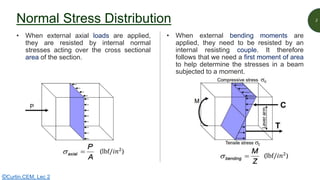
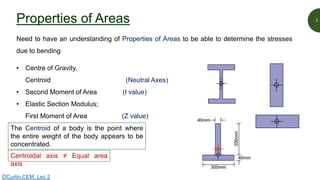
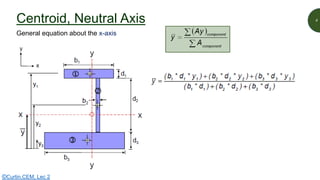
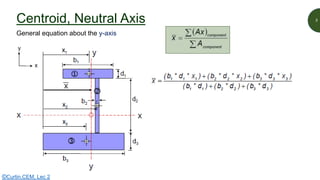
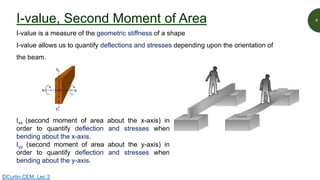
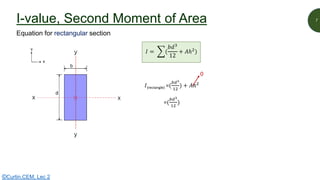
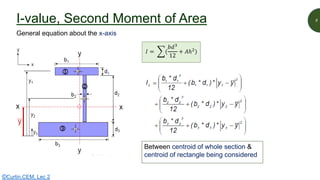
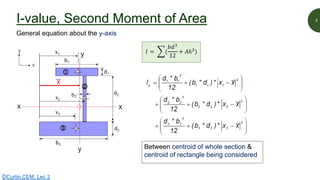
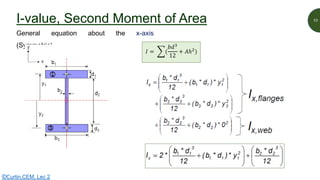
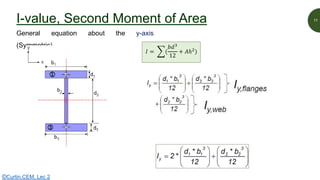
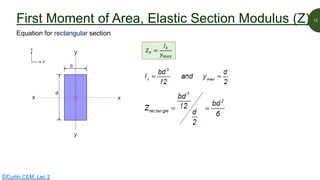
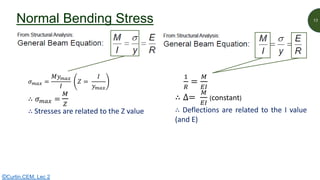
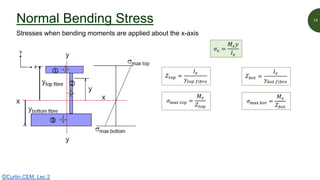
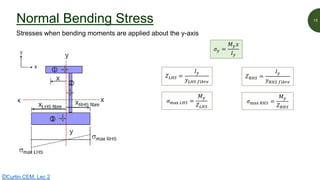
This document discusses key properties of areas that are important for determining stresses in structural elements. It defines centroid (also called neutral axis) as the point where the entire weight of a body appears concentrated. The second moment of area (I-value) is introduced as a measure of geometric stiffness that allows quantification of deflections and stresses depending on beam orientation. Elastic section modulus (Z-value) is equal to the second moment of area divided by the distance to the extreme fiber, and is used together with the bending moment to determine maximum normal stresses in a beam. Formulas are provided for calculating these properties for basic shapes like rectangles.