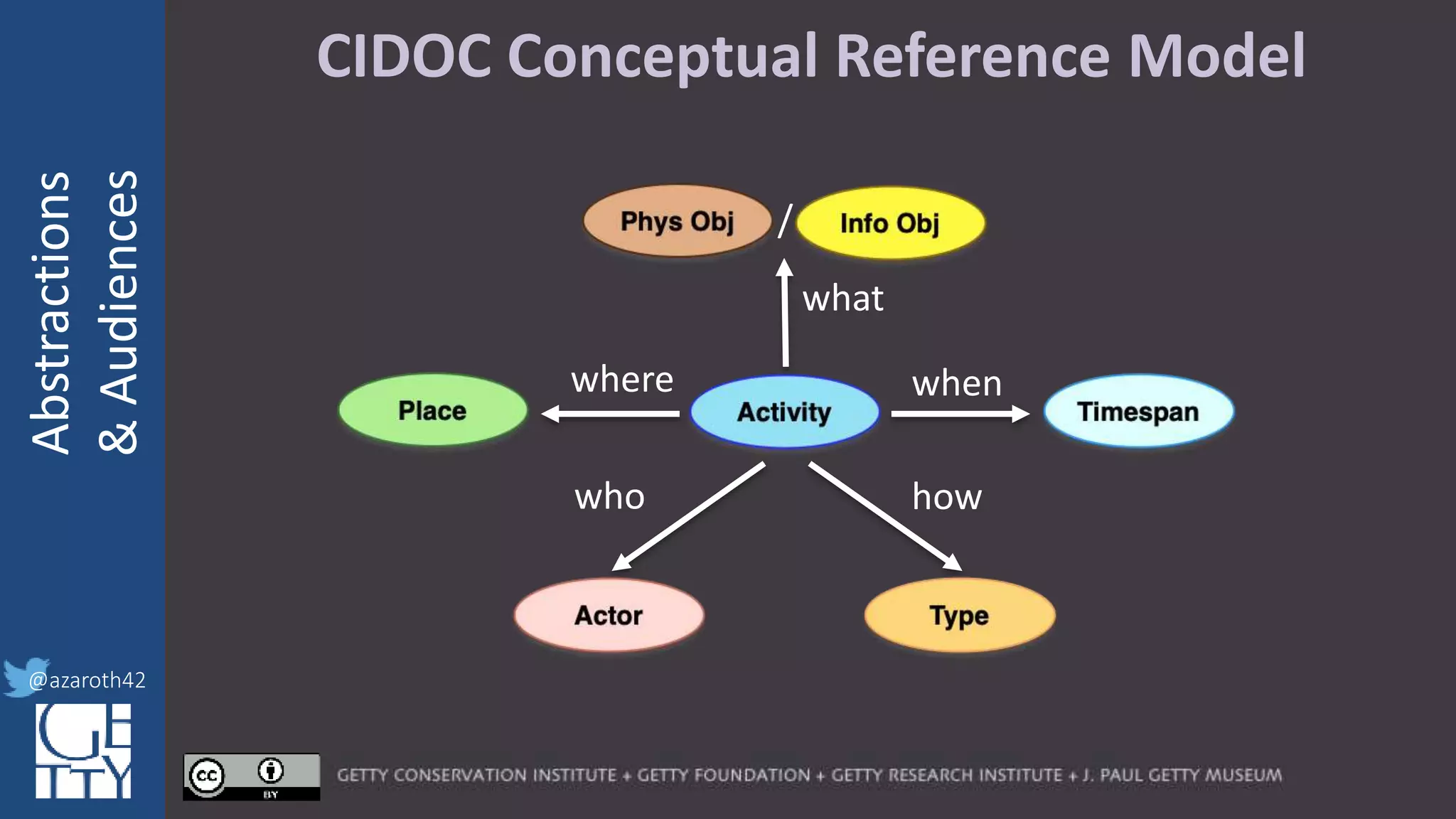
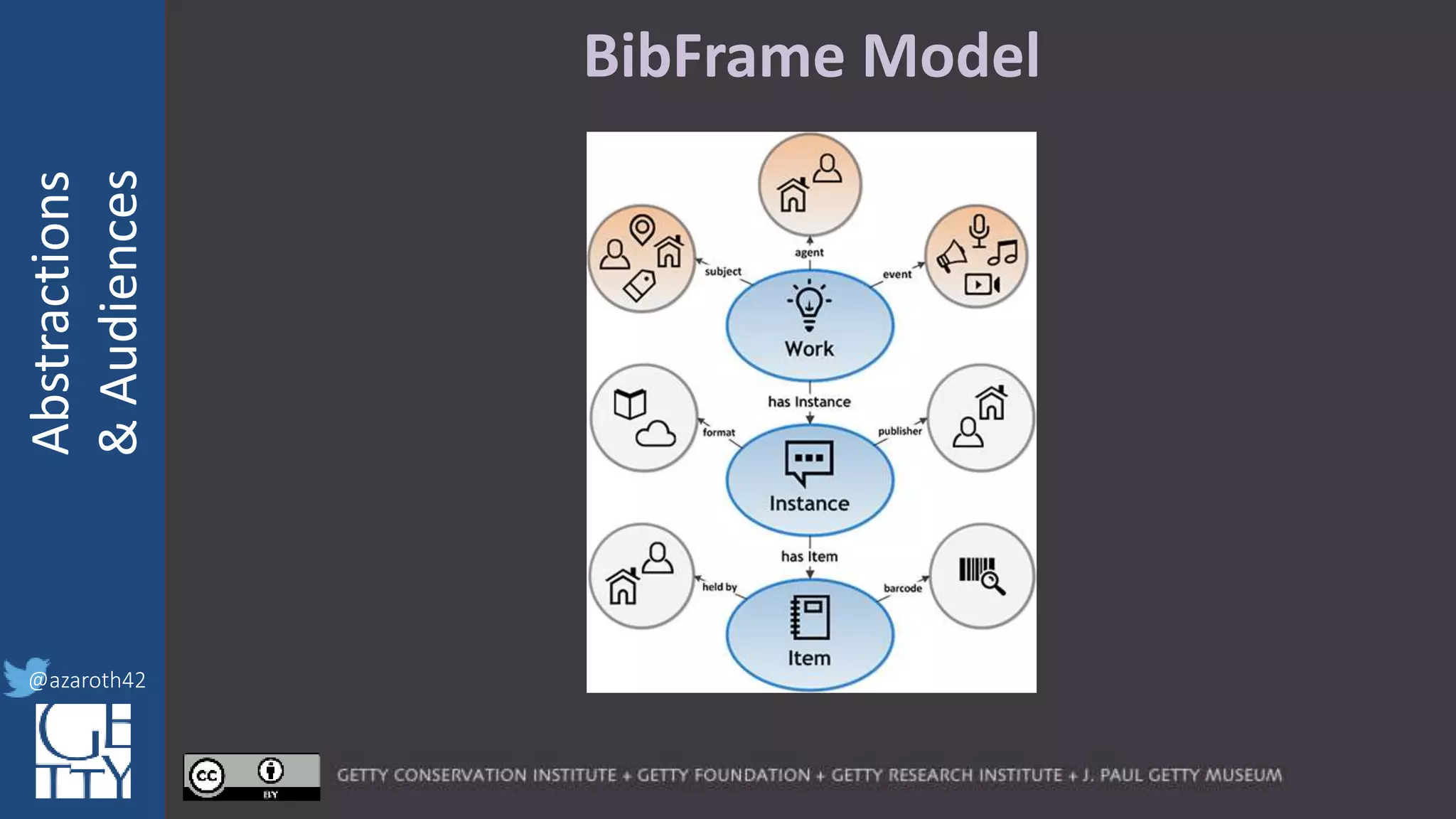
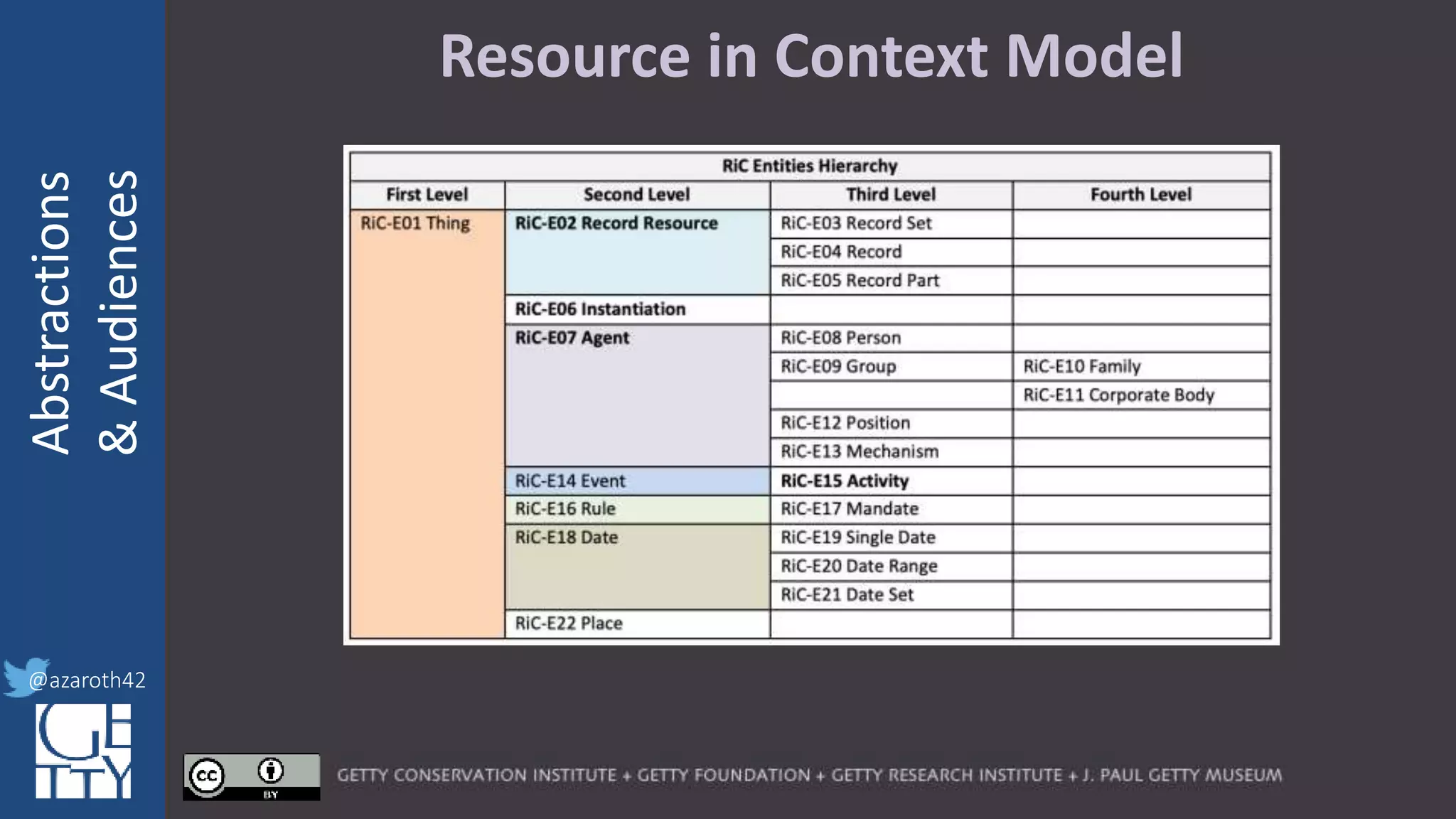
The document discusses the importance of interoperability, abstraction, and audience in cultural heritage data modeling, outlining the distinctions between models, ontologies, and vocabularies. It emphasizes the need for a socio-technical ecosystem that promotes usability, collaboration, and sustainable practices in digital cultural heritage, including the design of APIs and application profiles. Case studies like the CIDOC-CRM and Linked Art are presented to illustrate the practical implications of these concepts for engaging diverse audiences and enhancing access to heritage data.










