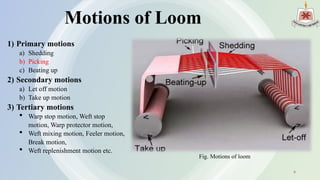
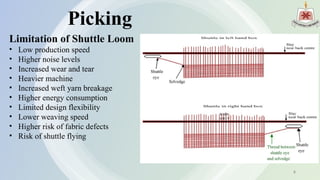
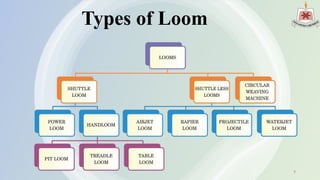
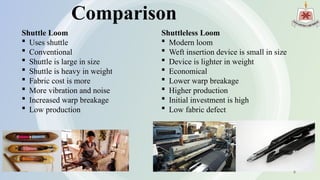
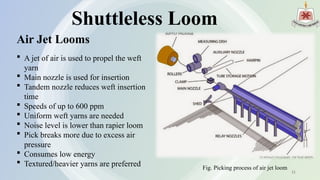
The presentation by Abdullah Al Rakib Shikder covers the fundamentals of looms, detailing various loom types, including shuttle looms and shuttleless options such as rapier, projectile, air jet, and water jet looms. It discusses the motions involved in weaving, comparisons of different loom types based on production speed and efficiency, and the limitations of each loom design. The future development section highlights advancements in machine design, automation, and energy efficiency.