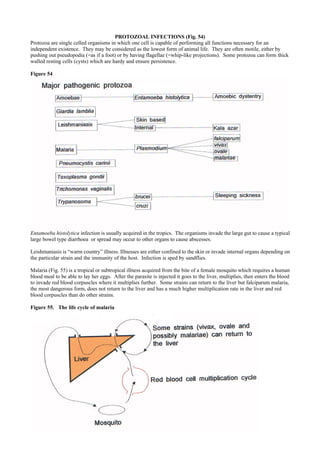
Protozoal Infections
- 1. PROTOZOAL INFECTIONS (Fig. 54) Protozoa are single celled organisms in which one cell is capable of performing all functions necessary for an independent existence. They may be considered as the lowest form of animal life. They are often motile, either by pushing out pseudopodia (=as if a foot) or by having flagellae (=whip-like projections). Some protozoa can form thick walled resting cells (cysts) which are hardy and ensure persistence. Figure 54 Entamoeba histolytica infection is usually acquired in the tropics. The organisms invade the large gut to cause a typical large bowel type diarrhoea or spread may occur to other organs to cause abscesses. Leishmaniasis is “warm country” illness. Illnesses are either confined to the skin or invade internal organs depending on the particular strain and the immunity of the host. Infection is sped by sandflies. Malaria (Fig. 55) is a tropical or subtropical illness acquired from the bite of a female mosquito which requires a human blood meal to be able to lay her eggs. After the parasite is injected it goes to the liver, multiplies, then enters the blood to invade red blood corpuscles where it multiplies further. Some strains can return to the liver but falciparum malaria, the most dangerous form, does not return to the liver and has a much higher multiplication rate in the liver and red blood corpuscles than do other strains. Figure 55. The life cycle of malaria
- 2. Pneumocystis carinii is now thought to be more related to fungi than to protozoan organisms. It is usually only a pathogen in those who have longterm immunosuppression because of disease (notably HIV), or by long-term immunosuppressive treatment given to prevent organ rejection. Toxoplasma gondii is spread by ingestion of the parasite from stools of cats or by eating incompletely cooked meat. It is a surprisingly common infection, but usually only causes problems in the immunosuppressed or if acquired by babies in utero. Trichomonas vaginalis is a sexually transmitted infection which seldom causes symptoms in the male, but gives rise to vaginal discharge in the female. Typanosoma brucei causes sleeping sickness, a disease confined to Africa. Trypanosoma cruzi causes Chagas disease, which causes a dysfunction of tubular organs, notably the gut and heart, and is confined to central and south America. Both are transmitted by insects.