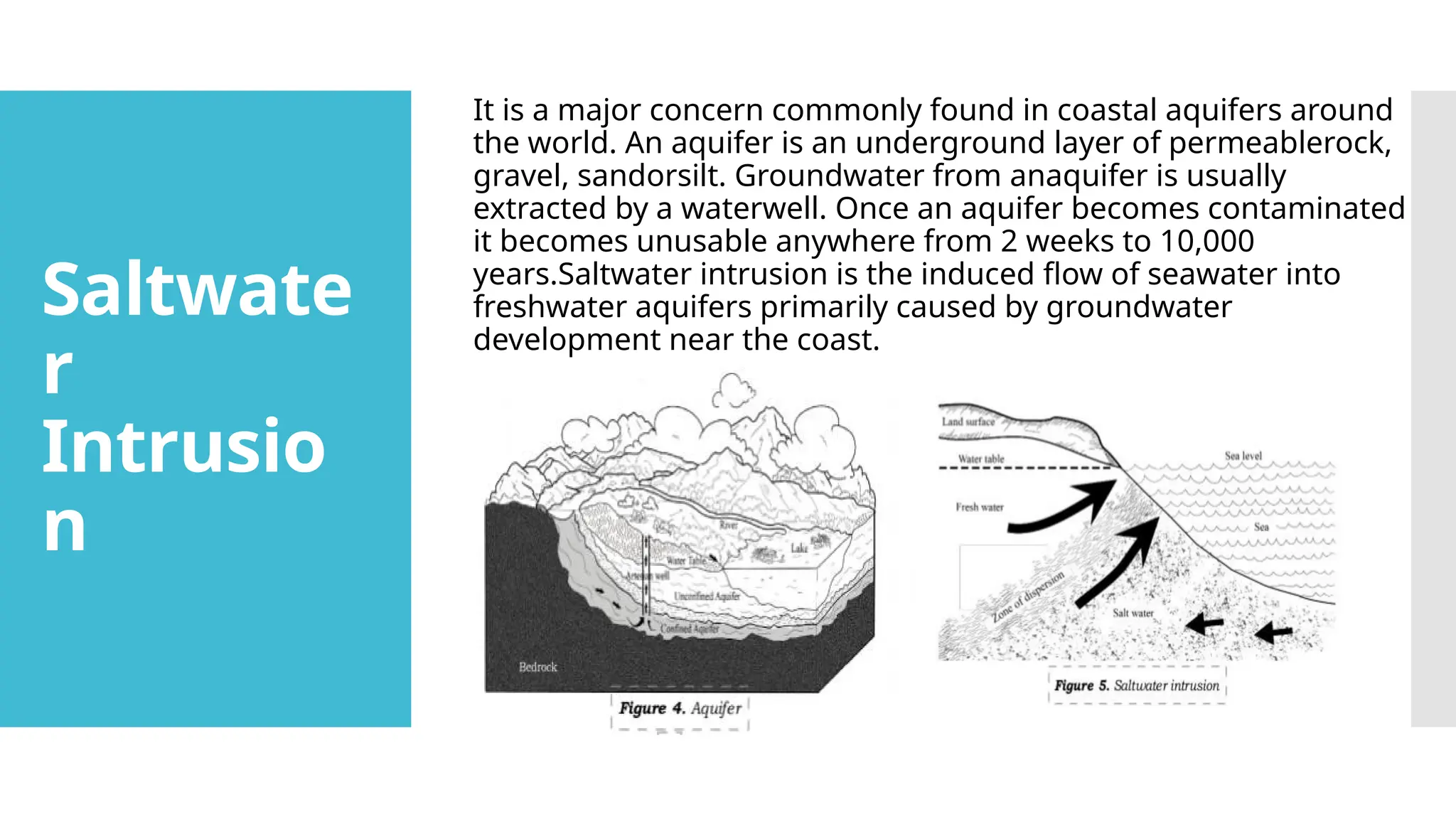
The document discusses marine and coastal processes, highlighting their dynamic nature and impact on sensitive ecosystems, human communities, and natural hazards. It defines coastal processes, such as waves and storm surges, and examines their consequences, including coastal erosion, saltwater intrusion, and submersion, which pose risks to life, property, and ecology. Oceanography is identified as the scientific field that studies these processes and their interactions with human activities.