![@azaroth42
rsanderson
@getty.edu
IIIF:Interoperabilituy
Abstractions
&Audiences
@azaroth42
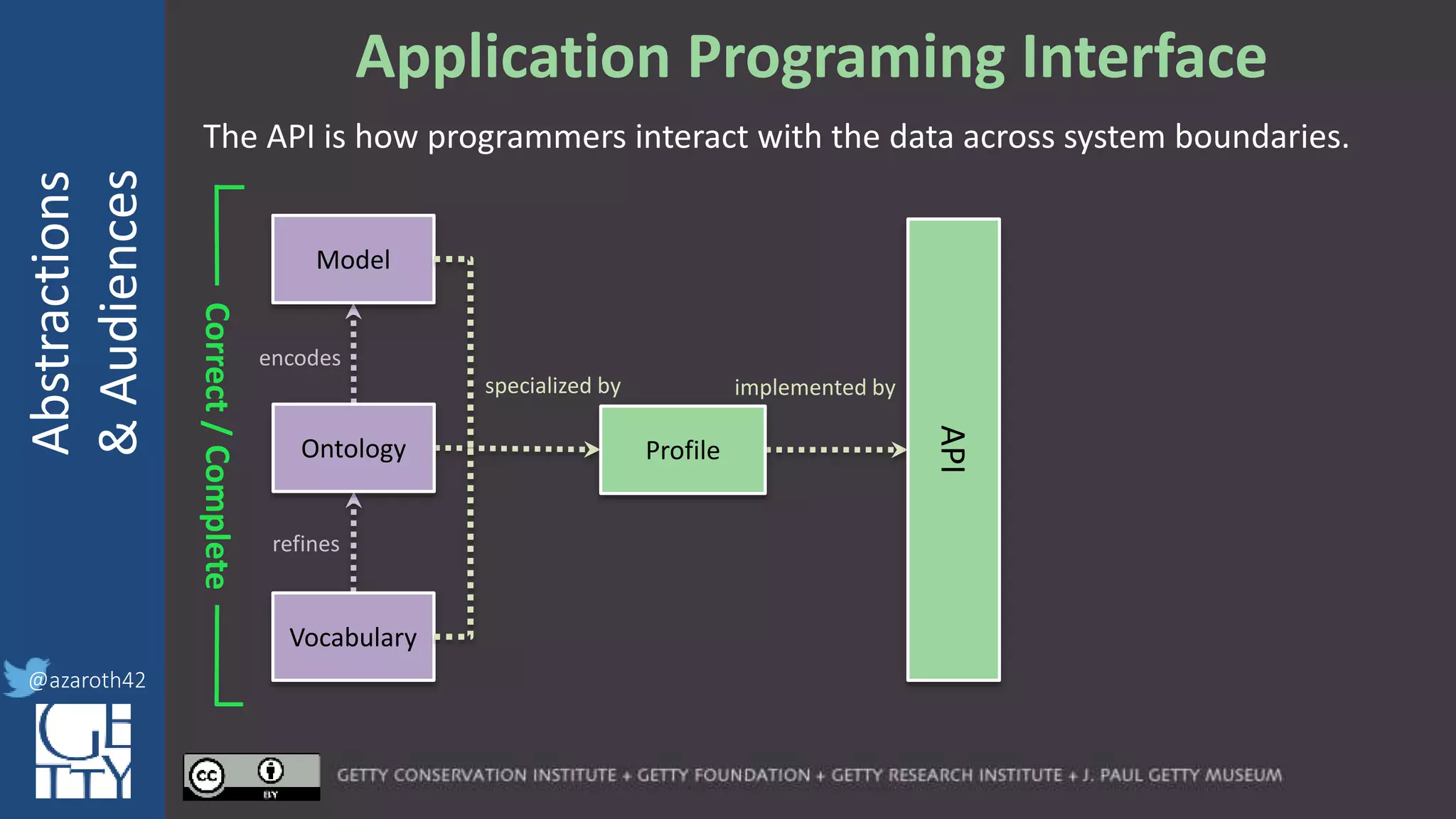
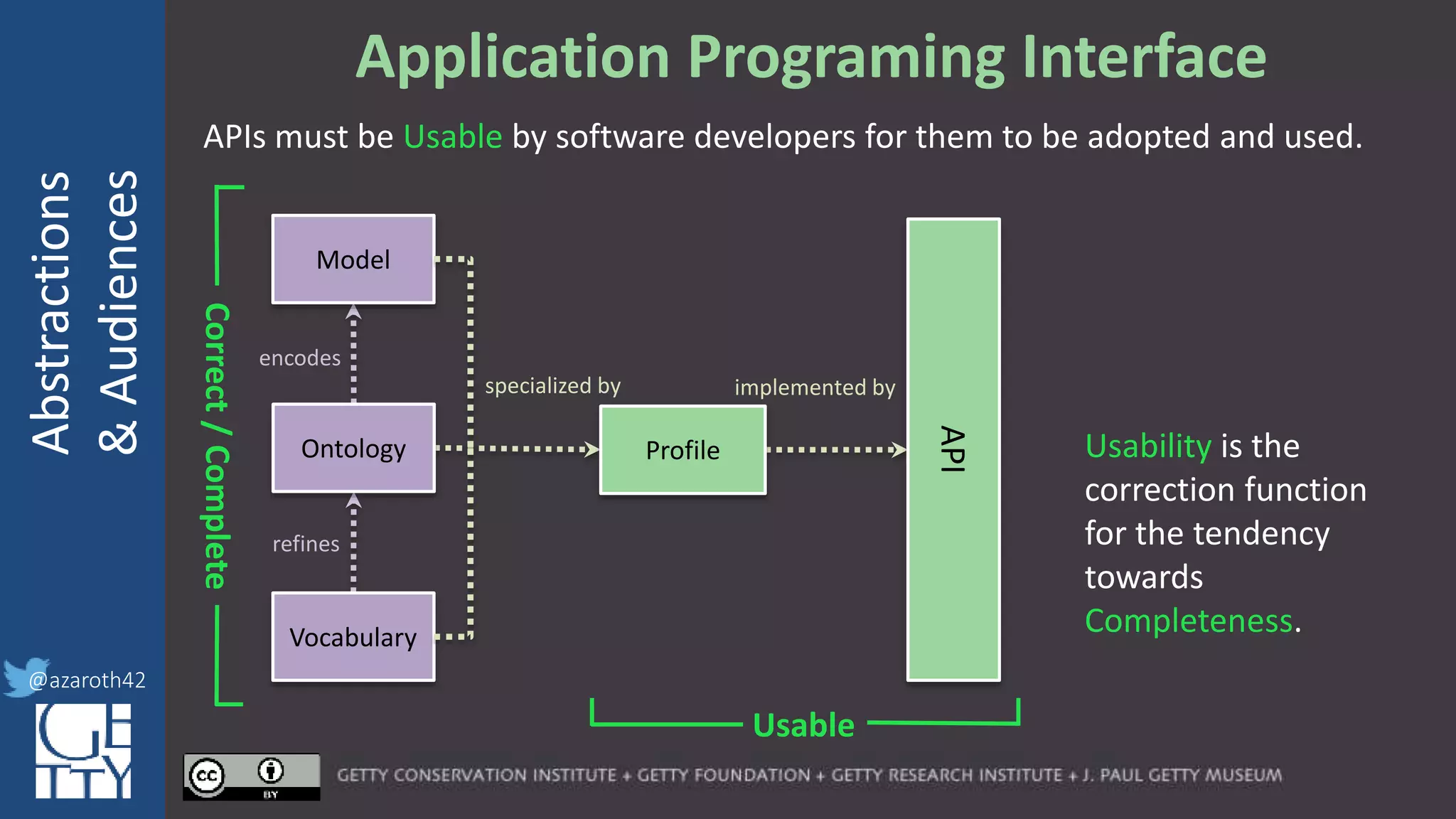
