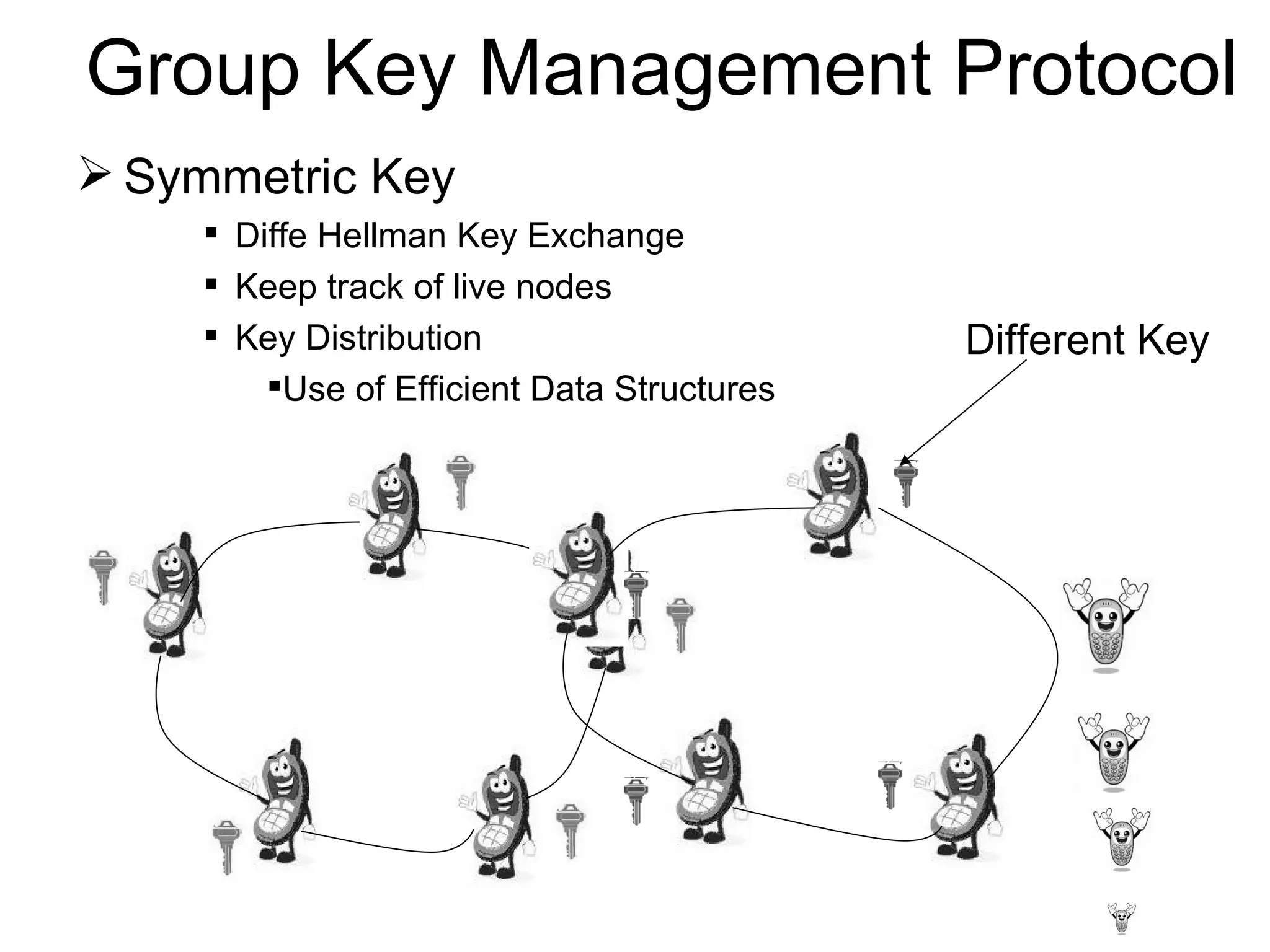
The document proposes an elliptic curve cryptographic (ECC) based group key establishment protocol for mobile ad hoc networks. ECC allows for smaller key sizes than traditional public key methods like RSA, making it suitable for resource constrained mobile devices. The proposed Group Key Management Protocol (GKMP) would use ECC to efficiently establish and distribute a shared group key for mobile ad hoc networks, handling changes in network topology like nodes joining or dropping out of the group. The protocol aims to satisfy security requirements for asynchronous and dynamic mobile ad hoc networks in an efficient manner.