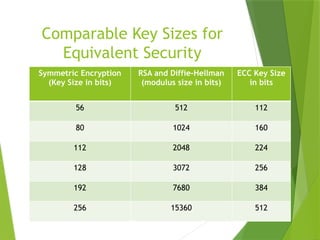
The document discusses elliptic curve cryptography (ECC), highlighting the mathematical basis of elliptic curves and their properties. It emphasizes ECC's advantages, such as shorter key lengths and reduced computational complexity, making it efficient and secure for various applications. Additionally, it outlines the ECC algorithm for key generation, encryption, and decryption, while mentioning the pros and cons of ECC compared to traditional cryptographic methods.