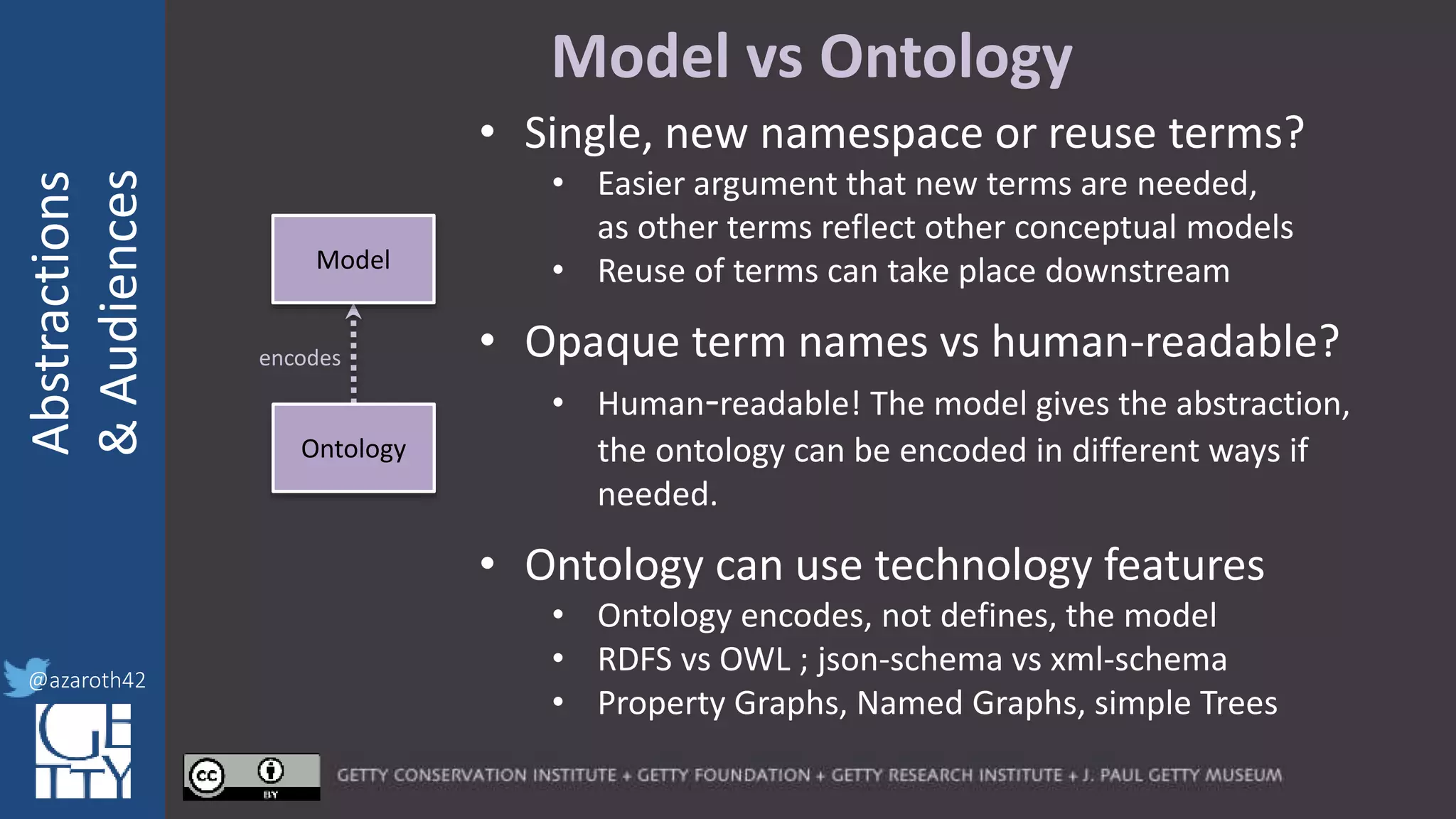
[Metadata] Application Profile
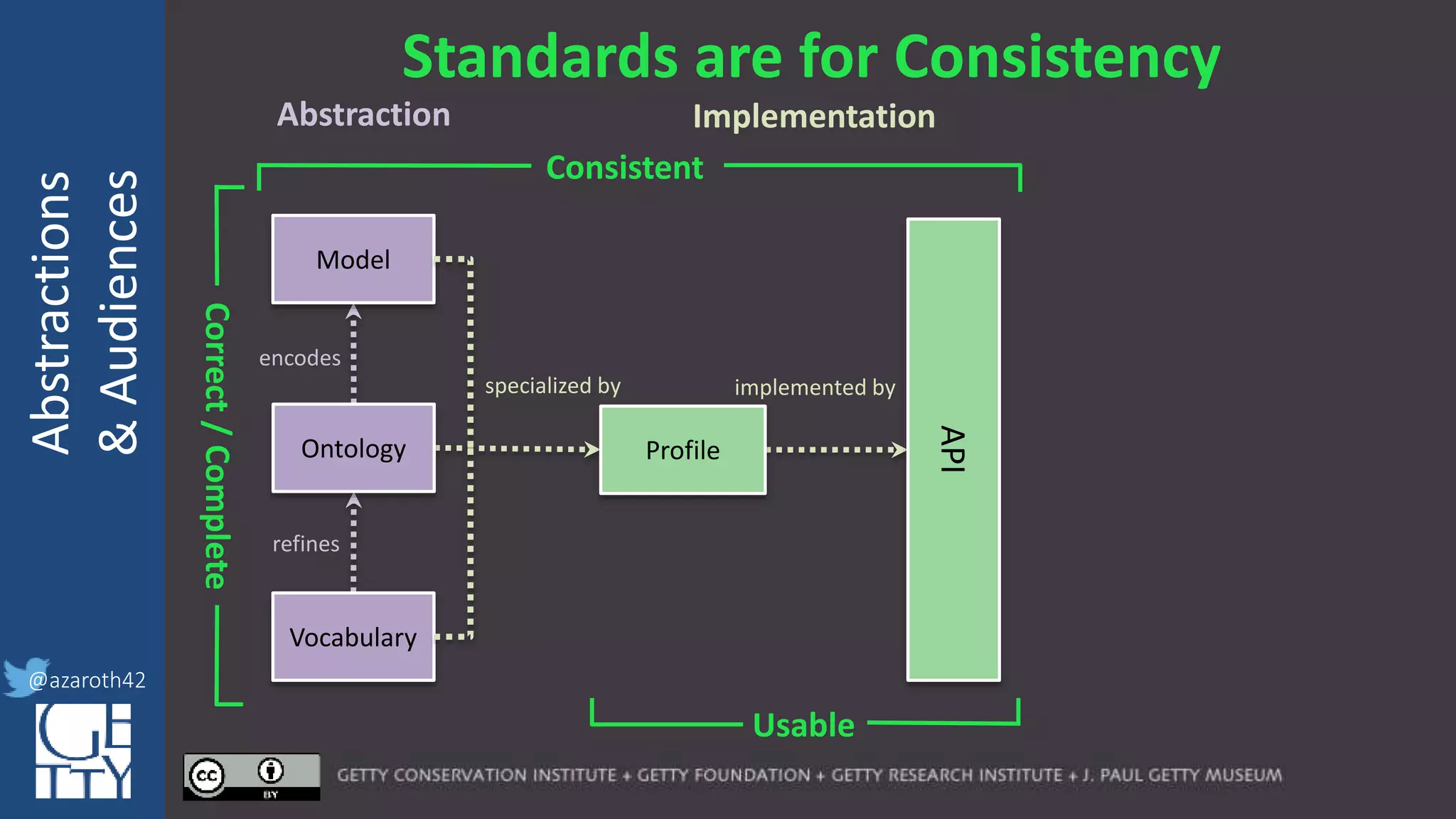
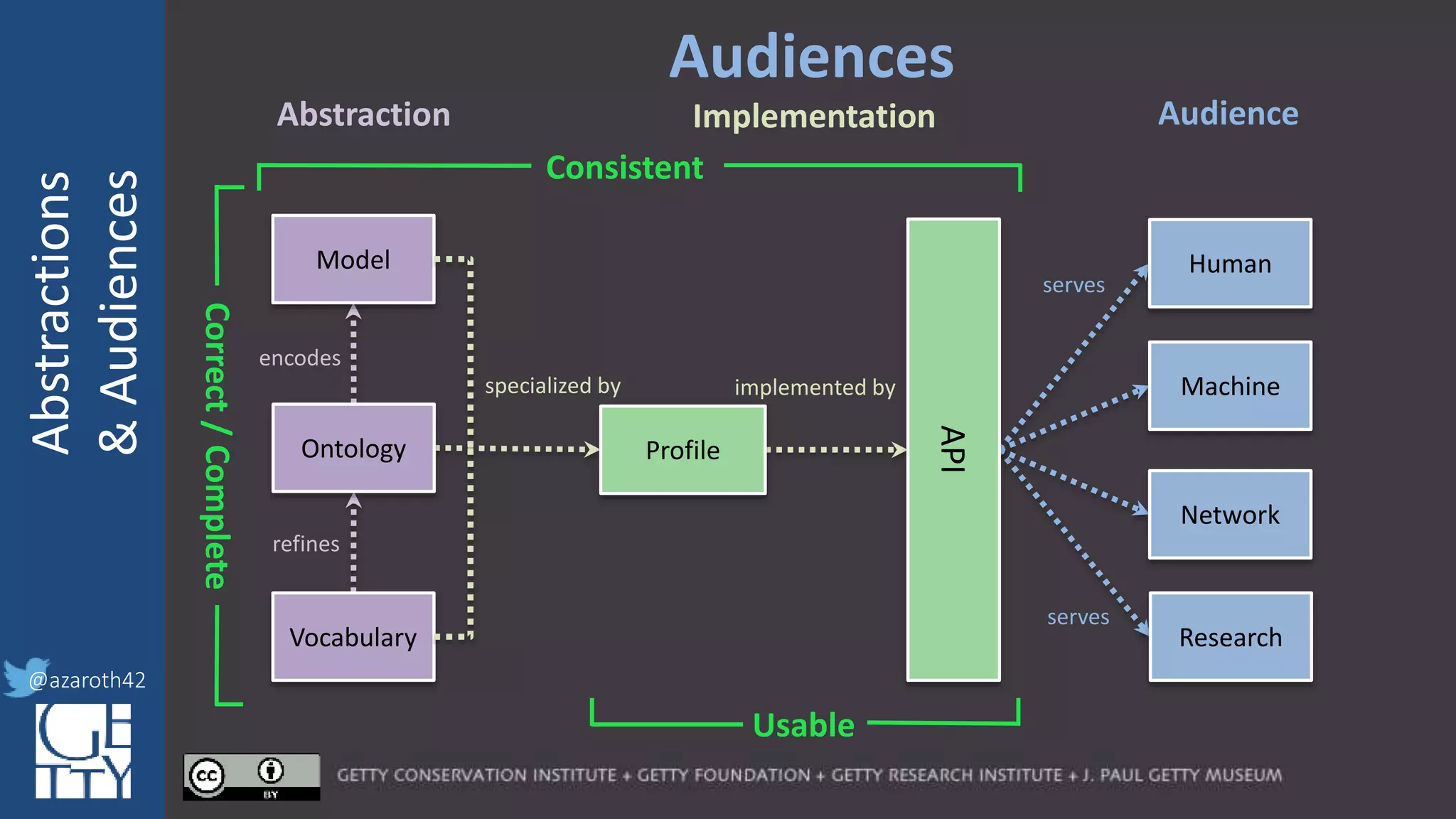
encodes
