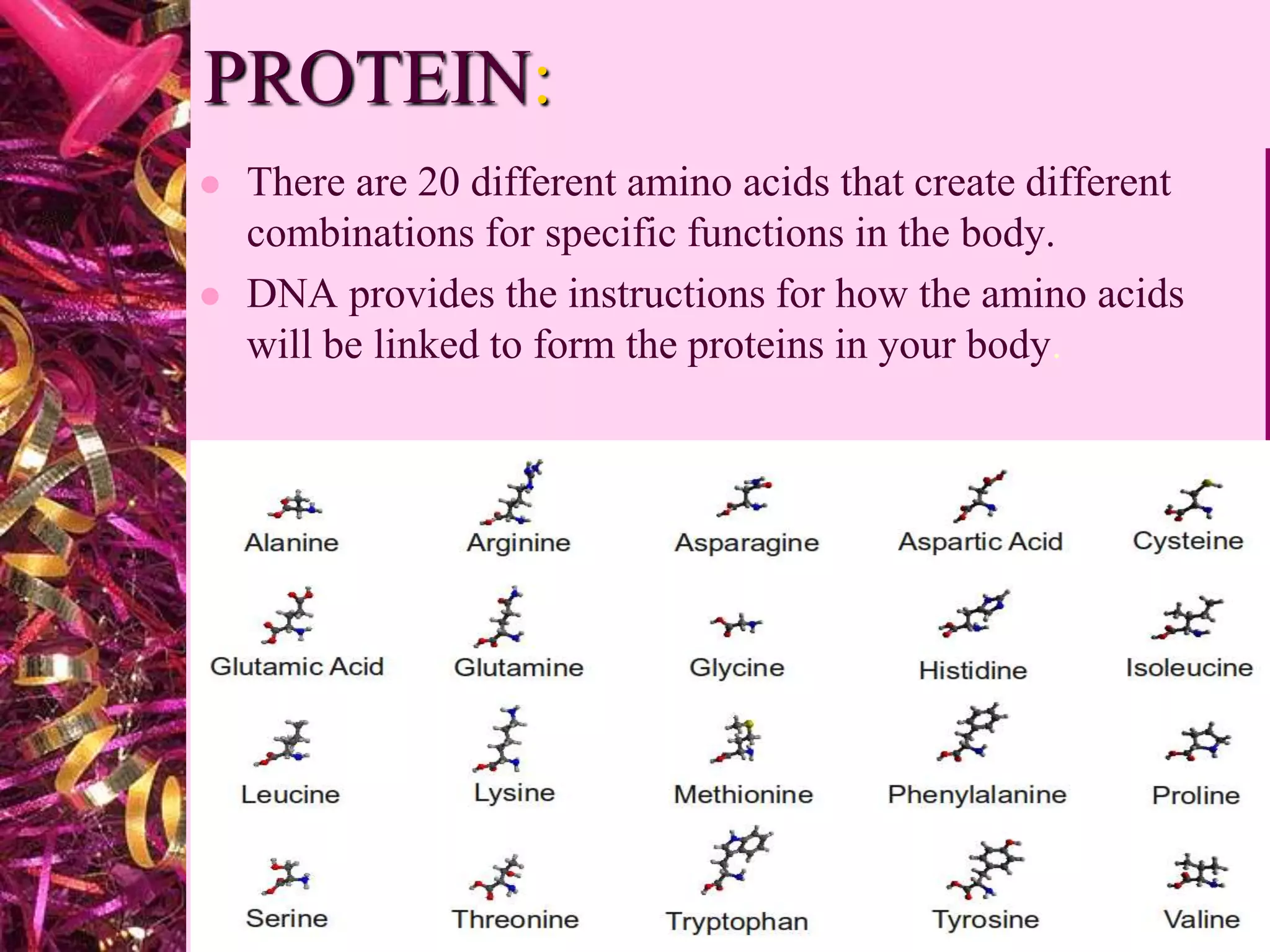
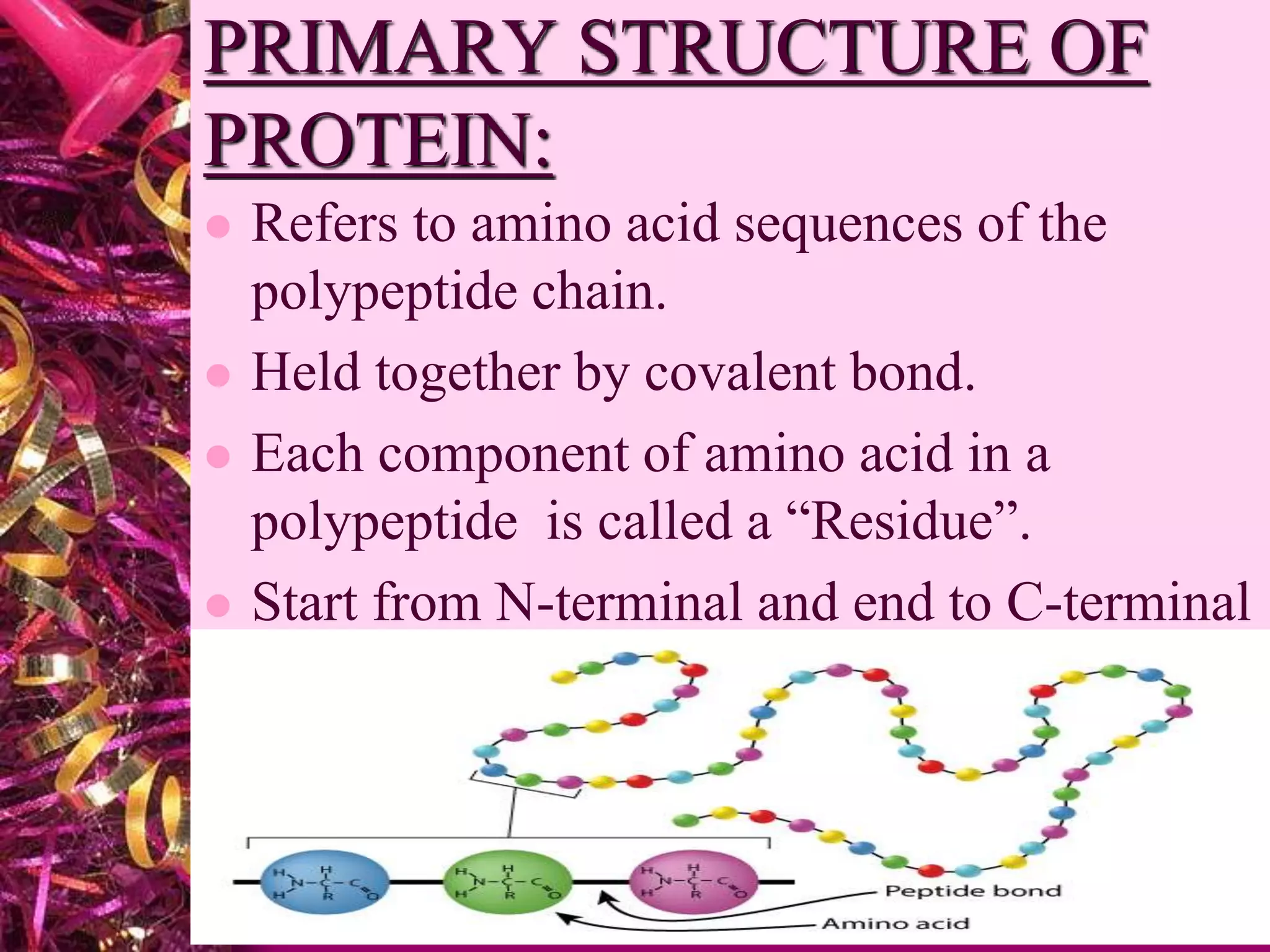
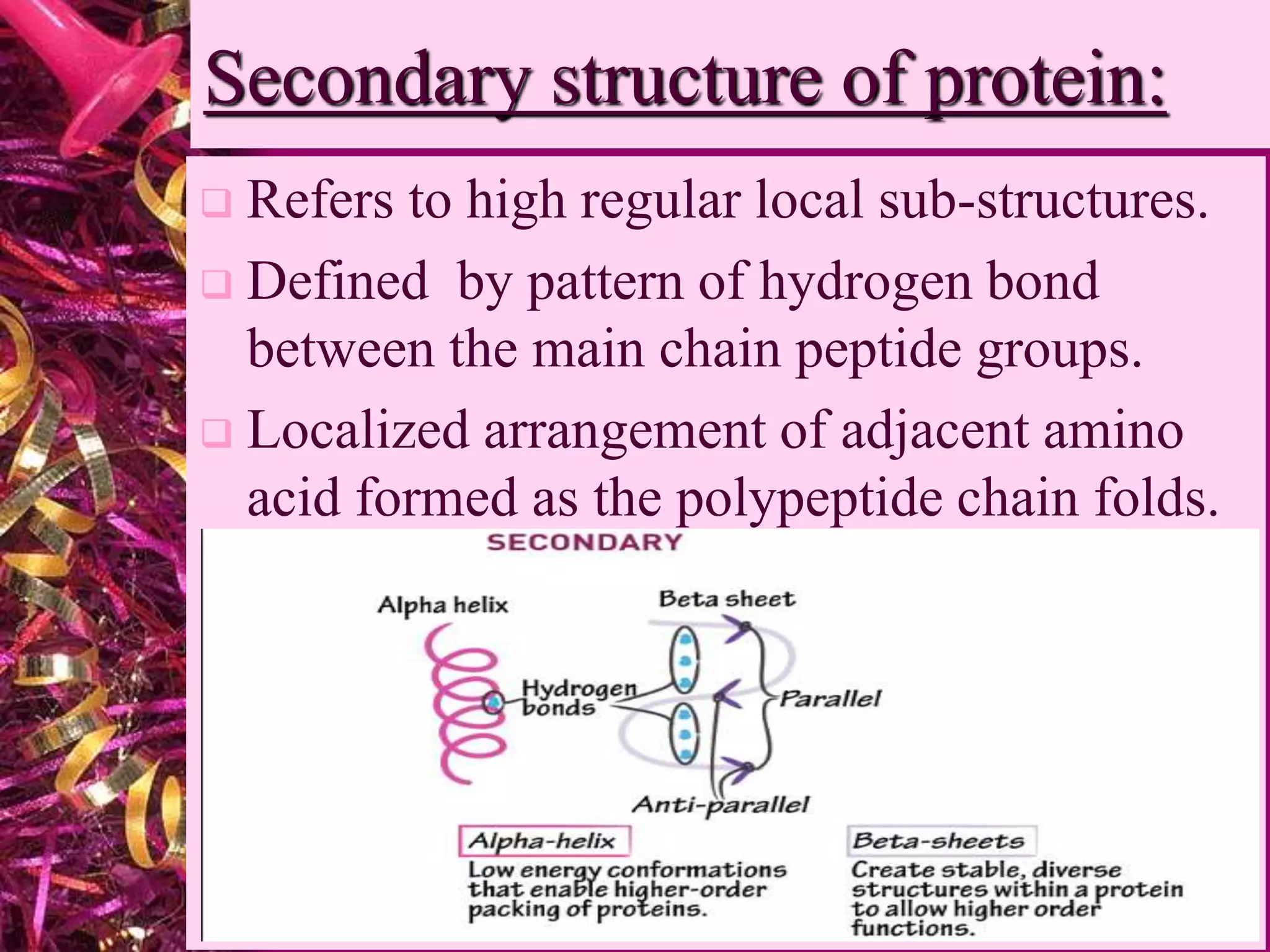
This document discusses protein structure and analysis. It defines proteins as biomolecules composed of amino acid chains that differ from other molecules by containing nitrogen. There are four levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. The primary structure refers to the amino acid sequence. Secondary structures include alpha helices and beta sheets formed by hydrogen bonds between amino acids. Tertiary structure describes the three-dimensional folding of the polypeptide. Quaternary structure is the arrangement of multiple protein subunits. Protein domains and interactions like disulfide bridges stabilize tertiary structures.