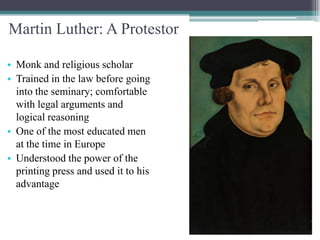
The Protestant Reformation began in 1517 as a protest against corruption and abuses within the Catholic Church, led by Martin Luther. Luther's 95 Theses criticized the Church's sale of indulgences and doctrine of salvation, and emphasized faith alone and scripture as the sole religious authority. The printing press helped spread his ideas to a wider audience. Other reformers like Calvin and Henry VIII also challenged Catholic doctrine. This led to over a century of religious conflict between Protestants and Catholics, culminating in the Thirty Years' War.