refines
specialized by
Correct/Complete
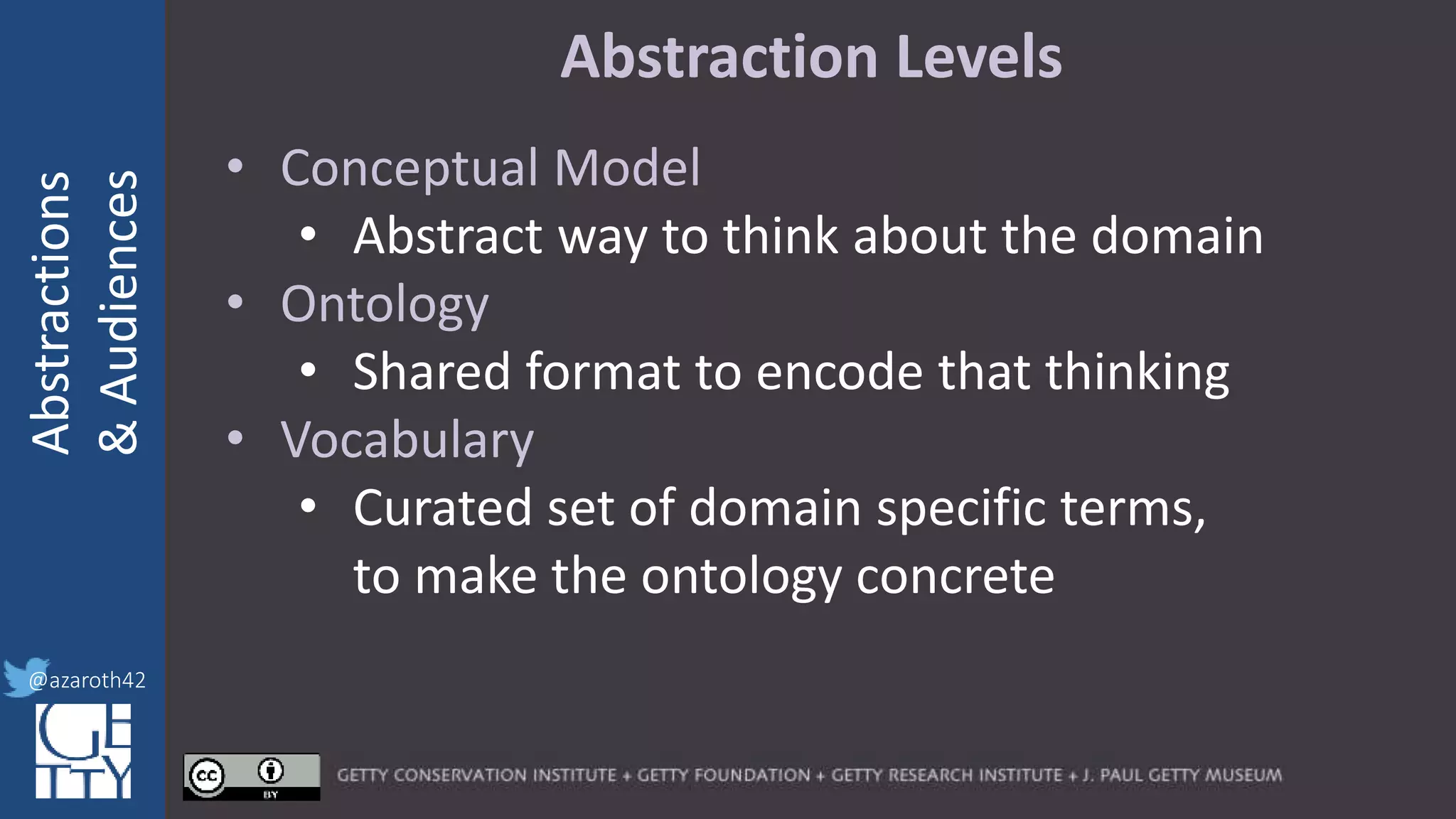
Model
Ontology
Vocabulary
Profile
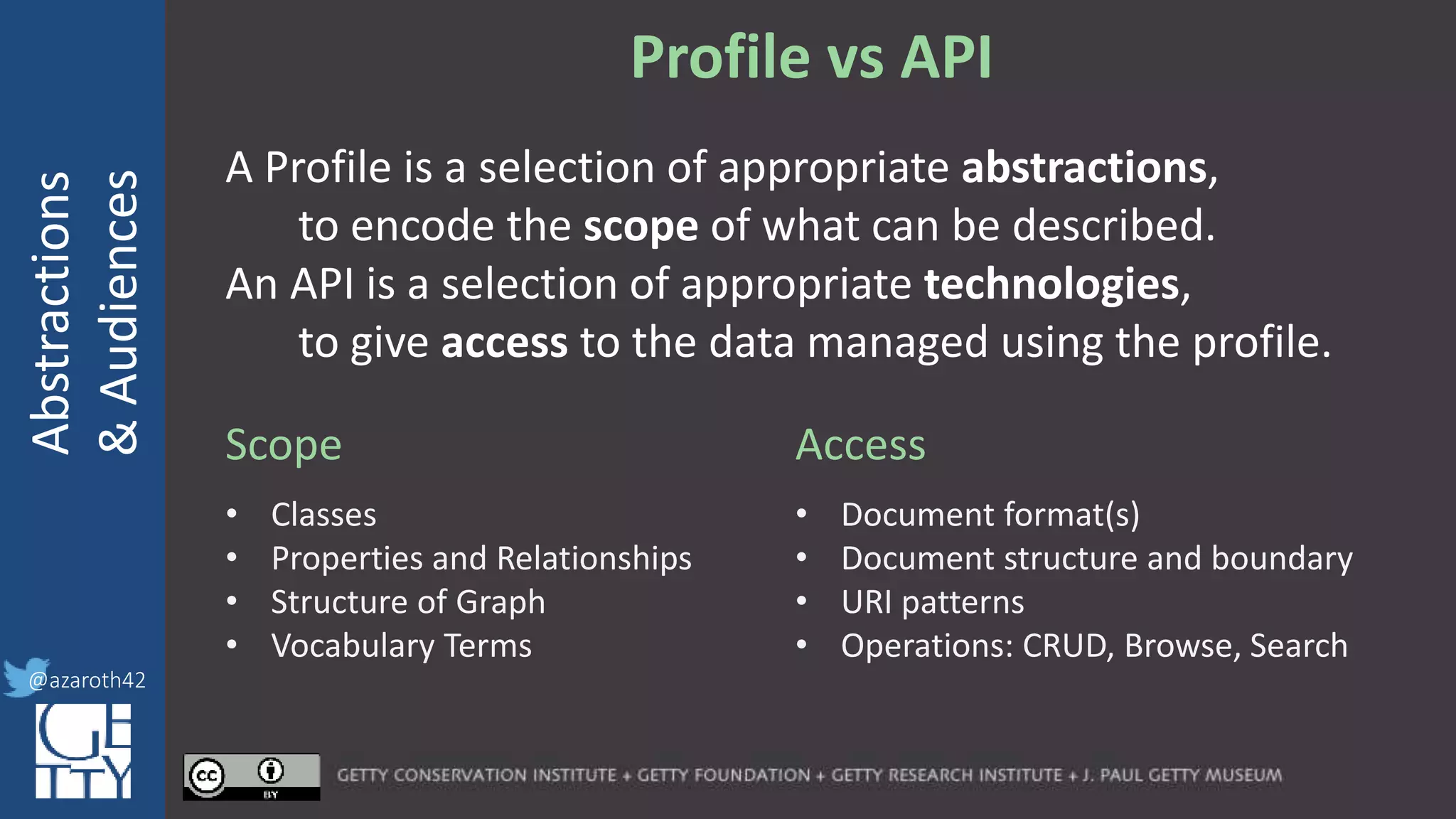
