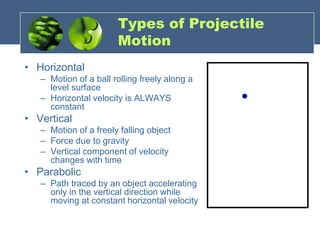
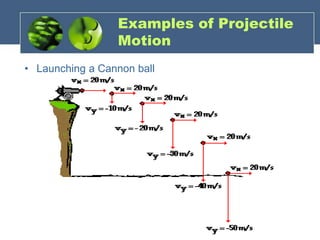
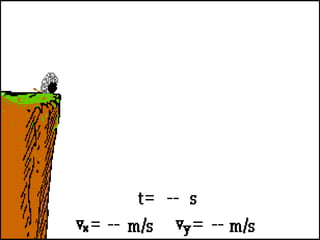
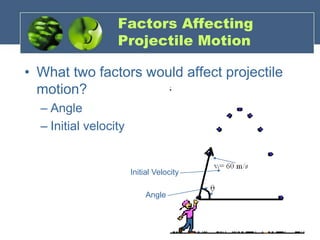
The document discusses one-dimensional and two-dimensional motion, particularly focusing on projectile motion, including types, equations, and factors affecting it. It includes various activities and questions to analyze the motion of a ball in sports contexts, such as when throwing a ball or shooting it in basketball. Additionally, it presents examples and calculations related to projectile motion to reinforce understanding of the concepts.