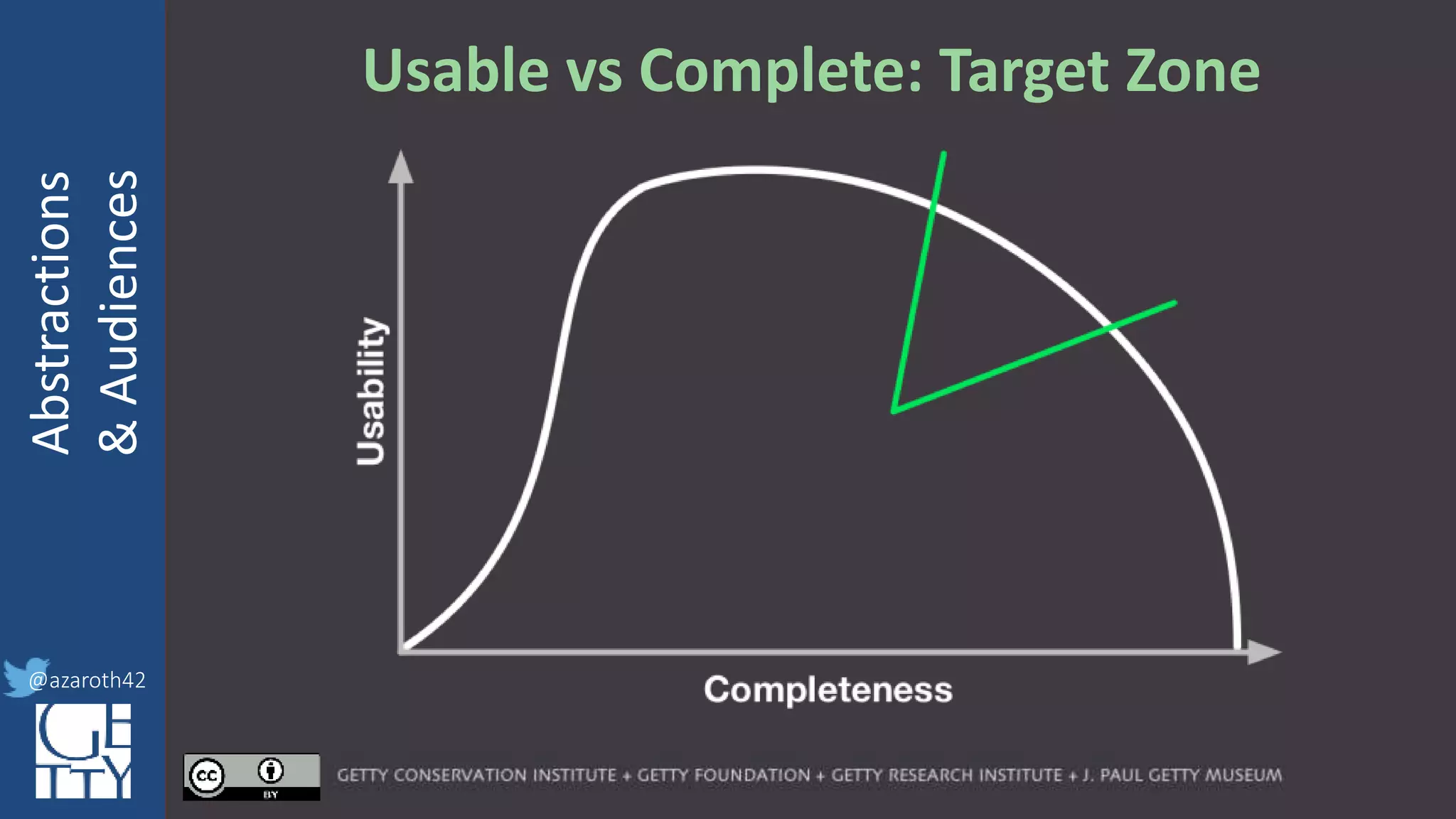
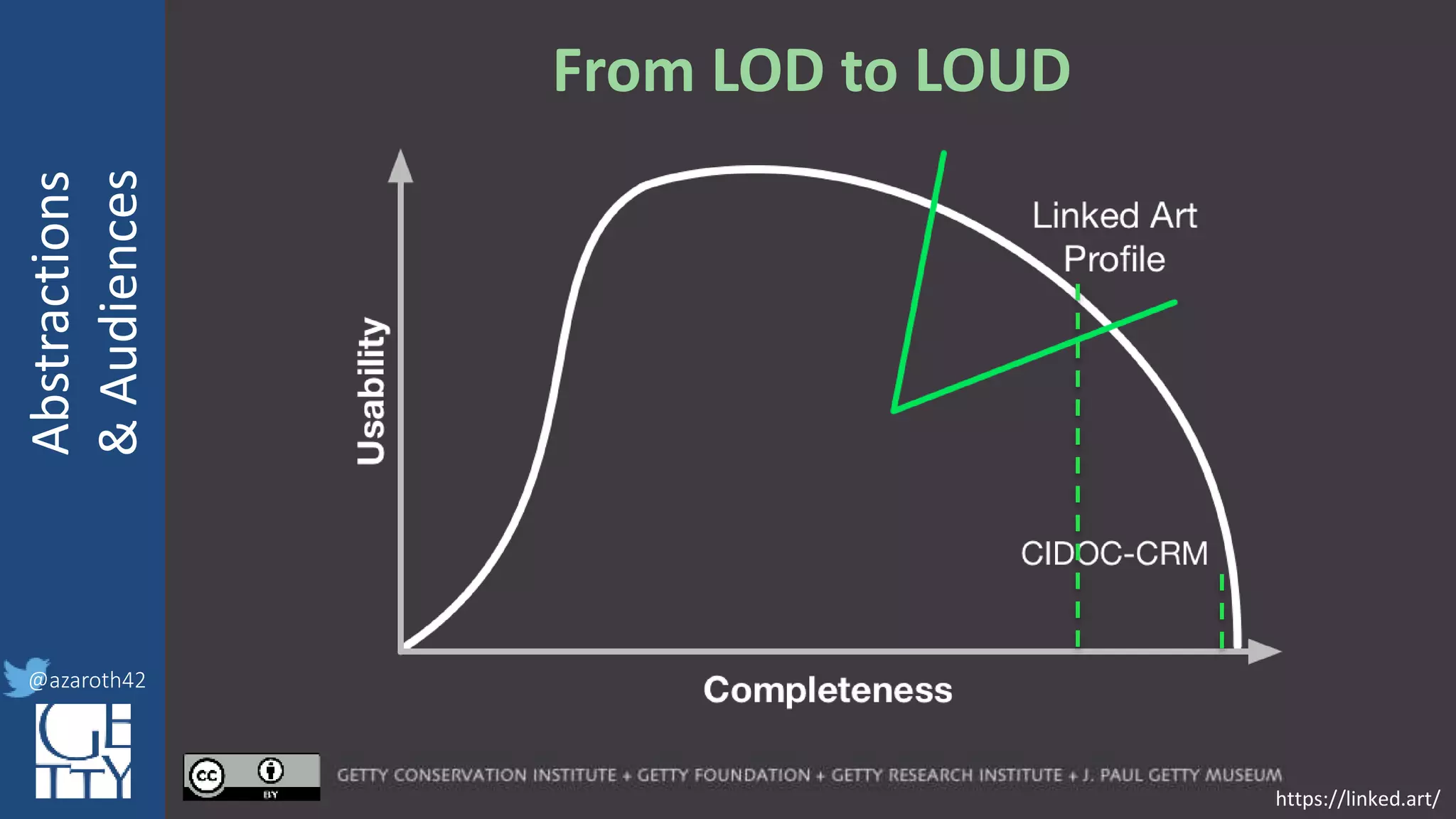
For any given domain, there must be
selection of appropriate abstractions,
documented as an application profile.
The more abstract the base, the more
specification is needed for the profile.
The profile needs to act as the friction to
balance Completeness with Usability.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/berkeleymodelabstractiontiers-200313200000/75/Tiers-of-Abstraction-and-Audience-in-Cultural-Heritage-Data-Modeling-21-2048.jpg)